
In particle physics, a meson is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10−15 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few tenths of a nanosecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons.

The charm quark, charmed quark, or c quark is an elementary particle of the second generation. It is the third-most-massive quark with a mass of 1.27±0.02 GeV/c2 as measured in 2022 and a charge of +2/3e. It carries charm, a quantum number. Charm quarks are found in hadrons such as the J/psi meson and the charmed baryons. Several bosons, including the W and Z bosons and the Higgs boson, can decay into charm quarks.
The bottom quark or b quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation heavy quark with a charge of −1/3 e.
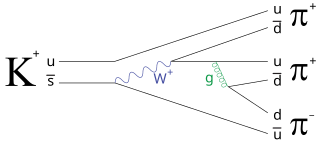
In particle physics, a kaon, also called a K meson and denoted
K
, is any of a group of four mesons distinguished by a quantum number called strangeness. In the quark model they are understood to be bound states of a strange quark and an up or down antiquark.

James Watson Cronin was an American particle physicist.

Jack Steinberger was a German-born American physicist noted for his work with neutrinos, the subatomic particles considered to be elementary constituents of matter. He was a recipient of the 1988 Nobel Prize in Physics, along with Leon M. Lederman and Melvin Schwartz, for the discovery of the muon neutrino. Through his career as an experimental particle physicist, he held positions at the University of California, Berkeley, Columbia University (1950–68), and the CERN (1968–86). He was also a recipient of the United States National Medal of Science in 1988, and the Matteucci Medal from the Italian Academy of Sciences in 1990.
The Panofsky Prize in Experimental Particle Physics is an annual prize of the American Physical Society. It is given to recognize and encourage outstanding achievements in experimental particle physics, and is open to scientists of any nation. It was established in 1985 by friends of Wolfgang K. H. Panofsky and by the Division of Particles and Fields of the American Physical Society. Panofsky was a physics professor at Stanford University and the first director of the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC). Several of the prize winners have subsequently won the Nobel Prize in Physics. As of 2021, the prize included a $10,000 award.

Nathan Isgur was a theoretical physicist from the U.S. and Canada.
The lambda baryons (Λ) are a family of subatomic hadron particles containing one up quark, one down quark, and a third quark from a higher flavour generation, in a combination where the quantum wave function changes sign upon the flavour of any two quarks being swapped. They are thus baryons, with total isospin of 0, and have either neutral electric charge or the elementary charge +1.

Neutral B meson oscillations are one of the manifestations of the neutral particle oscillation, a fundamental prediction of the Standard Model of particle physics. It is the phenomenon of B mesons changing between their matter and antimatter forms before their decay. The
B
s meson can exist as either a bound state of a strange antiquark and a bottom quark, or a strange quark and bottom antiquark. The oscillations in the neutral B sector are analogous to the phenomena that produce long and short-lived neutral kaons.
The
B
s meson is a meson composed of a bottom antiquark and a strange quark. Its antiparticle is the
B
s meson, composed of a bottom quark and a strange antiquark.
In particle physics, B mesons are mesons composed of a bottom antiquark and either an up, down, strange or charm quark. The combination of a bottom antiquark and a top quark is not thought to be possible because of the top quark's short lifetime. The combination of a bottom antiquark and a bottom quark is not a B meson, but rather bottomonium, which is something else entirely.
The D mesons are the lightest particle containing charm quarks. They are often studied to gain knowledge on the weak interaction. The strange D mesons (Ds) were called "F mesons" prior to 1986.

Anthony Ichiro Sanda is a Japanese-American particle physicist. Along with Ikaros Bigi, he was awarded the 2004 Sakurai Prize for his work on CP violation and B meson decays.
Ikaros Bigi is a German theoretical physicist. His research focuses on refining the Standard Model phenomenology.
George H. Trilling was a Polish-born American particle physicist. He was co-discoverer of the J/ψ meson which evinced the existence of the charm quark. Trilling joined the Physics Department faculty at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1960, where he was Department Chair from 1968 through 1972. Trilling was on sabbatical leave to CERN in 1973–74, where he worked on the study of the properties of charm particles, their decay modes and excited states. He was also Director of the Physics Division at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory from 1984 until 1987. Trilling was a principal proponent of the Superconducting Super Collider project and spokesperson for the Solenoidal Detector Collaboration. After the SSC was cancelled in 1993, Trilling transitioned most of the SDC team to collaborate on the ATLAS experiment at the LHC, which led to the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. Trilling was elected Vice-President of the American Physical Society, beginning his term on 1 January 1999, and was President of the society in 2001.
Natalie Ann Roe is an experimental particle physicist and observational cosmologist, and the Associate Laboratory Director for the Physical Sciences Area at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) since 2020. Previously, she was the Physics Division Director for eight years. She has been awarded as the Fellow of American Physical Society (APS) and American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) for her exceptional scientific career and contributions.

Mildred Widgoff was an American experimental particle physicist and astroparticle physicist who became the first female faculty member at the Brown University physics department.

Bradley Cox is an American physicist, academic and researcher. He is a Professor of Physics and the founder of the High Energy Physics Group at the University of Virginia.

Lucia Votano is an Italian astroparticle physicist, and the first woman to direct the Gran Sasso National Laboratory, from 2009 to 2012. Her research focuses on neutrinos, and she was the coordinator of the OPERA experiment, that led to the first detection of tau neutrinos from muon neutrino oscillation.











