| Look up pedate in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
In biology, a pedate structure is a structure that resembles feet, or has a quality of feet. It derives from the Latin verb "pedo", meaning "to furnish with feet".
| Look up pedate in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
In biology, a pedate structure is a structure that resembles feet, or has a quality of feet. It derives from the Latin verb "pedo", meaning "to furnish with feet".

Botanically, the term is used to describe compound leaves, veins, or other structures, where the divisions of that structure arise from a central point (as in a palmate structure), but the lateral divisions are further cleft in two. [1] More broadly, it can be used to describe a compound leaf with a terminal leaflet and branching axes to either side which curve outward and backward, to which leaflets are attached on the outer side of the curve. [2]
In animals, the term "pedate" is used to mean "having feet," a sense that includes the tube feet of echinoderms as well as the vertebrate foot.

A heterotroph is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology in describing the food chain.

An achene is a type of simple dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate and indehiscent. Achenes contain a single seed that nearly fills the pericarp, but does not adhere to it. In many species, what is called the "seed" is an achene, a fruit containing the seed. The seed-like appearance is owed to the hardening of the fruit wall (pericarp), which encloses the solitary seed so closely as to seem like a seed coat.

Pinnation is the arrangement of feather-like or multi-divided features arising from both sides of a common axis. Pinnation occurs in biological morphology, in crystals, such as some forms of ice or metal crystals, and in patterns of erosion or stream beds.
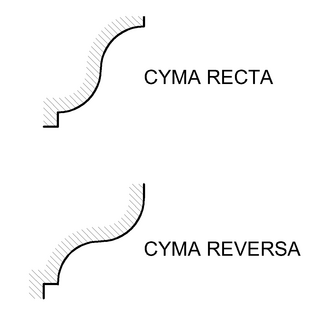
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or vice versa, have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions.

Mount Mazama is a complex volcano in the state of Oregon, United States, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountain collapsed following a major eruption approximately 7,700 years ago. The volcano is in Klamath County, in the southern Cascades, 60 miles (97 km) north of the Oregon–California border. Its collapse formed a caldera that holds Crater Lake. The mountain is in Crater Lake National Park. Mount Mazama originally had an elevation of 12,000 feet (3,700 m), but following its climactic eruption this was reduced to 8,157 feet (2,486 m). Crater Lake is 1,943 feet (592 m) deep, the deepest freshwater body in the US and the second deepest in North America after Great Slave Lake in Canada.
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own, defense, and interactions with other organisms.

A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves.
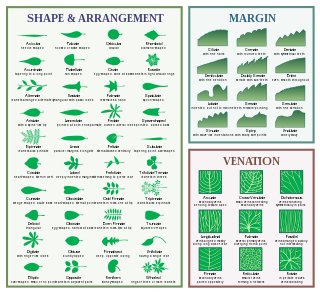
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple or compound. The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.

A wigwam, wickiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam (Ojibwe) is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term wickiup is generally used to refer to these kinds of dwellings in the Southwestern United States and Western United States, while wigwam is usually applied to these structures in the Northeastern United States as well as Ontario and Quebec in central Canada. The names can refer to many distinct types of Native American structures regardless of location or cultural group. The wigwam is not to be confused with the Native Plains teepee, which has a very different construction, structure, and use.

A chaeta or cheta is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms,. Polychaete annelids, are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals.

Cyclanthera pedata, known as caigua, is a herbaceous vine grown for its edible fruit, which is predominantly used as a vegetable. It is known from cultivation only, and its use goes back many centuries as evidenced by ancient phytomorphic ceramics from Peru depicting the fruits.
An oval is a closed curve in a plane which resembles the outline of an egg. The term is not very specific, but in some areas it is given a more precise definition, which may include either one or two axes of symmetry of an ellipse. In common English, the term is used in a broader sense: any shape which reminds one of an egg. The three-dimensional version of an oval is called an ovoid.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

The Psychological Warfare Division of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force was a joint Anglo-American organization set-up in World War II tasked with conducting (predominantly) white tactical psychological warfare against German troops and recently liberated countries in Northwest Europe, during and after D-Day. It was headed by US Brigadier-General Robert A. McClure. The Division was formed from staff of the US Office of War Information (OWI) and Office of Strategic Services (OSS) and the British Political Warfare Executive (PWE).
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names.

A leaf is the principal lateral appendage of the vascular plant stem, usually borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. The leaves, stem, flower and fruit together form the shoot system. Leaves are collectively referred to as foliage, as in "autumn foliage". In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue, the palisade mesophyll, is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus, palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper and lower surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata, the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light energy from the sun. A leaf with lighter-colored or white patches or edges is called a variegated leaf.
Acer eonegundo is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from a single partial fossil leaf. The species is known from Eocene sediments exposed in the US state of Nevada. It is placed into the living Acer section Negundo.

Rhus boothillensis is an extinct species of flowering plant in the sumac family Anacardiaceae. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington State, United States. The species was first described from fossil leaves found in the Klondike Mountain Formation. Rhus boothillensis likely hybridized with the other Klondike Mountain formation sumac species Rhus garwellii, Rhus malloryi, and Rhus republicensis.

Barghoornia is an extinct genus of flowering plants in the family Burseraceae containing the solitary species Barghoornia oblongifolia. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States.