Braille is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired, including people who are blind, deafblind or who have low vision. It can be read either on embossed paper or by using refreshable braille displays that connect to computers and smartphone devices. Braille can be written using a slate and stylus, a braille writer, an electronic braille notetaker or with the use of a computer connected to a braille embosser.

A process called Optical Character Recognition (OCR) converts printed texts into digital image files. It is a digital copier that uses automation to convert scanned documents into editable, shareable PDFs that are machine-readable. OCR may be seen in action when you use your computer to scan a receipt. The scan is then saved as a picture on your computer. The words in the image cannot be searched, edited, or counted, but you may use OCR to convert the image to a text document with the content stored as text. OCR software can extract data from scanned documents, camera photos, and image-only PDFs. It makes static material editable and does away with the necessity for human data entry.

EEPROM (also called E2PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip device to store relatively small amounts of data by allowing individual bytes to be erased and reprogrammed.
Code review is a software quality assurance activity in which one or several people check a program mainly by viewing and reading parts of its source code, and they do so after implementation or as an interruption of implementation. At least one of the persons must not be the code's author. The persons performing the checking, excluding the author, are called "reviewers".

Sonification is the use of non-speech audio to convey information or perceptualize data. Auditory perception has advantages in temporal, spatial, amplitude, and frequency resolution that open possibilities as an alternative or complement to visualization techniques.

The IBM 1403 line printer was introduced as part of the IBM 1401 computer in 1959 and had an especially long life in the IBM product line.
Words per minute, commonly abbreviated wpm, is a measure of words processed in a minute, often used as a measurement of the speed of typing, reading or Morse code sending and receiving.
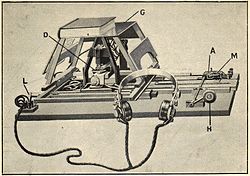
The Optacon is an electromechanical device that enables blind people to read printed material that has not been transcribed into Braille. The device consists of two parts: a scanner which the user runs over the material to be read, and a finger pad which translates the words into vibrations felt on the finger tips. The Optacon was conceived by John Linvill, a professor of Electrical Engineering at Stanford University, and developed with researchers at Stanford Research Institute. Telesensory Systems manufactured the device from 1971 until it was discontinued in 1996. Although effective once mastered, it was expensive and took many hours of training to reach competency. In 2005, TSI suddenly shut down. Employees were "walked out" of the building and lost accrued vacation time, medical insurance, and all benefits. Customers could not buy new machines or get existing machines fixed. Some work was done by other companies but no device with the versatility of the Optacon had been developed as of 2007. Many blind people continue to use their Optacons to this day. The Optacon offers capabilities that no other device offers including the ability to see a printed page or computer screen as it truly appears including drawings, typefaces, and specialized text layouts.
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
A via is an electrical connection between copper layers in a printed circuit board. Essentially a via is a small drilled hole that goes through two or more adjacent layers; the hole is plated with copper that forms electrical connection through the insulation that separates the copper layers.
A reading machine is a piece of assistive technology that allows blind people to access printed materials. It scans text, converts the image into text by means of optical character recognition and uses a speech synthesizer to read out what it has found.

The Teletype Corporation, a part of American Telephone and Telegraph Company's Western Electric manufacturing arm since 1930, came into being in 1928 when the Morkrum-Kleinschmidt Company changed its name to the name of its trademark equipment. Teletype Corporation, of Skokie, Illinois, was responsible for the research, development and manufacture of data and record communications equipment, but it is primarily remembered for the manufacture of electromechanical teleprinters.

In utility and industrial electric power transmission and distribution systems, a numerical relay is a computer-based system with software-based protection algorithms for the detection of electrical faults. Such relays are also termed as microprocessor type protective relays. They are functional replacements for electro-mechanical protective relays and may include many protection functions in one unit, as well as providing metering, communication, and self-test functions.
Telesensory Systems, Inc. (TSI) was an American corporation that invented, designed, manufactured, and distributed technological aids for blind and low vision persons. TSI's products helped visually impaired people work independently with computers and with ordinary printed materials.

John G. Linvill was an American professor (emeritus) of Electrical engineering at Stanford University, known for his pioneering work in higher education, integrated circuits and semiconductors, and for development of the Optacon reading machine for the blind.
James C. Bliss was an American electrical engineer and entrepreneur best known for his pioneering role in developing technological aids for visually impaired people.

Nasir Ahmed is an Indian-American electrical engineer and computer scientist. He is Professor Emeritus of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of New Mexico (UNM). He is best known for inventing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in the early 1970s. The DCT is the most widely used data compression transformation, the basis for most digital media standards and commonly used in digital signal processing. He also described the discrete sine transform (DST), which is related to the DCT.

Kathleen Goligher was an Irish spiritualist medium. Goligher was endorsed by engineer William Jackson Crawford who wrote three books about her mediumship, but was exposed as a fraud by physicist Edmund Edward Fournier d'Albe in 1921.

Edmund Edward Fournier d'Albe was an Irish physicist, astrophysicist and chemist. He was a university professor and distinguished himself in the study and popularization of electromagnetism, as well as the beginnings of astrophysics. He also experimented with improving radio and television.
This is a timeline of optical character recognition.