
PRINCE2 is a structured project management method and practitioner certification programme. PRINCE2 emphasises dividing projects into manageable and controllable stages.
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as government procurement or public procurement.

The Crown Commercial Service (CCS) is an executive agency and trading fund of the Cabinet Office of the UK Government. The CCS is responsible for managing the procurement of common goods and services, increasing savings for the taxpayer by centralising buying requirements, and leading on procurement policy on behalf of the government.
The e-Government Unit (eGU) was a unit of the Cabinet Office of the government of the United Kingdom responsible for helping various government departments use information technology to increase efficiency and improve electronic access to government services. It was therefore deeply involved in issues of e-Government.
Sustainable procurement or green procurement is a process whereby organizations meet their needs for goods, services, works and utilities in a way that achieves value for money on a life-cycle basis while addressing equity principles for sustainable development, therefore benefiting societies and the environment across time and geographies. Procurement is often conducted via a tendering or competitive bidding process. The process is used to ensure the buyer receives goods, services or works for the best possible price, when aspects such as quality, quantity, time, and location are compared. Procurement is considered sustainable when organizations broadens this framework by meeting their needs for goods, services, works, and utilities in a way that achieves value for money and promotes positive outcomes not only for the organization itself but for the economy, environment, and society. This framework is also known as the triple bottom line, which is a business accounting framework. The concept of TBL is narrowly prescribed, and even John Elkington, who coined the term in the 1990s, now advocates its recall. Indeed, procurement practitioners have drawn attention to the fact that buying from smaller firms, locally, is an important aspect of sustainable procurement in the public sector. Ethics, culture, safety, diversity, inclusion, justice, human rights and the environment are additionally listed as important aspects of SPP.

Government procurement or public procurement is the procurement of goods, services and works on behalf of a public authority, such as a government agency. Amounting to 12 percent of global GDP in 2018, government procurement accounts for a substantial part of the global economy.
The Gershon Efficiency Review was a review of efficiency in the UK public sector conducted in 2003-4 by Sir Peter Gershon.
The Property Services Agency (PSA) was an agency of the United Kingdom government, in existence from 1972 to 1993. Its role was to "provide, manage, maintain, and furnish the property used by the government, including defence establishments, offices, courts, research laboratories, training centres and land".
The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) was a UK government agency providing computer and telecoms support to government departments.
Forward Commitment Procurement (FCP) is a procurement model designed to be used to deliver cost-effective environmental products and services to the public sector and help to create the market conditions in which the environmental goods and services sector can thrive.
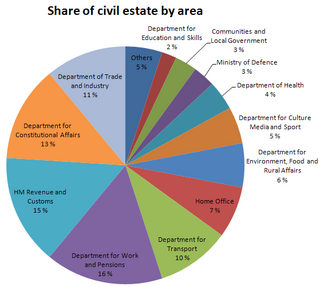
The public estate in the United Kingdom is the collection of all government-owned real property assets in the United Kingdom. The Office for National Statistics estimated in 2008 that the public estate has a book value of £380 billion, which is about £6,000 for every UK resident. Of this, approximately £240 billion is held by local government, while the rest—£130 billion—is held by the central government and public corporations.
Sir Peter Oliver Gershon, is a British businessman and former civil servant, former Chairman of Tate & Lyle, and since January 2012, Chairman of the FTSE 20 company National Grid. He is chiefly known for conducting the Gershon Review in 2004/2005 which recommended savings across the UK's public services and for being an adviser to the Conservative Party during the run up to the 2010 General Election. He has also been Chair of the Office of Government Commerce as well as sitting on the boards of several well known companies and organisations.
Public Contracts Scotland was established as the national advertising website for Scottish public sector organisations to post Official Journal of the European Union (OJEU) notices and low value contracts notices on the website and make subsequent awards. Since 1 January 2021 it reflects Scottish public procurement legislation, as the UK has left the European Union. The site also allows contracting authorities to invite suppliers to submit quotations electronically via the website’s secure tender postbox.
The Public Services Network (PSN) is a UK government's high-performance network, which helps public sector organisations work together, reduce duplication and share resources. It unified the provision of network infrastructure across the United Kingdom public sector into an interconnected "network of networks" to increase efficiency and reduce overall public expenditure. It is now a legacy network and public sector organisations are being migrated to using services on the public internet.

An invitation to tender is a formal, structured procedure for generating competing offers from different potential suppliers or contractors looking to obtain an award of business activity in works, supply, or service contracts, often from companies who have been previously assessed for suitability by means of a supplier questionnaire (SQ) or pre-qualification questionnaire (PQQ).
The UK Government G-Cloud is an initiative targeted at easing procurement by public-sector bodies in the United Kingdom of commodity information technology services that use cloud computing. The G-Cloud consists of:
AXELOS is a joint venture set up in 2014 by the Government of the United Kingdom and Capita, to develop, manage and operate qualifications in best practice, in methodologies formerly owned by the Office of Government Commerce (OGC). PeopleCert, an examination institute that was responsible for delivering AXELOS exams, acquired AXELOS in 2021.
Category management is an approach to the organisation of purchasing within a business organisation. Applying category management to purchasing activity benefits organisations by providing an approach to reduce the cost of buying goods and services, reduce risk in the supply chain, increase overall value from the supply base and gain access to more innovation from suppliers. It is a strategic approach which focuses on the vast majority of organisational spend. If applied effectively throughout an entire organisation, the results can be significantly greater than traditional transactional based purchasing negotiations, however the discipline of category management is sorely misunderstood.
At around £290 billion every year, public sector procurement accounts for around a third of all public expenditure in the UK. EU-based laws continue to apply to government procurement: procurement is governed by the Public Contracts Regulations 2015, Part 3 of the Small Business, Enterprise and Employment Act 2015, and the Public Contracts (Scotland) Regulations of 2015 and 2016. These regulations implement EU law, which applied in the UK prior to Brexit, and also contain rules known as the "Lord Young Rules" promoting access for small and medium enterprise (SMEs) to public sector contracts, based on Lord Young's Review Growing Your Business, published in 2013.







