
On 1 May 2004 ten new member states joined the European Union. This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council from 1 May until the end of 2004. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2005. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

Prior to 1 May 2004 the European Union had fifteen members. On that date ten new member states were admitted. This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council from the beginning of 2004 until 1 May. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2003. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
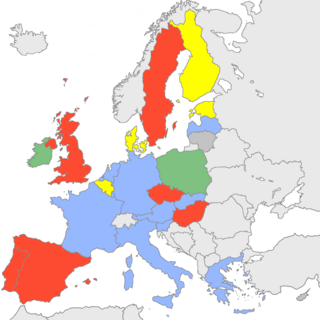
This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2006. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2002. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2001. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2008. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
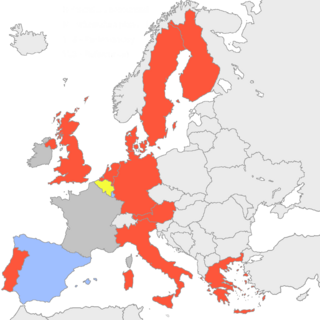
This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2000. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 1999. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2009. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2010. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2011. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2012. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 1998. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
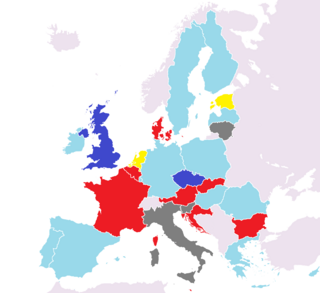
Since 1 July 2013 the European Union have twenty-eight members. Croatia joined the Union, therefore forcing a change of the influence each member-state has, as well as its Qualified Majority Voting. This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2013. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
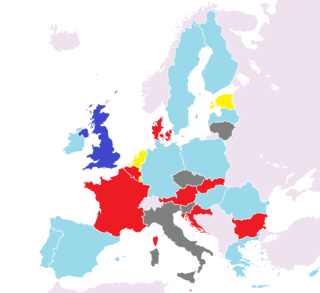
This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2014. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member state represented in the European Council during the year 2015. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the qualified majority system.
This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member state represented in the European Council during the year 2016. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the qualified majority system.
This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member state represented in the European Council during the year 2017. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the qualified majority system.















