Related Research Articles

In the United States, politics function within a framework of a constitutional federal republic and presidential system, with three distinct branches that share powers: the U.S. Congress which forms the legislative branch, a bicameral legislative body comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate; the executive branch, which is headed by the president of the United States, who serves as the country's head of state and government; and the judicial branch, composed of the Supreme Court and lower federal courts, and which exercises judicial power.

The Republican Party, also known as the GOP, is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. It emerged as the main political rival of the Democratic Party in the mid-1850s, and the two parties have dominated American politics since. The GOP was founded in 1854 by anti-slavery activists who opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which allowed for the potential expansion of chattel slavery into the western territories. The Republican Party today comprises diverse ideologies and factions, including centrist and right-libertarian factions, but conservatism is the party's majority ideology.
American electoral politics have been dominated by successive pairs of major political parties since shortly after the founding of the republic of the United States. Since the 1850s, the two largest political parties have been the Democratic Party and the Republican Party—which together have won every United States presidential election since 1852 and controlled the United States Congress since at least 1856. Despite keeping the same names, the two parties have evolved in terms of ideologies, positions, and support bases over their long lifespans, in response to social, cultural, and economic developments—the Democratic Party being the left-of-center party since the time of the New Deal, and the Republican Party now being the right-of-center party.
A wedge issue is a political or social issue, often of a controversial or divisive nature, which splits apart a demographic or population group. Wedge issues can be advertised or publicly aired in an attempt to strengthen the unity of a population, with the goal of enticing polarized individuals to give support to an opponent or to withdraw their support entirely out of disillusionment. The use of wedge issues gives rise to wedge politics. Wedge issues are also known as hot-button or third-rail issues.
Political polarization is the divergence of political attitudes away from the center, towards ideological extremes.
A party system is a concept in comparative political science concerning the system of government by political parties in a democratic country. The idea is that political parties have basic similarities: they control the government, have a stable base of mass popular support, and create internal mechanisms for controlling funding, information and nominations.
A swing vote is a vote that is seen as potentially going to any of a number of candidates in an election, or, in a two-party system, may go to either of the two dominant political parties. Such votes are usually sought after in election campaigns, since they can play a big role in determining the outcome.
An independent voter, often also called an unaffiliated voter or non-affiliated voter in the United States, is a voter who does not align themselves with a political party. An independent is variously defined as a voter who votes for candidates on issues rather than on the basis of a political ideology or partisanship; a voter who does not have long-standing loyalty to, or identification with, a political party; a voter who does not usually vote for the same political party from election to election; or a voter who self-describes as an independent.
A nonpartisan blanket primary is a primary election in which all candidates for the same elected office run against each other at once, regardless of the political party. Partisan elections are, on the other hand, segregated by political party. Nonpartisan blanket primaries are slightly different from most other elections systems with two-rounds/runoff, aka "jungle primaries" , in a few ways. The first round of a nonpartisan blanket primary is officially the "primary." Round two is the "general election." Round two must be held, even if one candidate receives a majority in the first round.
Latino Americans have received a growing share of the national vote in the United States due to their increasing population. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, 62.1 million Latinos live in the United States, representing 18.9% of the total U.S. population. This is a 23% increase since 2010. This racial/ethnic group is the second largest after non-Hispanic whites in the U.S. In 2020, the states with the highest Hispanic or Latino populations were; Arizona, California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, and Texas. According to the Brookings Institute, Latinos will become the nations largest minority by 2045 and the deciding population in future elections. With the help of laws and court case wins, Latinos have been able to receive the help needed to participate in American Politics. According to data provided by The Collaborative Multiracial Post-Election Survey (CMPS), 72% of Latinos believe that it is very/somewhat important to get their voice heard by voting. They have traditionally been a key Democratic Party constituency, but more recently have begun to split between the Democratic and Republican Party. Since the Latino population is large and diverse, a lot of political differences exist between gender, national origin, and generational groups.

