Related Research Articles

Pembrokeshire is a county in the south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and the rest by sea. The county is home to Pembrokeshire Coast National Park. The Park occupies more than a third of the area of the county and includes the Preseli Hills in the north as well as the 190-mile (310 km) Pembrokeshire Coast Path.

The Aberdeen Angus, sometimes simply Angus, is a Scottish breed of small beef cattle. It derives from cattle native to the counties of Aberdeen, Banff, Kincardine and Angus in north-eastern Scotland. In 2018 the breed accounted for over 17% of the UK beef industry.

The Welsh Corgi is a small type of herding dog that originated in Wales. The name corgi is derived from the Welsh words cor and ci, meaning "dwarf" and "dog", respectively.

Pembroke is both a town and a community in Pembrokeshire, Wales, with a population of 7,552. The names of both the town and the county have a common origin; both are derived from the Cantref of Penfro: Pen, "head" or "end", and bro, "region", "country", "land", which has been interpreted to mean either "Land's End" or "headland".
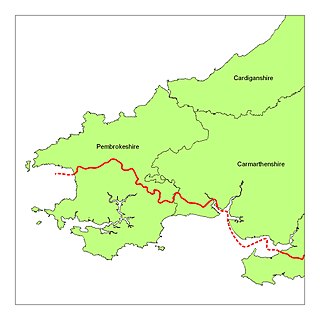
Little England beyond Wales is a name that has been applied to an area of southern Pembrokeshire and southwestern Carmarthenshire in Wales, which has been English in language and culture for many centuries despite its remoteness from England. Its origins may lie in the Irish, Norse, Norman, Flemish and Saxon settlement that took place in this area more than in other areas of South West Wales. Its northern boundary is known as the Landsker Line.

The Guernsey is a breed of dairy cattle from the island of Guernsey in the Channel Islands. It is fawn or red and white in colour, and is hardy and docile. Its milk is rich in flavour, high in fat and protein, and has a golden-yellow tinge due to its high β-carotene content. The Guernsey is one of three Channel Island cattle breeds, the others being the Alderney – now extinct – and the Jersey.

The Dairy Shorthorn is a British breed of dairy cattle. It derives from the Shorthorn cattle of Tees-side, in the North Riding of Yorkshire and in Northumbria in north-eastern England. The Shorthorn was for this reason at first known as the Durham or Teeswater.

The Shorthorn breed of cattle originated in the North East of England in the late eighteenth century. The breed was developed as dual-purpose, suitable for both dairy and beef production; however, certain blood lines within the breed always emphasised one quality or the other. Over time, these different lines diverged, and by the second half of the twentieth century, two separate breeds had developed – the Beef Shorthorn, and the Milking Shorthorn. All Shorthorn cattle are coloured red, white, or roan, although roan cattle are preferred by some, and completely white animals are not common. However, one type of Shorthorn has been bred to be consistently white – the Whitebred Shorthorn, which was developed to cross with black Galloway cattle to produce a popular blue roan crossbreed, the Blue Grey.

The Welsh Black is a dual-purpose breed of cattle native to Wales. This breed is one of the oldest in Britain, going back to pre-Roman times. The Welsh Black was a prized possession of Britain's people upon the invasion of the Saxons.

The Landsker Line is a term used for the language border in Wales between the largely Welsh-speaking and largely English-speaking areas in Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire. The English-speaking areas, south of the Landsker line and known as Little England beyond Wales, are notable for having been English linguistically and culturally for many centuries despite being far from the England–Wales border.

Glamorgan Cattle are a rare British cattle breed. Once common in the counties of Glamorgan, Monmouth, and Brecon, the breed was thought to have died out, until a remnant herd was found in the 1970s.
Pembrokeshire was a parliamentary constituency based on the county of Pembrokeshire in Wales. It returned one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, elected by the first past the post system.

The Shetland Islands of Scotland have long had their own distinct animal breeds, due to the remoteness of the archipelago. Below is a list of Shetland's domesticated animals.

