Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is an encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. PGP is used for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions and to increase the security of e-mail communications. Phil Zimmermann developed PGP in 1991.

GNU Privacy Guard is a free-software replacement for Symantec's PGP cryptographic software suite. The software is compliant with RFC 4880, the IETF standards-track specification of OpenPGP. Modern versions of PGP are interoperable with GnuPG and other OpenPGP-compliant systems.
An authenticator is a means used to confirm a user's identity, that is, to perform digital authentication. A person authenticates to a computer system or application by demonstrating that he or she has possession and control of an authenticator. In the simplest case, the authenticator is a common password.
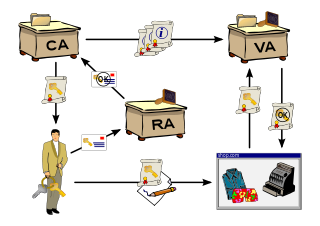
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. It is required for activities where simple passwords are an inadequate authentication method and more rigorous proof is required to confirm the identity of the parties involved in the communication and to validate the information being transferred.
In cryptography, Camellia is a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits. It was jointly developed by Mitsubishi Electric and NTT of Japan. The cipher has been approved for use by the ISO/IEC, the European Union's NESSIE project and the Japanese CRYPTREC project. The cipher has security levels and processing abilities comparable to the Advanced Encryption Standard.
In computer security, a key server is a computer that receives and then serves existing cryptographic keys to users or other programs. The users' programs can be running on the same network as the key server or on another networked computer.

GnuTLS is a free software implementation of the TLS, SSL and DTLS protocols. It offers an application programming interface (API) for applications to enable secure communication over the network transport layer, as well as interfaces to access X.509, PKCS #12, OpenPGP and other structures.
NX technology, commonly known as NX or NoMachine, is a remote access and remote control computer software, allowing remote desktop access and maintenance of computers. It is developed by the Luxembourg-based company NoMachine S.à r.l.. NoMachine is proprietary software and is free-of-charge for non-commercial use.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication framework frequently used in network and internet connections. It is defined in RFC 3748, which made RFC 2284 obsolete, and is updated by RFC 5247. EAP is an authentication framework for providing the transport and usage of material and parameters generated by EAP methods. There are many methods defined by RFCs, and a number of vendor-specific methods and new proposals exist. EAP is not a wire protocol; instead it only defines the information from the interface and the formats. Each protocol that uses EAP defines a way to encapsulate by the user EAP messages within that protocol's messages.

Seahorse is a GNOME front-end application for managing passwords, PGP and SSH keys. Seahorse integrates with a number of apps including Nautilus file manager, Epiphany browser and Evolution e-mail suite. It has HKP and LDAP key server support.
This is a technical feature comparison of different disk encryption software.

Gpg4win is an email and file encryption package for most versions of Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Outlook, which utilises the GnuPG framework for symmetric and public-key cryptography, such as data encryption, digital signatures, hash calculations etc.
In cryptography, Curve25519 is an elliptic curve used in elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) offering 128 bits of security and designed for use with the elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) key agreement scheme. It is one of the fastest curves in ECC, and is not covered by any known patents. The reference implementation is public domain software.
DNSCurve is a proposed secure protocol for the Domain Name System (DNS), designed by Daniel J. Bernstein.
ssh-keygen is a standard component of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol suite found on Unix, Unix-like and Microsoft Windows computer systems used to establish secure shell sessions between remote computers over insecure networks, through the use of various cryptographic techniques. The ssh-keygen utility is used to generate, manage, and convert authentication keys.
Libgcrypt is a cryptography library developed as a separated module of GnuPG. It can also be used independently of GnuPG, but depends on its error-reporting library Libgpg-error.

The YubiKey is a hardware authentication device manufactured by Yubico to protect access to computers, networks, and online services that supports one-time passwords (OTP), public-key cryptography, and authentication, and the Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) and FIDO2 protocols developed by the FIDO Alliance. It allows users to securely log into their accounts by emitting one-time passwords or using a FIDO-based public/private key pair generated by the device. YubiKey also allows for storing static passwords for use at sites that do not support one-time passwords. Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Twitter, and Facebook use YubiKey devices to secure employee accounts as well as end user accounts. Some password managers support YubiKey. Yubico also manufactures the Security Key, a similar lower cost device with only FIDO2/WebAuthn and FIDO/U2F support.
Nitrokey is an open-source USB key used to enable the secure encryption and signing of data. The secret keys are always stored inside the Nitrokey which protects against malware and attackers. A user-chosen PIN and a tamper-proof smart card protect the Nitrokey in case of loss and theft. The hardware and software of Nitrokey are open-source. The free software and open hardware enables independent parties to verify the security of the device. Nitrokey is supported on Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, and BSD.
The ROCA vulnerability is a cryptographic weakness that allows the private key of a key pair to be recovered from the public key in keys generated by devices with the vulnerability. "ROCA" is an acronym for "Return of Coppersmith's attack". The vulnerability has been given the identifier CVE-2017-15361.







