
In computing, multitasking is the concurrent execution of multiple tasks over a certain period of time. New tasks can interrupt already started ones before they finish, instead of waiting for them to end. As a result, a computer executes segments of multiple tasks in an interleaved manner, while the tasks share common processing resources such as central processing units (CPUs) and main memory. Multitasking automatically interrupts the running program, saving its state and loading the saved state of another program and transferring control to it. This "context switch" may be initiated at fixed time intervals, or the running program may be coded to signal to the supervisory software when it can be interrupted.
Software testing is the act of examining the artifacts and the behavior of the software under test by validation and verification. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software implementation. Test techniques include, but are not limited to:

An intranet is a computer network for sharing information, easier communication, collaboration tools, operational systems, and other computing services within an organization, usually to the exclusion of access by outsiders. The term is used in contrast to public networks, such as the Internet, but uses the same technology based on the Internet protocol suite.
Defensive programming is a form of defensive design intended to develop programs that are capable of detecting potential security abnormalities and make predetermined responses. It ensures the continuing function of a piece of software under unforeseen circumstances. Defensive programming practices are often used where high availability, safety, or security is needed.
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context.
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development process relying on software requirements being converted to test cases before software is fully developed, and tracking all software development by repeatedly testing the software against all test cases. This is as opposed to software being developed first and test cases created later.
Implementation is the realization of an application, execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, policy, or the administration or management of a process or objective.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The SDLC concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.
In software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation (V&V) is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and requirements so that it fulfills its intended purpose. It may also be referred to as software quality control. It is normally the responsibility of software testers as part of the software development lifecycle. In simple terms, software verification is: "Assuming we should build X, does our software achieve its goals without any bugs or gaps?" On the other hand, software validation is: "Was X what we should have built? Does X meet the high-level requirements?"
In software testing, test automation is the use of software separate from the software being tested to control the execution of tests and the comparison of actual outcomes with predicted outcomes. Test automation can automate some repetitive but necessary tasks in a formalized testing process already in place, or perform additional testing that would be difficult to do manually. Test automation is critical for continuous delivery and continuous testing.

An accounting information system (AIS) is a system of collecting, storing and processing financial and accounting data that are used by decision makers. An accounting information system is generally a computer-based method for tracking accounting activity in conjunction with information technology resources. The resulting financial reports can be used internally by management or externally by other interested parties including investors, creditors and tax authorities. Accounting information systems are designed to support all accounting functions and activities including auditing, financial accounting porting, -managerial/ management accounting and tax. The most widely adopted accounting information systems are auditing and financial reporting modules.
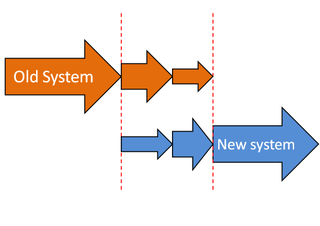
Phased adoption or phased implementation is a strategy of implementing an innovation in an organization in a phased way, so that different parts of the organization are implemented in different subsequent time slots. Phased implementation is a method of System Changeover from an existing system to a new one that takes place in stages. Other concepts that are used are: phased conversion, phased approach, phased strategy, phased introduction and staged conversion. Other methods of system changeover include direct changeover and parallel running.
In computing, adoption means the transfer (conversion) between an old system and a target system in an organization.
Parallel adoption is a method for transferring between a previous (IT) system to a target (IT) system in an organization. In order to reduce risk, the old and new system run simultaneously for some period of time after which, if the criteria for the new system are met, the old system is disabled. The process requires careful planning and control and a significant investment in labor hours.
Big bang adoption or direct changeover is when a new system is adopted instantly, with no transition period between the old and new systems.

In software engineering, structured analysis (SA) and structured design (SD) are methods for analyzing business requirements and developing specifications for converting practices into computer programs, hardware configurations, and related manual procedures.
An order management system, or OMS, is a computer software system used in a number of industries for order entry and processing.
Deployment is the realisation of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy.
A human resources management system (HRMS) or Human Resources Information System (HRIS) or Human Capital Management (HCM) is a form of Human Resources (HR) software that combines a number of systems and processes to ensure the easy management of human resources, business processes and data. Human resources software is used by businesses to combine a number of necessary HR functions, such as storing employee data, managing payroll, recruitment, benefits administration, time and attendance, employee performance management, and tracking competency and training records.
This article discusses a set of tactics useful in software testing. It is intended as a comprehensive list of tactical approaches to Software Quality Assurance (more widely colloquially known as Quality Assurance and general application of the test method.






