Pinus radiata, the Monterey pine, insignis pine or radiata pine, is a species of pine native to the Central Coast of California and Mexico. It is an evergreen conifer in the family Pinaceae.

Inositol, or more precisely myo-inositol, is a carbocyclic sugar that is abundant in the brain and other mammalian tissues; it mediates cell signal transduction in response to a variety of hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors and participates in osmoregulation.
The molecular formula C6H12O6 (molar mass: 180.16 g/mol) may refer to:

Inositol oxygenase, also commonly referred to as myo-inositol oxygenase (MIOX), is a non-heme di-iron enzyme that oxidizes myo-inositol to glucuronic acid. The enzyme employs a unique four-electron transfer at its Fe(II)/Fe(III) coordination sites and the reaction proceeds through the direct binding of myo-inositol followed by attack of the iron center by diatomic oxygen. This enzyme is part of the only known pathway for the catabolism of inositol in humans and is expressed primarily in the kidneys. Recent medical research regarding MIOX has focused on understanding its role in metabolic and kidney diseases such as diabetes, obesity and acute kidney injury. Industrially-focused engineering efforts are centered on improving MIOX activity in order to produce glucaric acid in heterologous hosts.

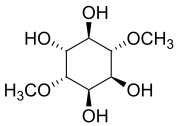
1D-chiro-Inositol is a member of a family of related substances often referred to collectively as "inositol", although that term encompasses several isomers of questionable biological relevance, including 1L-chiro-inositol. myo-Inositol is converted into DCI by an insulin dependent NAD/NADH epimerase enzyme. It is known to be an important secondary messenger in insulin signal transduction. DCI accelerates the dephosphorylation of glycogen synthase and pyruvate dehydrogenase, rate limiting enzymes of non-oxidative and oxidative glucose disposal. DCI may act to bypass defective normal epimerization of myo-inositol to DCI associated with insulin resistance and at least partially restore insulin sensitivity and glucose disposal. One pilot study found males taking it had increased androgens and reduced estrogen.
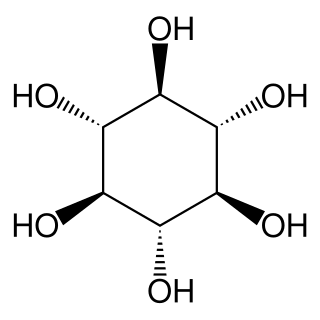
scyllo-Inositol is one of the stereoisomers of inositol. It is also known as scyllitol, cocositol, quercinitol, and 1,3,5/2,4,6-hexahydroxycyclohexane. scyllo-Inositol is a naturally occurring plant sugar alcohol found most abundantly in the coconut palm.
In enzymology, a sequoyitol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.143) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-pinitol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.142) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 1-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 3-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 4-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
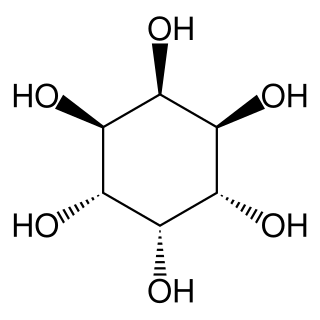
neo-Inositol is one of the stereoisomers of inositol. It is one of the nine isomeric forms of cyclohexanehexol; a group of small and chemically very stable polar molecules that have versatile properties. This stereoisomer is naturally occurring, but only in small amounts. It is also known as (1s,2R,3R,4s,5S,6S)-cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol or 1,2,3/4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol in the IUPAC naming system.
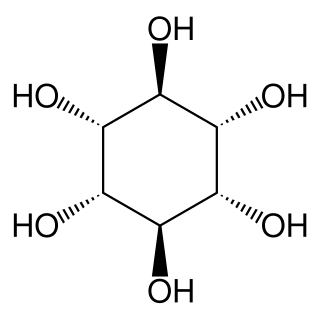
muco-Inositol is a critically important chemical in the gustatory (taste) modality of the mammalian nervous system. The generic form is coupled to a phospholipid of the outer lemma of the sensory neurons associated with the sodium ion sensitive channel of gustation.
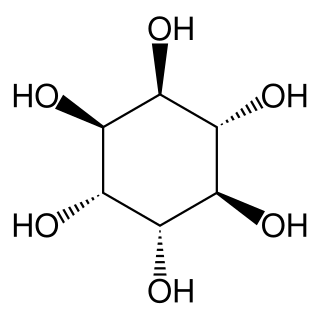
1L-chiro-Inositol (L-chiro-Inositol) is one of the isomers of inositol.
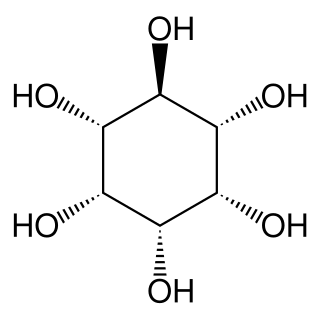
Epi-Inositol is one of the stereoisomers of inositol.

cis-Inositol is one of the isomers of inositol.

allo-Inositol is a stereoisomer of inositol.

In organic chemistry, a cyclitol is a cycloalkane containing at least three hydroxyl, each attached to a different ring carbon atom. The general formula for an unsubstituted cyclitol is C
nH
2n-x(OH)
x or C
nH
2nO
x where 3 ≤ x ≤ n.

Pinitol is a cyclitol, a cyclic polyol. It is a known anti-diabetic agent isolated from Sutherlandia frutescens leaves. Gall plant tannins can be differentiated by their content of pinitol. It was first identified in the sugar pine. It is also found in other plants, such as in the pods of the carob tree.

Hylastes ater is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae, the true weevils. It is a bark beetle, a member of the subfamily Scolytinae. Its common name is the black pine bark beetle. It is native to Europe and parts of Asia, including China and Korea. It is known as an introduced species in many other regions, including Australia, New Zealand, the Americas, and South Africa. It is a pest of pines and other trees, and it is widespread in areas where pine trees are cultivated. The species "is an important threat to the biosecurity of all forested countries."