Java Platform, Micro Edition or Java ME is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for embedded and mobile devices. Java ME was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Micro Edition or J2ME. As of December 22, 2006, the Java ME source code is licensed under the GNU General Public License, and is released under the project name phoneME.

Binary Runtime Environment for Wireless is an application development platform created by Qualcomm, originally for code division multiple access (CDMA) mobile phones, featuring third-party applications such as mobile games. It is offered in some feature phones but not in smartphones. First developed in 1999, as a platform for wireless applications on CDMA-based mobile phones, it debuted in September 2001. As a software platform that can download and run small programs for playing games, sending messages, and sharing photos, the main advantage of Brew MP is that the application developers can easily port their applications among all Brew MP devices by providing a standardized set of application programming interfaces. Software for Brew MP enabled handsets can be developed in C or C++ using the freely downloadable Brew MP software development kit (SDK). The BREW runtime library is part of the wireless device on-chip firmware or operating system to allow programmers to develop applications without needing to code for system interface or understand wireless applications. BREW is described as a pseudo operating system, but not a true mobile operating system. BREW is not a virtual machine such as Java ME, but it runs a native code.
Windows Mobile was a family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.

Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance, though its most widely used version is primarily developed by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008.

The Open Handset Alliance (OHA) is a consortium of 84 firms to develop open standards for mobile devices. Member firms include HTC, Sony, Dell, Intel, Motorola, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, Google, Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, T-Mobile, Sprint Corporation, Nvidia, and Wind River Systems.
A mobile operating system is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers and light-weight laptops and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

The iOS SDK, formerly the iPhone SDK, is a software development kit (SDK) developed by Apple Inc. The kit allows for the development of mobile apps on Apple's iOS and iPadOS operating systems.

Windows Phone (WP) is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones as the replacement successor to Windows Mobile and Zune. Windows Phone featured a new user interface derived from the Metro design language. Unlike Windows Mobile, it was primarily aimed at the consumer market rather than the enterprise market.

The Symbian Foundation was a non-profit organisation that stewarded the Symbian operating system for mobile phones which previously had been owned and licensed by Symbian Ltd. Symbian Foundation never directly developed the platform, but evangelised, co-ordinated and ensured compatibility. It also provided key services to its members and the community such as collecting, building and distributing Symbian source code. During its time it competed against the Open Handset Alliance and the LiMo Foundation.

The HTC Dream is a smartphone developed by HTC. First released in September 2008, the Dream was the first commercially released device to use the Linux-based Android operating system, which was purchased and further developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance to create an open competitor to other major smartphone platforms of the time, such as Symbian, BlackBerry OS, and iPhone OS. The operating system offers a customizable graphical user interface, integration with Google services such as Gmail, a notification system that shows a list of recent messages pushed from apps, and Android Market for downloading additional apps.
Titanium SDK is an open-source framework that allows the creation of native mobile applications on platforms iOS and Android from a single JavaScript codebase. Titanium SDK is presently developed by non-profit software foundation TiDev, Inc.
Bada is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Samsung Electronics for devices such as mid- to high-end smartphones and tablet computers. The name is derived from "바다 (bada)", meaning "ocean" or "sea" in Korean. All phones running Bada were branded with the name Wave, unlike Samsung's Android devices which are branded as Galaxy.

Symbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. It was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for personal digital assistants in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010, at a time when smartphones were in limited use, when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably less popular in North America.
ooVoo was a video chat and a messaging app developed by ooVoo LLC and owned by Krush Technologies, LLC. ooVoo had applications for Android, iOS, Mac OS X, Microsoft Windows, Windows Phone, and Facebook. The original Microsoft Windows app was released in 2007. It was discontinued on November 25, 2017.

MeeGo is a discontinued Linux distribution hosted by the Linux Foundation, using source code from the operating systems Moblin and Maemo. Primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market, MeeGo was designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet computers, mobile computing and communications devices, in-vehicle infotainment devices, SmartTV / ConnectedTV, IPTV-boxes, smart phones, and other embedded systems.

Solar2D is a free and open-source, cross-platform software development kit originally developed by Corona Labs Inc. and now maintained by Vlad Shcherban. Released in late 2009, it allows software programmers to build 2D mobile applications for iOS, Android, and Kindle, desktop applications for Windows, Linux and macOS, and connected TV applications for Apple TV, Fire TV and Android TV.
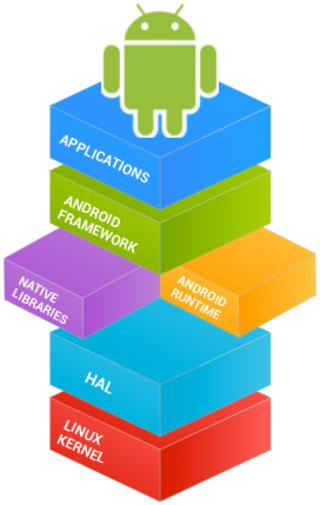
Android software development is the process by which applications are created for devices running the Android operating system. Google states that "Android apps can be written using Kotlin, Java, and C++ languages" using the Android software development kit (SDK), while using other languages is also possible. All non-Java virtual machine (JVM) languages, such as Go, JavaScript, C, C++ or assembly, need the help of JVM language code, that may be supplied by tools, likely with restricted API support. Some programming languages and tools allow cross-platform app support. Third party tools, development environments, and language support have also continued to evolve and expand since the initial SDK was released in 2008. The official Android app distribution mechanism to end users is Google Play; it also allows staged gradual app release, as well as distribution of pre-release app versions to testers.

Sailfish OS is a Linux-based operating system based on free software, and open source projects such as Mer as well as including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.

Borqs Technologies Inc., founded in 2007, designs, develops and deploys Internet of Things products and solutions. In addition to developing the first commercial-grade software to support video telephony for Android, Borqs was selected by Qualcomm in 2016 to partner in developing the world's first 4G Android wearable, which includes smartwatches for children and adults, as well as watches designed for fitness. Borqs marked its debut as a public company on August 18, 2017, changing its name to Borqs Technologies, Inc. Listed on The NASDAQ Stock Market, under the trading symbol, BRQS. Borqs has research and development centers in China and India, and presence in the US, Japan and Korea.

The Nokia Asha platform is a mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for low-end borderline smartphones, based on software from Smarterphone which was acquired by Nokia. The platform inherits UI similarities mostly from MeeGo "Harmattan", and replaces Series 40 on Nokia's low-end devices. The user interface design team was headed by Peter Skillman, who had worked previously on webOS and the design of MeeGo for the Nokia N9.















