Related Research Articles

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966, which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The bank also maintains 31 field offices around the world to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific and non-regional developed countries. From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The United Nations Economic and Social Council is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields of the organization, specifically in regards to the fifteen specialised agencies, the eight functional commissions, and the five regional commissions under its jurisdiction.

Port Moresby, also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific outside of Australia and New Zealand. It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the south-western coast of the Papuan Peninsula of the island of New Guinea. The city emerged as a trade centre in the second half of the 19th century. During World War II, it was a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43 as a staging point and air base to cut off Australia from Southeast Asia and the Americas.

ASEAN, officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration between its members and countries in the Asia-Pacific. The union has a total area of 4,522,518 km2 (1,746,154 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 668 million.

The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.

The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation between countries and territories of Oceania, including formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations. It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", so as to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia. It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
The standard of living in India varies from state to state. In 2021, extreme poverty was fully eradicated to as low as 0.8% and India is no longer the nation with the largest population under poverty.

Air Niugini Limited is the national airline of Papua New Guinea, based in Air Niugini House on the property of Port Moresby International Airport, Port Moresby. It operates a domestic network from Port Moresby to 12 major airports while its subsidiary company, Link PNG, operates routes to minor airports. It also operates international services in Asia, Oceania, and Australia on a weekly basis. Its main base is Port Moresby International Airport, which is located in 7 Mile, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. Niugini is the Tok Pisin word for New Guinea.

Kitimat is a district municipality in the North Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. It is a member municipality of the Regional District of Kitimat–Stikine regional government. The Kitimat Valley is part of the most populous urban district in northwest British Columbia, which includes Terrace to the north along the Skeena River Valley. The city was planned and built by the Aluminum Company of Canada (Alcan) during the 1950s. Its post office was approved on June 6, 1952.

The London Plan is the statutory spatial development strategy for the Greater London area in the United Kingdom that is written by the Mayor of London and published by the Greater London Authority.

The International Trade Centre (ITC) is a multilateral agency which has a joint mandate with the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the United Nations (UN) through the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).

Ross Gregory Garnaut is an Australian economist, currently serving as a vice-chancellor's fellow and professorial fellow of economics at the University of Melbourne. He is the author of numerous publications in scholarly journals on international economics, public finance and economic development, particularly in relation to East Asia and the Southwest Pacific.
The Pacific Agreement on Closer Economic Relations (PACER) is an umbrella agreement between members of the Pacific Islands Forum which provides a framework for the future development of trade cooperation.
Gregory Lawrence Urwin PSM CSI was an Australian career diplomat and top Pacific specialist. Urwin held the post of Secretary General of the Pacific Islands Forum, an important inter-governmental regional organisation from 2004 until 2 May 2008. Urwin had been the longest serving Australian diplomat in the Pacific at the time of his death in 2008. Urwin was also the first non-Pacific Islander to become Secretary General of the Pacific Island Forum.

Henry Tuakeu Puna is a Cook Islands politician, and the current secretary-general of the Pacific Islands Forum. He was Prime Minister of the Cook Islands from November 2010 to October 2020. Since 2006 he has been leader of the Cook Islands Party.

The Polynesian Leaders Group (PLG) is an international governmental cooperation group bringing together four independent countries and eight self-governing territories in Polynesia.

The Pacific Institute of Public Policy (PiPP) is an independent, non-profit, regionally focused think tank based in Port Vila, Vanuatu. The stated aim of PiPP is to stimulate and support informed policy debate in the Pacific. A central feature of PiPP's model of engagement with policy stakeholders is the distribution of research via several media including: research syntheses, discussion papers, forums, public debates, social networking, audio and video podcasts, press, radio and television. PiPP was established on November 21, 2007 under the Vanuatu Charitable Associations (Incorporation) Act [CAP.140]. PiPP covers policy issues across the following Pacific Island Countries: Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu

The Development Policy Centre (Devpol) is an aid and development policy think tank based at the Crawford School of Public Policy in the College of Asia and the Pacific at the Australian National University. Devpol undertakes independent research and promotes practical initiatives to improve the effectiveness of Australian aid, to support the development of Papua New Guinea and the Pacific Islands region, and to contribute to better global development policy.
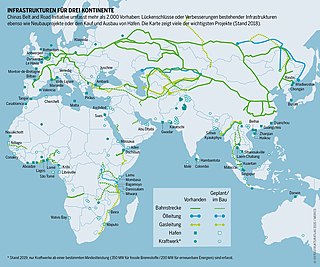
The Belt and Road Initiative, known within China as the One Belt One Road or OBOR for short, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013 to invest in more than 150 countries and international organizations. It is considered a centerpiece of the Chinese leader Xi Jinping's foreign policy. The BRI forms a central component of Xi's "Major Country Diplomacy" strategy, which calls for China to assume a greater leadership role for global affairs in accordance with its rising power and status. It has been compared to the American Marshall Plan. As of January 2023, 151 countries were listed as having signed up to the BRI.
References
- ↑ Maggie Tait (27 October 2005). "Pacific leaders agree to regional plan". New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ "Port Moresby Statement of 6th Pacific Civil Forum". Scoop. 3 November 2005. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ "Pacific Plan Review Report available to Public". Scoop. 20 December 2013. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ "Leaders keen to make Pacific Plan work". RNZ. 6 May 2014. Retrieved 2 March 2021.