
Epic Games, Inc. is an American video game and software developer and publisher based in Cary, North Carolina. The company was founded by Tim Sweeney as Potomac Computer Systems in 1991, originally located in his parents' house in Potomac, Maryland. Following its first commercial video game release, ZZT (1991), the company became Epic MegaGames, Inc. in early 1992 and brought on Mark Rein, who has been its vice president since. After moving the headquarters to Cary in 1999, the studio changed its name to Epic Games.

Deep Silver is an Austrian video game publisher and a division of Plaion.

Behaviour Interactive Inc. is a Canadian video game developer based in Montreal. The studio is best known for the multiplayer horror game Dead by Daylight.

Unity is a cross-platform game engine developed by Unity Technologies, first announced and released in June 2005 at Apple Worldwide Developers Conference as a Mac OS X game engine. The engine has since been gradually extended to support a variety of desktop, mobile, console, augmented reality, and virtual reality platforms. It is particularly popular for iOS and Android mobile game development, is considered easy to use for beginner developers, and is popular for indie game development.

People Can Fly is a Polish video game developer based in Warsaw. The studio was founded in February 2002 by Adrian Chmielarz, previously the co-founder of Metropolis Software, together with acquaintances Michał Kosieradzki and Andrzej Poznański. The studio's first game was Painkiller (2004). Its success led to a deal with THQ for the game Come Midnight, which allowed the studio to expand. After the game was cancelled, People Can Fly found itself in financial trouble. Epic Games acquired a majority share in People Can Fly in August 2007 and collaborated with the studio on projects such as Bulletstorm (2011) and Gears of War: Judgment (2013).
Kongregate is an American web gaming portal and video game publisher. Its website features over 124,000 online games and 30+ mobile games available to the public. The company also publishes games for PC, mobile, and home consoles. It was purchased by GameStop Corporation in 2010 before being acquired by Modern Times Group MT AB in 2017.
Improbable Worlds Limited is a multinational technology company founded in 2012 and headquartered in London, England. It makes metaverse infrastructure and applications, as well as simulation software for video games and corporate use. It reported revenues of £78m in fiscal 2022, up 260% over 2021.

Zynga Inc. is an American developer running social video game services. It was founded in April 2007, with headquarters in San Mateo, California. The company primarily focuses on mobile and social networking platforms. Zynga states its mission as "connecting the world through games".
Ngmoco, LLC was an American-based publisher of video games for the iOS and Android platforms, and a subsidiary of DeNA Co., Ltd. The company was founded by former Electronic Arts executive Neil Young in July 2008. Since its founding, ngmoco has had more than seven million combined game installs. Venture capital firms Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers and Norwest Venture Partners, among others, have financed the company with a combined total of US$40.6 million. The company is most well known for their publishing of the Rolando game series and Eliminate Pro.
Humble Bundle, Inc. is a digital storefront for video games, which grew out of its original offering of Humble Bundles, collections of games sold at a price determined by the purchaser and with a portion of the price going towards charity and the rest split between the game developers. Humble Bundle continues to offer these limited-time bundles, but have expanded to include a greater and more persistent storefront. The Humble Bundle concept was initially run by Wolfire Games in 2010, but by its second bundle, the Humble Bundle company was spun out to manage the promotion, payments, and distribution of the bundles. In October 2017, the company was acquired by Ziff Davis through its IGN Entertainment subsidiary.

Kabam is a Canadian video game developer and publisher founded in 2006 and headquartered in Vancouver, with offices in Montreal, San Francisco, and Austin, Texas. The company develops and publishes massively multiplayer social games such as Marvel Contest of Champions and Transformers: Forged to Fight for mobile devices. Before expanding into gaming, Kabam established itself as a social applications developer with focusing on entertainment and sports.
Supermono Studios is a video game publisher and application development studio based in London, UK. They are best known for developing games for iOS and Android, with MiniSquadron, EpicWin, and Forever Drive being their most successful and popular titles.

Maximum Games, Inc. is an American video game publisher based in Walnut Creek, California. Originally founded in 2009 as a publisher of family-oriented titles for the Nintendo DS and Nintendo Wii, the company shifted to publishing games of all genres for all ages across all platforms shortly after inception.

Dauntless is a free-to-play action role-playing game developed by Phoenix Labs and published and distributed by Epic Games. The game initially launched in beta in May 2018 for Microsoft Windows. An early access version launched on May 21, 2019 for PlayStation 4 and Xbox One, including full support for cross-platform play, and was fully released for those platforms on September 26, 2019. A Nintendo Switch version was released on December 10, 2019. Versions for PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X/S were released on December 2, 2021.
Snapshot Games is a Bulgarian video game developer headquartered in Sofia. Snapshot Games was founded in 2013 by Julian Gollop and David Kaye. Gollop is recognized for creating the X-COM video game franchise in the 1990s with X-COM: UFO Defense and X-COM: Apocalypse. Gollop also is the CEO of Snapshot Games. In addition to Gollop, the company includes about eight developers who are industry veterans with years of previous experience working for Ubisoft Sofia, Crytek Black Sea, and other Bulgaria studios.
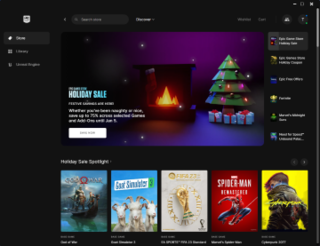
The Epic Games Store is a video game digital distribution service and storefront operated by Epic Games. It launched in December 2018 as a software client, for Microsoft Windows and macOS, and online storefront. The service provides friends list management, game matchmaking, and other features. Epic Games has further plans to expand the feature set of the storefront but it does not plan to add as many features as other digital distribution platforms, such as discussion boards or user reviews, instead using existing social media platforms to support these.

Stillfront Group is a Sweden-based company specialized in the acquisition and management of mobile and browser game studios.











