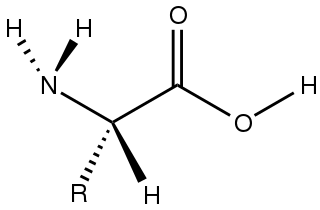
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, from which proteins are composed. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code.

Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a Clostridium tetani infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.

Cysteine is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HOOC−CH(−NH2)−CH2−SH. The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, only L-cysteine is found in nature.
Serine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC.

Threonine is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Threonine is synthesized from aspartate in bacteria such as E. coli. It is encoded by all the codons starting AC.
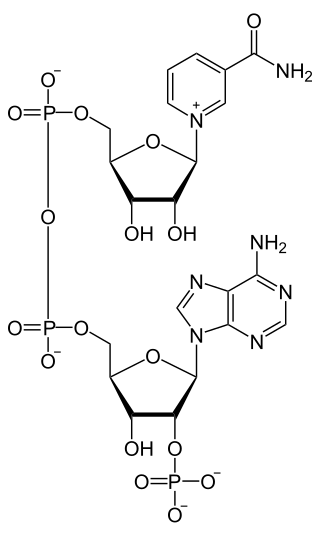
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life.
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term nonribosomal peptide typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article.
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
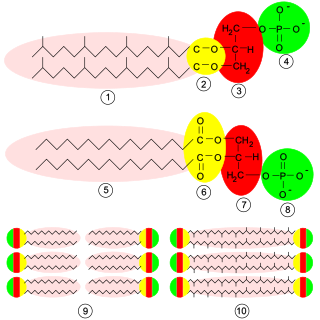
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.

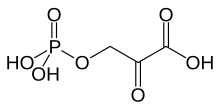
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. The anion is often termed as PGA when referring to the Calvin-Benson cycle. In the Calvin-Benson cycle, 3-phosphoglycerate is typically the product of the spontaneous scission of an unstable 6-carbon intermediate formed upon CO2 fixation. Thus, two equivalents of 3-phosphoglycerate are produced for each molecule of CO2 that is fixed. In glycolysis, 3-phosphoglycerate is an intermediate following the dephosphorylation (reduction) of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.

Cycloserine, sold under the brand name Seromycin, is a GABA transaminase inhibitor and an antibiotic, used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used, along with other antituberculosis medications, for active drug resistant tuberculosis. It is given by mouth.

Sulfur assimilation is the process by which living organisms incorporate sulfur into their biological molecules. In plants, sulfate is absorbed by the roots and then be transported to the chloroplasts by the transipration stream where the sulfur are reduced to sulfide with the help of a series of enzymatic reactions. Furthermore, the reduced sulfur is incorporated into cysteine, an amino acid that is a precursor to many other sulfur-containing compounds. In animals, sulfur assimilation occurs primarily through the diet, as animals cannot produce sulfur-containing compounds directly. Sulfur is incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, which are used to build proteins and other important molecules. Besides, With the rapid development of economy, the increase emission of sulfur results in environmental issues, such as acid rain and hydrogen sulfilde.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).
Palmitoyl-CoA is an acyl-CoA thioester. It is an "activated" form of palmitic acid and can be transported into the mitochondrial matrix by the carnitine shuttle system, and once inside can participate in beta-oxidation. Alternatively, palmitoyl-CoA is used as a substrate in the biosynthesis of sphingosine.

Quisqualic acid is an agonist of the AMPA, kainate, and group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. It is one of the most potent AMPA receptor agonists known. It causes excitotoxicity and is used in neuroscience to selectively destroy neurons in the brain or spinal cord. Quisqualic acid occurs naturally in the seeds of Quisqualis species.

Chlorophyllase is an essential enzyme in chlorophyll metabolism. It is a membrane proteins commonly known as chlase (EC 3.1.1.14, CLH) with systematic name chlorophyll chlorophyllidohydrolase. It catalyzes the reaction

In enzymology, a serine O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit 1, also known as SPTLC1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SPTLC1 gene.
The glycine cleavage system (GCS) is also known as the glycine decarboxylase complex or GDC. The system is a series of enzymes that are triggered in response to high concentrations of the amino acid glycine. The same set of enzymes is sometimes referred to as glycine synthase when it runs in the reverse direction to form glycine. The glycine cleavage system is composed of four proteins: the T-protein, P-protein, L-protein, and H-protein. They do not form a stable complex, so it is more appropriate to call it a "system" instead of a "complex". The H-protein is responsible for interacting with the three other proteins and acts as a shuttle for some of the intermediate products in glycine decarboxylation. In both animals and plants, the glycine cleavage system is loosely attached to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Mutations in this enzymatic system are linked with glycine encephalopathy.
Srinivasan Chandrasekaran is an Indian organic and organometallic chemist, academic and a former chair of the Department of Organic Chemistry and the Division of Chemical Sciences and a former Dean of the Faculty of Science at Indian Institute of Science. He was known for his researches on organic reaction mechanisms and organic synthesis. and was an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, The World Academy of Sciences and the Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1989, for his contributions to chemical sciences.