The pebble-bed reactor (PBR) is a design for a graphite-moderated, gas-cooled nuclear reactor. It is a type of very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR), one of the six classes of nuclear reactors in the Generation IV initiative.

Koeberg Nuclear Power Station is a nuclear power station in South Africa. It is currently the only one on the entire African continent. It is located 30 km north of Cape Town, near Melkbosstrand on the west coast of South Africa. Koeberg is owned and operated by the country's only national electricity supplier, Eskom.

The Pebble Bed Modular Reactor (PBMR) is a particular design of pebble bed reactor developed by South African company PBMR (Pty) Ltd from 1994 until 2009. PBMR facilities include gas turbine and heat transfer labs at the Potchefstroom Campus of North-West University, and at Pelindaba, a high pressure and temperature helium test rig, as well as a prototype fuel fabrication plant. A planned test reactor at Koeberg Nuclear Power Station was not built.

Areva S.A. is a French multinational group specializing in nuclear power headquartered in Courbevoie, France. Before its 2016 corporate restructuring, Areva was majority-owned by the French state through the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (54.37%), Banque publique d'investissement (3.32%), and Agence des participations de l'État (28.83%). Électricité de France, of which the French government has a majority ownership stake, owned 2.24%; Kuwait Investment Authority owned 4.82% as the second largest shareholder after the French state.
Eskom Hld SOC Ltd or Eskom (Afrikaans: Elektrisiteitsvoorsieningskommissie) is a South African electricity public utility. Eskom was established in 1923 as the Electricity Supply Commission (ESCOM). Eskom represents South Africa in the Southern African Power Pool. The utility is the largest producer of electricity in Africa, and was among the top utilities in the world in terms of generation capacity and sales. It is the largest of South Africa's state owned enterprises. Eskom operates a number of notable power stations, including Matimba Power Station and Medupi Power Station in Lephalale, Kusile Power Station in Witbank, Kendal Power Station, and Koeberg Nuclear Power Station in the Western Cape Province, the only nuclear power plant in Africa.

Earthlife Africa is a South African environmental and anti-nuclear organisation founded in August 1988, in Johannesburg. Initially conceived of as a South African version of Greenpeace, the group began by playing a radical, anti-apartheid, activist role. ELA is arguably now more of a reformist lobby or pressure group. Considered by some to be a key voice in the emerging environmental justice movement, Earthlife Africa has been criticised for being too radical, and by others for "working with traditional conservation movements" in furthering the environmental struggle.
Generation IVreactors are nuclear reactor design technologies that are envisioned as successors of generation III reactors. The Generation IV International Forum (GIF) – an international organization that coordinates the development of generation IV reactors – specifically selected six reactor technologies as candidates for generation IV reactors. The designs target improved safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost. The World Nuclear Association in 2015 suggested that some might enter commercial operation before 2030.

A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is a type of gas-cooled nuclear reactor which use uranium fuel and graphite moderation to produce very high reactor core output temperatures. All existing HTGR reactors use helium coolant. The reactor core can be either a "prismatic block" or a "pebble-bed" core. China Huaneng Group currently operates HTR-PM, a 250 MW HTGR power plant in Shandong province, China.
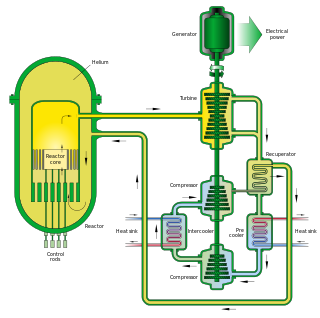
The gas-cooled fast reactor (GFR) system is a nuclear reactor design which is currently in development. Classed as a Generation IV reactor, it features a fast-neutron spectrum and closed fuel cycle for efficient conversion of fertile uranium and management of actinides. The reference reactor design is a helium-cooled system operating with an outlet temperature of 850 °C (1,560 °F) using a direct Brayton closed-cycle gas turbine for high thermal efficiency. Several fuel forms are being considered for their potential to operate at very high temperatures and to ensure an excellent retention of fission products: composite ceramic fuel, advanced fuel particles, or ceramic clad elements of actinide compounds. Core configurations are being considered based on pin- or plate-based fuel assemblies or prismatic blocks, which allows for better coolant circulation than traditional fuel assemblies.
The Koeberg Alert alliance is an anti-nuclear activist organisation which emerged from an earlier pressure group in Cape Town called "Stop Koeberg" in 1983. Both were intended to halt construction of the first nuclear power station in South Africa at Duynefontein, 28 km NNW of Cape Town: the Koeberg Nuclear Power Station.

A Next Generation Nuclear Plant (NGNP) is a specific proposed generation IV very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR) that could be coupled to a neighboring hydrogen production facility. It could also produce electricity and supply process heat. Up to 30% of this heat could be used to produce hydrogen via high-temperature electrolysis significantly reducing the cost of the process. The envisioned reactor design is helium-cooled, using graphite-moderated thermal neutrons, and TRISO fueled.

As a member of the nuclear non-proliferation treaty, South Africa uses nuclear science for peaceful means. South Africa's nuclear programme includes both nuclear energy and nuclear medicine. In the past there was also a military component, and South Africa previously possessed nuclear weapons, which were subsequently dismantled.
South Africa has a large energy sector, being the third-largest economy in Africa. The country consumed 227 TWh of electricity in 2018. The vast majority of South Africa's electricity was produced from coal, with the fuel responsible for 88% of production in 2017. South Africa is the 7th largest coal producer in the world. As of July 2018, South Africa had a coal power generation capacity of 39 gigawatts (GW). South Africa is the world's 14th largest emitter of greenhouse gases. South Africa is planning to shift away from coal in the electricity sector and the country produces the most solar and wind energy by terawatt-hours in Africa. The country aims to decommission 34 GW of coal-fired power capacity by 2050. It also aims to build at least 20 GW of renewable power generation capacity by 2030. South Africa aims to generate 77,834 megawatts (MW) of electricity by 2030, with new capacity coming significantly from renewable sources to meet emission reduction targets. Through its goals stated in the Integrated Resource Plan, it announced the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme, which aims to increase renewable power generation through private sector investment.
Duynefontein is a proposed site for new nuclear power station. It is a coastal site next to and just north of Koeberg Nuclear Power Station.
X-energy is an American private nuclear reactor and fuel design engineering company. It is developing a Generation IV high-temperature gas-cooled pebble-bed nuclear reactor design. Since its founding in 2009, it has received various government grants and contracts, notably through the Department of Energy's (DOE) Advanced Reactor Concept Cooperative Agreement in 2016 and its Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program (ARDP) in 2020.

The South African energy crisis or load shedding is an ongoing period of widespread national blackouts of electricity supply. It began in the later months of 2007 towards the end of Thabo Mbeki's second term as president, and continues to the present. The South African government-owned national power utility, and primary power generator, Eskom, and various parliamentarians attributed these rolling blackouts to insufficient generation capacity.

The Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme (REIPPPP) is an initiative by the South African government aimed at increasing electricity capacity through private sector investment in solar photovoltaic and concentrated solar, onshore wind power, small hydro, landfill gas, biomass, and biogas. As of 2023, a total of 123 projects have been awarded to the private sector. Private sector investment totalling R256 billion has been committed to the REIPPPP. Four of the six Bid Windows have come online, totalling 6200 MW of installed capacity.
The Integrated Resource Plan (IRP) is a plan aimed at estimating South Africa's electricity demand. It takes into account how the demand of electricity will be met and the expense of such a demand. The plan refers to electricity generation and expansion programmes.