
Digital Equipment Corporation, using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until he was forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline.
Samba is a free software re-implementation of the SMB networking protocol, and was originally developed by Andrew Tridgell. Samba provides file and print services for various Microsoft Windows clients and can integrate with a Microsoft Windows Server domain, either as a Domain Controller (DC) or as a domain member. As of version 4, it supports Active Directory and Microsoft Windows NT domains.

OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide.
DECnet is a suite of network protocols created by Digital Equipment Corporation. Originally released in 1975 in order to connect two PDP-11 minicomputers, it evolved into one of the first peer-to-peer network architectures, thus transforming DEC into a networking powerhouse in the 1980s. Initially built with three layers, it later (1982) evolved into a seven-layer OSI-compliant networking protocol.

Ultrix is the brand name of Digital Equipment Corporation's (DEC) discontinued native Unix operating systems for the PDP-11, VAX, MicroVAX and DECstations.

Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol used to share files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. On Microsoft Windows, the SMB implementation consists of two vaguely named Windows services: "Server" and "Workstation". It uses NTLM or Kerberos protocols for user authentication. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism.

NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol.
IPX/SPX stands for Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange. IPX and SPX are networking protocols used initially on networks using the Novell NetWare operating systems. They also became widely used on networks deploying Microsoft Windows LANS, as they replaced NetWare LANS, but are no longer widely used. IPX/SPX was also widely used prior to and up to Windows XP, which supported the protocols, while later Windows versions do not, and TCP/IP took over for networking.

Windows NT 3.1 is the first major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, released on July 27, 1993.
A remote access service (RAS) is any combination of hardware and software to enable the remote access tools or information that typically reside on a network of IT devices.
LAN Manager is a discontinued network operating system (NOS) available from multiple vendors and developed by Microsoft in cooperation with 3Com Corporation. It was designed to succeed 3Com's 3+Share network server software which ran atop a heavily modified version of MS-DOS.

A diskless node is a workstation or personal computer without disk drives, which employs network booting to load its operating system from a server.
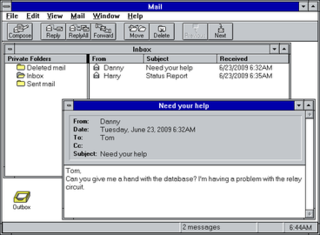
Microsoft Mail was the name given to several early Microsoft e-mail products for local area networks, primarily two architectures: one for Macintosh networks, and one for PC architecture-based LANs. All were eventually replaced by the Exchange and Outlook product lines.
Local Area Transport (LAT) is a non-routable networking technology developed by Digital Equipment Corporation to provide connection between the DECserver terminal servers and Digital's VAX and Alpha and MIPS host computers via Ethernet, giving communication between those hosts and serial devices such as video terminals and printers. The protocol itself was designed in such a manner as to maximize packet efficiency over Ethernet by bundling multiple characters from multiple ports into a single packet for Ethernet transport.
The 3Com 3Server was a headless dedicated network-attached storage machine designed to run 3Com local area network (LAN) server software, 3+Share.
IBM Storage Protect is a data protection platform that gives enterprises a single point of control and administration for backup and recovery. It is the flagship product in the IBM Spectrum Protect family.
In computer networking, DECserver initially referred to a highly successful family of asynchronous console server / terminal server / print server products introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) and later referred to a class of UNIX-variant application and file server products based upon the MIPS processor. In February 1998, DEC sold its Network Products Business to Cabletron, which then spun out as its own company, Digital Networks, in September 2000.
CT Connect is a software product that allows computer applications to monitor and control telephone calls. This monitoring and control is called computer-telephone integration, or CTI. CT Connect implements CTI by providing server software that supports the CTI link protocols used by a range of telephone systems, and client software that provides an application programming interface (API) for telephony functions.
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which was released on July 27, 1993, and it lives on today since the latest version of Windows, 11, includes its technology.
Lawrence W. White - PATHWORKS Product Manager