Welsh Mountain sheep are small, hardy sheep from the higher parts of the Welsh mountains. The males have horns, and the females are polled (hornless); they have no wool on the face or legs, and they have long tails. There are a number of varieties, bred for sheep farming in Wales. These are mainly colour variations, but some are being developed as separate breeds.
The Welsh Road, also known as the Welshman's Road or the Bullock Road, was a drover's road running through the English Midlands, used for transporting cattle from North Wales to the markets of South East England.

The Welsh is a breed of domestic pig native to Wales. It is a large white breed known for its hardiness in outdoor (extensive) farming, its long, pear-shaped body and its lop-ears. The breed was first mentioned in the 1870s, and after the Howitt committee report in 1955, became the third most common sire in the United Kingdom after the Large White pig and British Landrace pig. The Welsh pig experienced a decline in numbers in the late twentieth century because consumer demands had changed and the carcase was considered too fatty. In 2005 the breed was considered endangered and later came under the auspices of the Rare Breeds Survival Trust. Since then numbers have expanded somewhat, and by 2012, the registered breeding herd had increased to over 1000 animals.

William Youatt was an English veterinary surgeon and animal welfare writer.

Agriculture in Wales has in the past been a major part of the economy of Wales, a largely rural country that forms part of the United Kingdom. Wales is mountainous and has a mild, wet climate. This results in only a small proportion of the land area being suitable for arable cropping, but grass for the grazing of livestock is present in abundance. As a proportion of the national economy, the importance of agriculture has become much reduced; a high proportion of the population now live in the towns and cities in the south of the country and tourism has become an important form of income in the countryside and on the coast. Arable cropping is limited to the flatter parts and elsewhere dairying and livestock farming predominate.

Welsh cuisine encompasses the cooking styles, traditions and recipes associated with Wales. While there are many dishes that can be considered Welsh due to their ingredients and/or history, dishes such as cawl, Welsh rarebit, laverbread, Welsh cakes, bara brith and Glamorgan sausage have all been regarded as symbols of Welsh food. Some variation in dishes exists across the country, with notable differences existing in the Gower Peninsula, a historically isolated rural area which developed self-sufficiency in food production.

Pembrokeshire has been called "the cottage garden of Wales", due to its good soil and the beneficial effects of the Gulf Stream, which provide a mild climate and a longer growing season than other parts of the country. The good climate and soil meant that the south of the peninsula was coveted by the Norsemen and Normans because it had "great plentie" of corn and cattle The county has prime agricultural land, much of which is located at about 70m above sea level, while to the north, the Preseli Hills rise to 500m above sea level and form uplands that are made up of heather and bracken, which are used for grazing sheep. Consequently, Pembrokeshire is classed as one of the most fertile counties in Wales, with its 392,300 agricultural acres having 14% of its land classed as of good quality, 67% being classed as medium quality and 19% being classed as poor quality. However, agricultural production is subject to market forces and in the 1890s, as a result of the Panic of 1893, a deep agricultural depression led to the area under cultivation falling by a third. Many labourers and farmers had no option but to emigrate to the New World and many of the large farming estates were sold. World War I brought prosperity again, but by the 1930s, as a result of the Great Depression, there was another agricultural depression which lasted until World War II. During the Post-war period agriculture has benefited from marketing schemes and marketing boards, which have helped in the regulation, marketing and distribution of the county's agricultural production.
References
- ↑ Colyer, J. "Some Welsh Breeds of Cattle in the Nineteenth Century" (PDF). p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2006.
- 1 2 Colyer, J. "Some Welsh Breeds of Cattle in the Nineteenth Century" (PDF). p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2006.
- ↑ C. S. Read, Journal of the Royal Agricultural Society of England x, I849, p139
- ↑ W. Youatt, Cattle, their breeds, management and disease, 1834, pp. 72-3.
- ↑ "THE CATTLE OF PEMBROKESHIRE". The Sydney Stock and Station Journal . Vol. XXII, no. 79. New South Wales, Australia. 30 December 1910. p. 8. Retrieved 2 September 2018– via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ J. Bannister. A synopsis of husbandry, I799, p. 47
- Twm Elias, Welsh Farm Animals 1: Cattle, Gwasg Carreg Gwalch, 2000.