
Babylonian law is a subset of cuneiform law that has received particular study due to the large amount of archaeological material that has been found for it. So-called "contracts" exist in the thousands, including a great variety of deeds, conveyances, bonds, receipts, accounts, and most important of all, actual legal decisions given by the judges in the law courts. Historical inscriptions, royal charters and rescripts, dispatches, private letters and the general literature afford welcome supplementary information. Even grammatical and lexicographical texts contain many extracts or short sentences bearing on law and custom. The so-called "Sumerian Family Laws" are preserved in this way.

A wife is a woman in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until their marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgment. On the death of her partner, a wife is referred to as a widow. The rights and obligations of a wife to her partner and her status in the community and law vary between cultures and have varied over time.
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.
A legal fiction is a fact assumed or created by courts, which is then used in order to help reach a decision or to apply a legal rule. The concept is used almost exclusively in common law jurisdictions, particularly in England and Wales.
In Islam, a mahr is the obligation, in the form of money or possessions paid by the groom, to the bride at the time of Islamic marriage. While the mahr is often money, it can also be anything agreed upon by the bride such as jewelry, home goods, furniture, a dwelling or some land. Mahr is typically specified in the marriage contract signed upon marriage.

The legal rights of women refers to the social and human rights of women. One of the first women's rights declarations was the Declaration of Sentiments. The dependent position of women in early law is proved by the evidence of most ancient systems.

In Islam, nikah is a contract between two people. Both the groom and the bride are to consent to the marriage of their own free wills. A formal, binding contract – verbal or on paper – is considered integral to a religiously valid Islamic marriage, and outlines the rights and responsibilities of the groom and bride. Divorce in Islam can take a variety of forms, some executed by a husband personally and some executed by a religious court on behalf of a plaintiff wife who is successful in her legal divorce petition for valid cause. Islamic marital jurisprudence allows Muslim men to be married to multiple women.
In law, a presumption is an "inference of a particular fact". There are two types of presumptions: rebuttable presumptions and irrebuttable presumptions. A rebuttable presumption will either shift the burden of production or the burden of proof ; in short, a fact finder can reject a rebuttable presumption based on other evidence. Conversely, a conclusive/irrebuttable presumption cannot be challenged by contradictory facts or evidence. Sometimes, a presumption must be triggered by a predicate fact—that is, the fact must be found before the presumption applies.
Seisin denotes the legal possession of a feudal fiefdom or fee, that is to say an estate in land. It was used in the form of "the son and heir of X has obtained seisin of his inheritance", and thus is effectively a term concerned with conveyancing in the feudal era. The person holding such estate is said to be "seized of it", a phrase which commonly appears in inquisitions post mortem. The monarch alone "held" all the land of England by his allodial right and all his subjects were merely his tenants under various contracts of feudal tenure.
In the common law, emblements are annual crops produced by cultivation legally belonging to the tenant with the implied right for its harvest, and are treated as the tenant's property.
Chose is a term used in common law tradition to refer to rights in property, specifically a combined bundle of rights. A chose is the enforcement right which a party possesses in an object. The use of chose extends from the English use of French within the courts. In English and commonwealth law, all personal things fall into one of two categories, either choses in action or choses in possession. English law uses chose to refer to a bundle of rights, traditionally relating to property which may be utilised in certain circumstances. Thus, a chose in action refers to a bundle of personal rights which can only be enforced or claimed by a chose-holder bringing an action through the court to enforce the action. In English law, this category is enormously wide. This is contrasted with a chose in possession which is a bundle of rights which can be enforced or acquired by taking physical possession of the object. This may be, for example, a legal mortgage. Both choses in possession and choses in action represent separate proprietary interests. What differs between each is the method in which each chose may be enforced. This is dependent on the possessory nature of the reference object.

Dower is a provision accorded traditionally by a husband or his family, to a wife for her support should she become widowed. It was settled on the bride by agreement at the time of the wedding, or as provided by law.
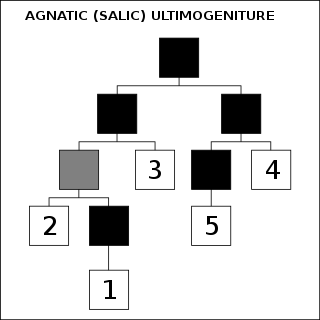
Ultimogeniture, also known as postremogeniture or junior right, is the tradition of inheritance by the last-born of a privileged position in a parent's wealth or office. The tradition has been far rarer historically than primogeniture or partible inheritance.

Myra Colby Bradwell was an American publisher and political activist. She attempted in 1869 to become the first woman to be admitted to the Illinois bar to practice law, but was denied admission by the Illinois Supreme Court in 1870 and the United States Supreme Court in 1873, in rulings upholding a separate women's sphere. Bradwell had founded and published Chicago Legal News from 1868, reporting on the law and continued that work. Meanwhile, influenced by her case, in 1872 the Illinois legislature passed a state law prohibiting gender discrimination in admission to any occupation or profession.

The Married Women's Property Act 1882 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that significantly altered English law regarding the property rights of married women, which besides other matters allowed married women to own and control property in their own right.

A husband is a male in a marital relationship, who may also be referred to as a spouse. The rights and obligations of a husband regarding his spouse and others, and his status in the community and in law, vary between societies and cultures, and have varied over time.
A putative marriage is an apparently valid marriage, entered into in good faith on the part of at least one of the partners, but that is legally invalid due to a technical impediment, such as a preexistent marriage on the part of one of the partners. Unlike someone in a common-law, statutory, or ceremonial marriage, a putative spouse is not legally married. Instead, a putative spouse believes themselves to be married in good faith and is given legal rights as a result of this person's reliance upon this good-faith belief.

Elizabeth of Austria was Queen of Poland by marriage. She was the eldest of fifteen children of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, and his wife Anne of Bohemia and Hungary. A member of the House of Habsburg, she was married to Sigismund II Augustus, who was already crowned as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania even though both of his parents were still alive and well. The marriage was short and unhappy. Elizabeth was of frail health, experiencing epileptic seizures, and died at age 18.
In law, sequestration is the act of removing, separating, or seizing anything from the possession of its owner under process of law for the benefit of creditors or the state.
In Louisiana law, extra-dotal property is that property which forms no part of the dowry of a woman, but is hers alone. It is also called "paraphernal property", from the Greek for "beyond the dowry", which gives us the word "paraphernalia".