American political ideologies conventionally align with the left–right political spectrum, with most Americans identifying as conservative, liberal, or moderate. Contemporary American conservatism includes social conservatism, classical liberalism and economic liberalism. The former ideology developed as a response to communism and the civil rights movement, while the latter two ideologies developed as a response to the New Deal. Contemporary American liberalism includes progressivism, welfare capitalism and social liberalism, developing during the Progressive Era and the Great Depression. Besides modern conservatism and liberalism, the United States has a notable libertarian movement, developing during the mid-20th century as a revival of classical liberalism. Historical political movements in the United States have been shaped by ideologies as varied as republicanism, populism, separatism, fascism, socialism, monarchism, and nationalism.
Alan Ira Abramowitz is an American political scientist and author, known for his research and writings on American politics, elections in the United States, and political parties in the United States.
Matthew S. Levendusky is an American political scientist, best known for his 2009 book The Partisan Sort: How Liberals Became Democrats and Conservatives Became Republicans. His work has primarily focused on explaining political polarization, but also includes media analyses and topics related to public opinion and American foreign policy. Levendusky is currently associate professor of political science at the University of Pennsylvania.
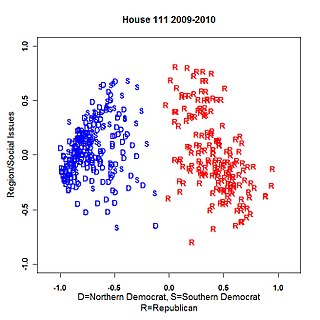
NOMINATE is a multidimensional scaling application developed by US political scientists Keith T. Poole and Howard Rosenthal in the early 1980s to analyze preferential and choice data, such as legislative roll-call voting behavior. In its most well-known application, members of the US Congress are placed on a two-dimensional map, with politicians who are ideologically similar being close together. One of these two dimensions corresponds to the familiar left–right political spectrum.
The term issue voting describes when voters cast their vote in elections based on political issues. In the context of an election, issues include "any questions of public policy which have been or are a matter of controversy and are sources of disagreement between political parties.” According to the theory of issue voting, voters compare the candidates' respective principles against their own in order to decide for whom to vote.
Voting behavior refers to how people decide how to vote. This decision is shaped by a complex interplay between an individual voter's attitudes as well as social factors. Voter attitudes include characteristics such as ideological predisposition, party identity, degree of satisfaction with the existing government, public policy leanings, and feelings about a candidate's personality traits. Social factors include race, religion and degree of religiosity, social and economic class, educational level, regional characteristics, and gender. The degree to which a person identifies with a political party influences voting behavior, as does social identity. Voter decision-making is not a purely rational endeavor but rather is profoundly influenced by personal and social biases and deeply held beliefs as well as characteristics such as personality, memory, emotions, and other psychological factors. Voting advice applications and avoidance of wasted votes through strategic voting can impact voting behavior.
Nolan Matthew McCarty is an American political scientist specializing in U.S. politics, democratic political institutions, and political methodology. He has made notable contributions to the study of partisan polarization, the politics of economic inequality, theories of policy-making, and the statistical analysis of legislative voting.
Negative partisanship is the tendency of some voters to form their political opinions primarily in opposition to political parties they dislike. Whereas traditional partisanship involves supporting the policy positions of one's own party, its negative counterpart in turn means opposing those positions of a disliked party. It has been claimed to be the cause of severe polarization in American politics. It has also been studied in the Canadian context, as well as in Australia and New Zealand. Cross-national studies indicate that negative partisanship undermines public satisfaction with democracy, which threatens democratic stability. Traditional partisans, on the other hand, are more likely to support their country's democracy, which promotes democratic stability.

Political polarization is a prominent component of politics in the United States. Scholars distinguish between ideological polarization and affective polarization, both of which are apparent in the United States. In the last few decades, the U.S. has experienced a greater surge in ideological polarization and affective polarization than comparable democracies.

Political polarization is the bimodal distribution, meaning that two obvious peaks of opinion in the political sense. It can be observed through people's choices, sociopolitical approaches, and even where they live. In the last years, political polarization has caused many political results in the governments and the law-making organs. However it may not be classified as a "negative" aspect, and it can be used by politicians to examine the social and economic parts to develop in a country. Citizens would be more prone to do skeptical analysis on the subjects, and gain more meaning in their lives. Mexico, Turkey, India, South Africa, Brazil and Venezuela are amongst the countries that have the highest polarization.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Mason, Lilliana (2015). ""I Disrespectfully Agree": The Differential Effects of Partisan Sorting on Social and Issue Polarization". American Journal of Political Science. 59 (1): 128–145. doi:10.1111/ajps.12089. ISSN 0092-5853. JSTOR 24363600.
- 1 2 3 McCarty, Nolan (2019-12-05), "What is Political Polarization?", Polarization, Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/wentk/9780190867782.003.0002, ISBN 978-0-19-086778-2 , retrieved 2022-01-26
- ↑ Abramowitz, Alan; Fiorina, Morris. "Polarized or Sorted? Just What's Wrong With Our Politics, Anyway?". The American Interest. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- 1 2 Mummolo, Jonathan; Nall, Clayton (2016-10-13). "Why Partisans Do Not Sort: The Constraints on Political Segregation". The Journal of Politics. 79 (1): 45–59. doi:10.1086/687569. ISSN 0022-3816. S2CID 9272199.
- ↑ Tam Cho, Wendy K.; Gimpel, James G.; Hui, Iris S. (2012). "Voter Migration and the Geographic Sorting of the American Electorate". Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 103 (4): 856–870. doi:10.1080/00045608.2012.720229. ISSN 0004-5608. S2CID 34925586.