
In sociology, habitus is the way that people perceive and respond to the social world they inhabit, by way of their personal habits, skills, and disposition of character.
An instructional theory is "a theory that offers explicit guidance on how to better help people learn and develop." It provides insights about what is likely to happen and why with respect to different kinds of teaching and learning activities while helping indicate approaches for their evaluation. Instructional designers focus on how to best structure material and instructional behavior to facilitate learning.

Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, communication science and political science.

Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of quantitative methods and of qualitative approaches.
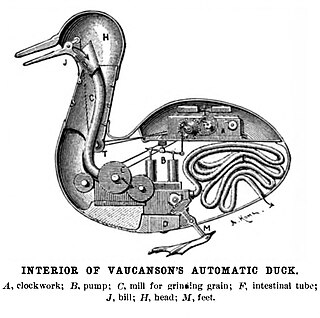
Reductionism is any of several related philosophical ideas regarding the associations between phenomena which can be described in terms of other simpler or more fundamental phenomena. It is also described as an intellectual and philosophical position that interprets a complex system as the sum of its parts.

An organization or organisation, is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.

Erving Goffman was a Canadian-born American sociologist, social psychologist, and writer, considered by some "the most influential American sociologist of the twentieth century".

Institutions are humanly devised structures of rules and norms that shape and constrain individual behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions and norms are all examples of institutions. Institutions vary in their level of formality and informality.

Political sociology is an interdisciplinary field of study concerned with exploring how governance and society interact and influence one another at the micro to macro levels of analysis. Interested in the social causes and consequences of how power is distributed and changes throughout and amongst societies, political sociology's focus ranges across individual families to the state as sites of social and political conflict and power contestation.

Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to humans' particular use of shared language to create common symbols and meanings, for use in both intra- and interpersonal communication. According to Macionis, symbolic interactionism is "a framework for building theory that sees society as the product of everyday interactions of individuals". In other words, it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds, and in return, how these worlds shape individual behaviors. It is a framework that helps understand how society is preserved and created through repeated interactions between individuals. The interpretation process that occurs between interactions helps create and recreate meaning. It is the shared understanding and interpretations of meaning that affect the interaction between individuals. Individuals act on the premise of a shared understanding of meaning within their social context. Thus, interaction and behavior is framed through the shared meaning that objects and concepts have attached to them. From this view, people live in both natural and symbolic environments.

Structural functionalism, or simply functionalism, is "a framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability".

Peter Ludwig Berger was an Austrian-born American sociologist and Protestant theologian. Berger became known for his work in the sociology of knowledge, the sociology of religion, study of modernization, and theoretical contributions to sociological theory.
The theory of structuration is a social theory of the creation and reproduction of social systems that is based on the analysis of both structure and agents, without giving primacy to either. Furthermore, in structuration theory, neither micro- nor macro-focused analysis alone is sufficient. The theory was proposed by sociologist Anthony Giddens, most significantly in The Constitution of Society, which examines phenomenology, hermeneutics, and social practices at the inseparable intersection of structures and agents. Its proponents have adopted and expanded this balanced position. Though the theory has received much criticism, it remains a pillar of contemporary sociological theory.

In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally related groups or sets of roles, with different functions, meanings, or purposes. Examples of social structure include family, religion, law, economy, and class. It contrasts with "social system", which refers to the parent structure in which these various structures are embedded. Thus, social structures significantly influence larger systems, such as economic systems, legal systems, political systems, cultural systems, etc. Social structure can also be said to be the framework upon which a society is established. It determines the norms and patterns of relations between the various institutions of the society.
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general principles and specific parameters that for particular languages are either turned on or off. For example, the position of heads in phrases is determined by a parameter. Whether a language is head-initial or head-final is regarded as a parameter which is either on or off for particular languages. Principles and parameters was largely formulated by the linguists Noam Chomsky and Howard Lasnik. Many linguists have worked within this framework, and for a period of time it was considered the dominant form of mainstream generative linguistics.
Cognitive semantics is part of the cognitive linguistics movement. Semantics is the study of linguistic meaning. Cognitive semantics holds that language is part of a more general human cognitive ability, and can therefore only describe the world as people conceive of it. It is implicit that different linguistic communities conceive of simple things and processes in the world differently, not necessarily some difference between a person's conceptual world and the real world.
In the social sciences, framing comprises a set of concepts and theoretical perspectives on how individuals, groups, and societies organize, perceive, and communicate about reality.

Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about social order and social change. While some sociologists conduct research that may be applied directly to social policy and welfare, others focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of social processes and phenomenological method. Subject matter can range from micro-level analyses of society to macro-level analyses.
The social sciences are the sciences concerned with societies, human behaviour, and social relationships.
Organizational Information Theory (OIT) is a communication theory, developed by Karl Weick, offering systemic insight into the processing and exchange of information within organizations and among its members. Unlike the past structure-centered theory, OIT focuses on the process of organizing in dynamic, information-rich environments. Given that, it contends that the main activity of organizations is the process of making sense of equivocal information. Organizational members are instrumental to reduce equivocality and achieve sensemaking through some strategies — enactment, selection, and retention of information. With a framework that is interdisciplinary in nature, organizational information theory's desire to eliminate both ambiguity and complexity from workplace messaging builds upon earlier findings from general systems theory and phenomenology.








