
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some base, called a significand, scaled by an integer exponent of that base. Numbers of this form are called floating-point numbers.

In computer programming, an arithmetic shift is a shift operator, sometimes termed a signed shift. The two basic types are the arithmetic left shift and the arithmetic right shift. For binary numbers it is a bitwise operation that shifts all of the bits of its operand; every bit in the operand is simply moved a given number of bit positions, and the vacant bit-positions are filled in. Instead of being filled with all 0s, as in logical shift, when shifting to the right, the leftmost bit is replicated to fill in all the vacant positions.
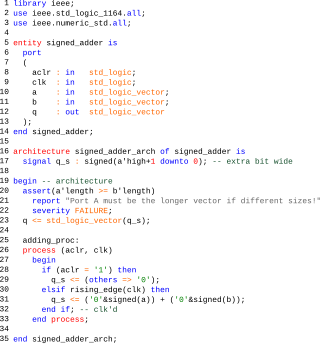
VHDL is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gates, for design entry, documentation, and verification purposes. The language was developed for the US military VHSIC program in the 1980s, and has been standardized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as IEEE Std 1076; the latest version of which is IEEE Std 1076-2019. To model analog and mixed-signal systems, an IEEE-standardized HDL based on VHDL called VHDL-AMS has been developed.
In computing, NaN, standing for Not a Number, is a particular value of a numeric data type which is undefined as a number, such as the result of 0/0. Systematic use of NaNs was introduced by the IEEE 754 floating-point standard in 1985, along with the representation of other non-finite quantities such as infinities.
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is also used in the verification of analog circuits and mixed-signal circuits, as well as in the design of genetic circuits. In 2009, the Verilog standard was merged into the SystemVerilog standard, creating IEEE Standard 1800-2009. Since then, Verilog has been officially part of the SystemVerilog language. The current version is IEEE standard 1800-2023.
In computer programming, a bitwise operation operates on a bit string, a bit array or a binary numeral at the level of its individual bits. It is a fast and simple action, basic to the higher-level arithmetic operations and directly supported by the processor. Most bitwise operations are presented as two-operand instructions where the result replaces one of the input operands.
The IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic is a technical standard for floating-point arithmetic originally established in 1985 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standard addressed many problems found in the diverse floating-point implementations that made them difficult to use reliably and portably. Many hardware floating-point units use the IEEE 754 standard.
In computing, signed number representations are required to encode negative numbers in binary number systems.
SystemC is a set of C++ classes and macros which provide an event-driven simulation interface. These facilities enable a designer to simulate concurrent processes, each described using plain C++ syntax. SystemC processes can communicate in a simulated real-time environment, using signals of all the datatypes offered by C++, some additional ones offered by the SystemC library, as well as user defined. In certain respects, SystemC deliberately mimics the hardware description languages VHDL and Verilog, but is more aptly described as a system-level modeling language.
In computing, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another, called the modulus of the operation.
In computing, signedness is a property of data types representing numbers in computer programs. A numeric variable is signed if it can represent both positive and negative numbers, and unsigned if it can only represent non-negative numbers.
In the C programming language, data types constitute the semantics and characteristics of storage of data elements. They are expressed in the language syntax in form of declarations for memory locations or variables. Data types also determine the types of operations or methods of processing of data elements.
PicoBlaze is the designation of a series of three free soft processor cores from Xilinx for use in their FPGA and CPLD products. They are based on an 8-bit RISC architecture and can reach speeds up to 100 MIPS on the Virtex 4 FPGA's family. The processors have an 8-bit address and data port for access to a wide range of peripherals. The license of the cores allows their free use, albeit only on Xilinx devices, and they come with development tools. Third-party tools are available from Mediatronix and others. Also PacoBlaze, a behavioral and device independent implementation of the cores exists and is released under the BSD License. The PauloBlaze is an open source VHDL implementation under the Apache License.
In logic, a four-valued logic is any logic with four truth values. Several types of four-valued logic have been advanced.
C++11 is a version of a joint technical standard, ISO/IEC 14882, by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), for the C++ programming language. C++11 replaced the prior version of the C++ standard, named C++03, and was later replaced by C++14. The name follows the tradition of naming language versions by the publication year of the specification, though it was formerly named C++0x because it was expected to be published before 2010.
Value change dump (VCD) (also known less commonly as "variable change dump") is an ASCII-based format for dumpfiles generated by EDA logic simulation tools. The standard, four-value VCD format was defined along with the Verilog hardware description language by the IEEE Standard 1364-1995 in 1996. An extended VCD format defined six years later in the IEEE standard 1364-2001 supports the logging of signal strength and directionality. The simple and yet compact structure of the VCD format has allowed its use to become ubiquitous and to spread into non-Verilog tools such as the VHDL simulator GHDL and various kernel tracers. A limitation of the format is that it is unable to record the values that are stored in memories.
MyHDL is a Python-based hardware description language (HDL).
Unums are a family of number formats and arithmetic for implementing real numbers on a computer, proposed by John L. Gustafson in 2015. They are designed as an alternative to the ubiquitous IEEE 754 floating-point standard. The latest version is known as posits.
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in elementary algebra the values of the variables are numbers. Second, Boolean algebra uses logical operators such as conjunction (and) denoted as ∧, disjunction (or) denoted as ∨, and negation (not) denoted as ¬. Elementary algebra, on the other hand, uses arithmetic operators such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division. Boolean algebra is therefore a formal way of describing logical operations in the same way that elementary algebra describes numerical operations.
C23, formally ISO/IEC 9899:2024, is the current open standard for the C programming language, which supersedes C17. It was started in 2016 informally as C2x, and was published on October 31, 2024. The freely available draft most similar to the one published is document N3220. The first WG14 meeting for the C2x draft was held in October 2019, virtual remote meetings were held in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, then various teleconference meetings continued to occur through 2024.


