Related Research Articles

Invertebrates is an umbrella term describing animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column, which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians and sponges.

Placozoa is a phylum of marine and free-living (non-parasitic) animals. They are simple blob-like animals without any body part or organ, and are merely aggregates of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by engulfment, reproducing by fission or budding, placozoans are described as "the simplest animals on Earth." Structural and molecular analyses have supported them as among the most basal animals, thus, constituting the most primitive metazoan phylum.

Symbion is a genus of commensal aquatic animals, less than 0.5 mm wide, found living attached to the mouthparts of cold-water lobsters. They have sac-like bodies, and three distinctly different forms in different parts of their two-stage life-cycle. They appear so different from other animals that they were assigned their own, new phylum Cycliophora shortly after they were discovered in 1995. This was the first new phylum of multicelled organism to be discovered since the Loricifera in 1983.
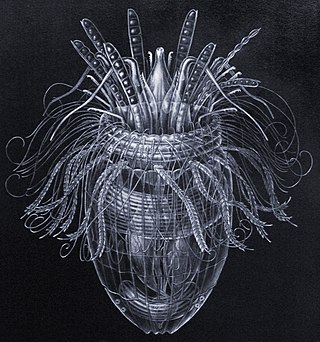
Loricifera is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals with 43 described species. and approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to ca. 1 mm.

The Chaetognatha or chaetognaths are a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, they are mostly nektonic; however about 20% of the known species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from 2 to 120 millimetres.
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla.
This timeline of biology and organic chemistry captures significant events from before 1600 to the present.

The rotifers, commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals.
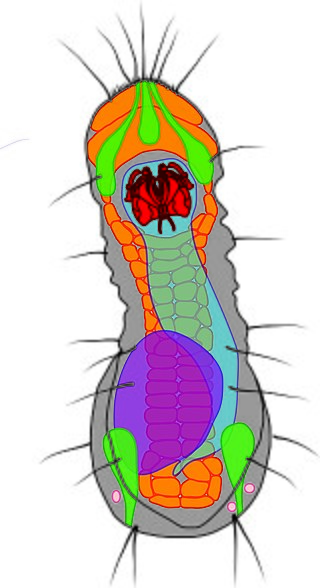
Limnognathia maerski is a microscopic freshwater animal, discovered living in warm springs on Disko Island, Greenland, in 1994. Since then, it has also been found on the Crozet Islands of Antarctica as well as in the British Isles, suggesting a worldwide distribution, although there are likely different species yet to be described.
Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen is a Danish invertebrate biologist, noted for the discovery of three new phyla of microscopic animals: the Loricifera in 1983, the Cycliophora in 1995, and the Micrognathozoa in 2000. He is also considered one of the world's leading experts on tardigrades. His recent field of work revolves mostly around arctic biology.

The Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry is a research institute of the Max Planck Society located in Martinsried, a suburb of Munich. The institute was founded in 1973 by the merger of three formerly independent institutes: the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, the Max Planck Institute of Protein and Leather Research, and the Max Planck Institute of Cell Chemistry.

Xenoturbella is a genus of very simple bilaterians up to a few centimeters long. It contains a small number of marine benthic worm-like species.

Symbion pandora is a jug-shaped microscopic aquatic animal that dwells on the mouth-parts of Norway lobsters. The animals are less than ½ mm wide, with sac-like bodies, and three distinctly different forms in different parts of their three-stage life cycle.
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals, and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life, in part, shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, and amphibians, which rely on aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water.

Brian J. Ford HonFLS HonFRMS is an independent research biologist, author, and lecturer, who publishes on scientific issues for the general public. He has also been a television personality for more than 40 years. Ford is an international authority on the microscope. Throughout his career, Ford has been associated with many academic bodies. He was elected a Fellow of Cardiff University in 1986, was appointed Visiting Professor at the University of Leicester, and has been awarded Honorary Fellowship of the Royal Microscopical Society and of the Linnean Society of London. In America, he was awarded the inaugural Köhler Medal and was recently recipient of the Ernst Abbe medal awarded by the New York Microscopical Society. In 2004 he was awarded a personal fellowship from NESTA, the National Endowment for Science, Technology and the Arts. During those three years he delivered 150 lectures in scores of countries, meeting 10,000 people in over 350 universities around the world.

Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a single clade.

Marine invertebrates are the invertebrates that live in marine habitats. Invertebrate is a blanket term that includes all animals apart from the vertebrate members of the chordate phylum. Invertebrates lack a vertebral column, and some have evolved a shell or a hard exoskeleton. As on land and in the air, marine invertebrates have a large variety of body plans, and have been categorised into over 30 phyla. They make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans.

Gnathifera is a clade of generally small spiralians characterized by complex jaws made of chitin. It comprises the phyla Gnathostomulida, Rotifera and Micrognathozoa. Chaetognatha has recently been recognised as closely related to the group, with it either being included within Gnathifera or the broader group Chaetognathifera. It may also include the Cycliophora.

Spinoloricus cinziae is an animal species described in 2014 in the phylum Loricifera.
References
- 1 2 3 "Peter Funch". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- 1 2 "Peter Funch". Aarhus University Research on the Anthropocene. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ↑ Marshall, Michael (28 April 2010). "Zoologger: The most bizarre life story on Earth?". NewScientist. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ↑ Gordon, Dennis P. (2009). "Towards a management hierarchy (classification) for the Catalogue of Life". In Bisby, F.A.; Roskov, Y.R.; Orrell, T.M.; Nicolson, D.; et al. (eds.). Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life (Draft discussion document). 2009 Annual Checklist. Reading, UK: Species 2000. Archived from the original (CD-ROM) on 2009-08-08.
- ↑ "Peter FUNCH | Professor (Associate) | Aarhus University | AU | Department of Biology PHD". ResearchGate. Retrieved 30 January 2024.