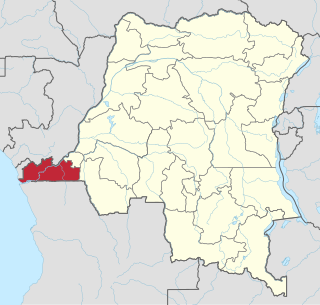
Kongo Central, formerly Bas-Congo is one of the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its capital is Matadi.

Bandundu is one of eleven former provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It bordered the provinces of Kinshasa and Bas-Congo to the west, Équateur to the north, and Kasai-Occidental to the east. The provincial capital is also called Bandundu.

Kongo or Kikongo is one of the Bantu languages spoken by the Kongo people living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Gabon and Angola. It is a tonal language. It was spoken by many of those who were taken from the region and sold as slaves in the Americas. For this reason, while Kongo still is spoken in the above-mentioned countries, creolized forms of the language are found in ritual speech of Afro-American religions, especially in Brazil, Cuba, Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic and Haiti. It is also one of the sources of the Gullah language and the Palenquero creole in Colombia. The vast majority of present-day speakers live in Africa. There are roughly seven million native speakers of Kongo, with perhaps two million more who use it as a second language.

The culture of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is extremely varied, reflecting the great diversity and different customs which exist in the country. Congolese culture combines the influence of tradition to the region, but also combines influences from abroad which arrived during the era of colonization and continue to have a strong influence, without destroying the individuality of many tribal customs.

The Kingdom of Kongo was a kingdom in Central Africa. It was located in present-day northern Angola, the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and the Republic of the Congo. At its greatest extent it reached from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Kwango River in the east, and from the Congo River in the north to the Kwanza River in the south. The kingdom consisted of several core provinces ruled by the Manikongo, the Portuguese version of the Kongo title Mwene Kongo, meaning "lord or ruler of the Kongo kingdom", but its sphere of influence extended to neighboring kingdoms, such as Ngoyo, Kakongo, Loango, Ndongo, and Matamba, the latter two located in what is Angola today.
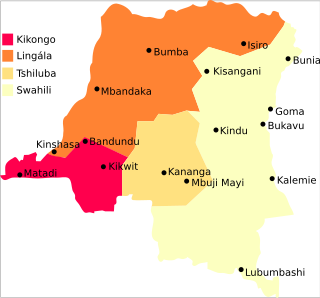
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken. Ethnologue lists 215 living languages. The official language, since the colonial period, is French. Four other languages, three of them Bantu based, have the status of national language: Kikongo, Lingala, Swahili and Tshiluba.
Kituba is a widely used lingua franca in Central Africa. It is a creole language based on Kikongo, a Bantu language. It is a national language in Republic of the Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Jean Cuvelier (1882–1962) was a Belgian Redemptorist missionary and bishop of Matadi in Belgian Congo from 1930 until his death in 1962. Cuvelier was notable for his interest in the history of the Kingdom of Kongo, which he saw as a route to evangelization in his time. By stressing the Christian nature of the old kingdom, he hoped to increase the attachment of Kongo parishioners to the Catholic Church as opposed to Protestantism or traditional religions.

Álvaro VI of Kongo, sometimes called Nimi a Lukeni a Nzenze a Ntumba, was a ruler of the Kingdom of Kongo.
Álvaro VII (Mpanzu-a-Mabondo) was king of the Kingdom of Congo from 1665 to 1666.
The Italian Capuchin Girolamo da Montesarchio spent twenty years in the mid-17th century in the Kingdom of Kongo in West Africa. His manuscript account, Viaggio al Congho, provides modern historians a rich source of information on the region's history and society. The manuscript, preserved in the Archivio Provinciale dei Cappucini di Provincia di Toscana, Montughi Convent, Florence, was first edited and published in 1976. Montesarchio's account supplements the material in Giovanni Cavazzi da Montecuccolo's Istorica descrizione, printed in 1687.

Kwilu is a province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It's one of the 21 provinces created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwilu, Kwango, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwilu was formed from the Kwilu district and the independently administered cities of Bandundu and Kikwit. Bandundu is the provincial capital.
Idiofa Territory is an administrative area in the Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The capital is the town of Idiofa.
Vanga (vɑːɳɢ/ə/) is a town in Kwilu province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, approximately 340 kilometres (210 mi) east of the capital city Kinshasa. Vanga is in Bulungu Territory. Vanga is known for its large medical center that supports the greater Bandundu region.
Wamba Airport is an airstrip serving the village of Kikongo Sur Wamba in Kwilu Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. The runway lies between the village and the Wamba River.
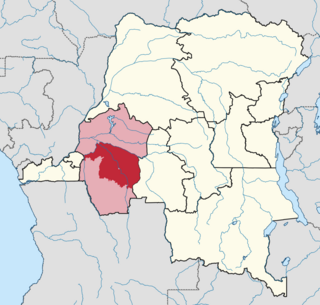
Kwilu District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded to the present province of Kwilu.
Yvon Kimpiobi or Kimpiob-Ninafiding Nki-Ekundi was a Congolese politician who served twice as the President of the Chamber of Deputies of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

The Kwilu rebellion (1963–1965) was a civil uprising which took place in the West of what is the modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo. The rebellion took place in the wider context of the Cold War and the Congo Crisis. Led by Pierre Mulele, a follower of ousted Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba, a faction of rebel Maoists staged a revolt against the government in the Kwilu District. Based around the struggle for independence, the rebellion was encouraged by economic, social, and cultural grievances. Supported by communist China, rebels used mainly guerrilla warfare against government forces. The rebellion was concurrent with the Simba rebellion occurring in other areas of the Congo during this time. While the rebellion was suppressed in the early months of 1965, it had lasting political impacts, leading to the dissolution of Kwilu as an official province.









