Observer status is a privilege granted by some organizations to non-members to give them an ability to participate in the organization's activities. Observer status is often granted by intergovernmental organizations (IGO) to non-member parties and international nongovernmental organizations (INGO) that have an interest in the IGO's activities. Observers generally have a limited ability to participate in the IGO, lacking the ability to vote or propose resolutions.
The United Nations General Assembly may grant entities observer status. The United Nations welcomes many international agencies, entities, and two non-member states as observers, State of Palestine and Vatican City. Observers have the right to speak at United Nations General Assembly meetings, but not to vote on resolutions.
Non-member observer states are recognized as sovereign states, and are free to submit a petition to join as a full member at their discretion. At present, State of Palestine and Holy See are the observer states at the United Nations, [1] Also, Holy See includes both state as Vatican City and sovereign entity. Switzerland also maintained such status until it became a member state. Among others, the Sovereign Military Order of Malta and the European Union also have observer status; they are not states under international law, but they are sovereign entities. [2] [3]
Observer status is granted by a United Nations General Assembly resolution at some point in time. Other international organizations (including other UN agencies) may also grant observer status.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Constitution does not recognise an observer status but the Rules of Procedure of its highest decision-making body World Health Assembly (WHA) give the Director-General right to invite observers to the annual Assembly meeting, provided that they are "States having made application for membership, territories on whose behalf application for associate membership has been made, and States which have signed but not accepted the Constitution."
From 1997 to 2008, the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, applied for observer status in the WHO every year, under different names including "Republic of China", "Taiwan Health Entity" and "Taiwan". All these efforts failed, mainly due to firm objections from the People's Republic of China (PRC) which does not recognize the ROC and considers Taiwan as one of its provinces. The Cross-Strait Relations (between the PRC and ROC governments) significantly improved in 2008 and 2009, and the PRC government agreed to negotiate over this issue. On April 29, 2009, the Director-General, Margaret Chan invited the Department of Health of the ROC to attend the 2009 World Health Assembly under "Chinese Taipei", [4] [5] a compromised name which both the PRC and ROC accept. This status only lasted for eight years and ended in 2016 following the election of DPP presidential candidate Tsai Ing-wen. [6]
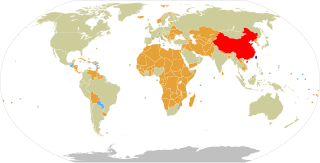
The Republic of China (ROC), often known informally as Taiwan, currently has formal diplomatic relations with 12 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs Vatican City, as of 5 January 2024. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates under the One China principle. The government of the Republic of China has the 31st largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.
The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement which advocates the formal declaration of an independent and sovereign Taiwanese state, as opposed to Chinese unification or the status quo in Cross-Strait relations.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
The political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a long-running dispute on the political status of Taiwan, currently controlled by the Republic of China (ROC). This dispute arose in the mid-twentieth century, and is ongoing.
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th-century diplomacy. A successor state often acquires a new international legal personality, which is distinct from a continuing state, also known as a continuator or historical heir, which despite change to its borders retains the same legal personality and possess all its existing rights and obligations.
"Chinese Taipei" is the term used in various international organizations and tournaments for groups or delegations representing the Republic of China (ROC), a country commonly known as Taiwan.
China is one of the charter members of the United Nations and is one of five permanent members of its Security Council.
As a result of the surrender and occupation of Japan at the end of World War II, the islands of Taiwan and Penghu were placed under the governance of the Republic of China (ROC), ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT), on 25 October 1945. Following the February 28 massacre in 1947, martial law was declared in 1949 by the Governor of Taiwan, Chen Cheng, and the ROC Ministry of National Defense. Following the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the ROC government retreated from the mainland as the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. The KMT retreated to Taiwan and declared Taipei the temporary capital of the ROC. For many years, the ROC and PRC each continued to claim in the diplomatic arena to be the sole legitimate government of "China". In 1971, the United Nations expelled the ROC and replaced it with the PRC.

The United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758 was passed in response to the United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1668 that required any change in China's representation in the UN be determined by a two-thirds vote referring to Article 18 of the UN Charter. The resolution, passed on 25 October 1971, recognized the People's Republic of China as "the only legitimate representative of China to the United Nations" and removed "the representatives of Chiang Kai-shek" from the United Nations.

The Anti-Secession Law is a law of the People's Republic of China, passed by the 3rd Session of the 10th National People's Congress. It was ratified on March 14, 2005, and went into effect immediately. President Hu Jintao promulgated the law with Presidential Decree No. 34. Although the law, at ten articles, is relatively short, Article 8 formalized the long-standing policy of the PRC to use military means against Taiwan independence in the event peaceful means become otherwise impossible. The law does not explicitly equate "China" with the People's Republic of China.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

As of 2 January 2024, there are 193 member states in the United Nations (UN), each of which is a member of the United Nations General Assembly.
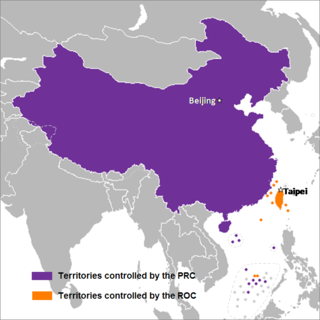
The term "Two Chinas" refers to the geopolitical situation where two political entities exist under the name "China".

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States.

The World Turned Upside Down is a sculpture by the Turner Prize-winning artist Mark Wallinger, on Sheffield Street, London, within the campus of the London School of Economics. The name World Turned Upside Down comes from a 17th-century English ballad. The sculpture, measuring 13 feet (4 m) in diameter, features a globe resting on its North Pole and was unveiled in March 2019. It reportedly cost over £200,000, which was funded by alumni donations.
The People's Republic of China was established in 1949 and was not recognized by the United Nations (UN) as the legitimate government of China until 1971. Prior to then, the Republic of China represented the interests of China, with both it and the PRC claiming to be the only legitimate representative of whole China. In 1950, the PRC requested its admission to the UN and the expulsion of the representatives of the Kuomintang from the United Nations Security Council; the request was unsuccessful, after which the Soviet Union initiated a boycott of the UN. Following that, annual motions for the PRC's recognition were introduced by a variety of UN member states, until the PRC was formally recognized in October 1971.