
The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency NASA to explore other planets. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built 10 robotic interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the inner Solar System - visiting the planets Venus, Mars and Mercury for the first time, and returning to Venus and Mars for additional close observations.

Pioneer 11 is a 260-kilogram (570 lb) robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar winds, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to encounter Saturn, the second to fly through the asteroid belt, and the second to fly by Jupiter. Later, Pioneer 11 became the second of five artificial objects to achieve an escape velocity allowing it to leave the Solar System. Due to power constraints and the vast distance to the probe, the last routine contact with the spacecraft was on September 30, 1995, and the last good engineering data was received on November 24, 1995.

Mariner 1, built to conduct the first American planetary flyby of Venus, was the first spacecraft of NASA's interplanetary Mariner program. Developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and originally planned to be a purpose-built probe launched summer 1962, Mariner 1's design was changed when the Centaur proved unavailable at that early date. Mariner 1, were then adapted from the lighter Ranger lunar spacecraft. Mariner 1 carried a suite of experiments to determine the temperature of Venus as well to measure magnetic fields and charged particles near the planet and in interplanetary space.
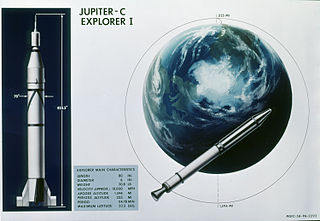
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union's Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2, beginning the Cold War Space Race between the two nations.

The Surveyor program was a NASA program that, from June 1966 through January 1968, sent seven robotic spacecraft to the surface of the Moon. Its primary goal was to demonstrate the feasibility of soft landings on the Moon. The Surveyor craft were the first American spacecraft to achieve soft landing on an extraterrestrial body. The missions called for the craft to travel directly to the Moon on an impact trajectory, a journey that lasted 63 to 65 hours, and ended with a deceleration of just over three minutes to a soft landing.
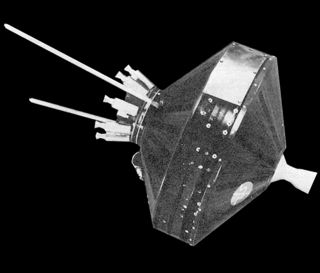
Pioneer 0 was a failed United States space probe that was designed to go into orbit around the Moon, carrying a television camera, a micrometeorite detector and a magnetometer, as part of the first International Geophysical Year (IGY) science payload. It was designed and operated by the Air Force Ballistic Missile Division as the first spacecraft in the Pioneer program and was the first attempted launch beyond Earth orbit by any country, but the rocket failed shortly after launch. The probe was intended to be called Pioneer, but the launch failure precluded that name.

Pioneer 1 was an American space probe, the first under the auspices of NASA, which was launched by a Thor-Able rocket on 11 October 1958. It was intended to orbit the Moon and make scientific measurements, but due to a guidance error failed to achieve lunar orbit and was ultimately destroyed upon reentering Earth's atmosphere. The flight, which lasted 43 hours and reached an apogee of 113,800 km, was the second and most successful of the three Thor-Able space probes.

Pioneer 3 was a spin-stabilized spacecraft launched at 05:45:12 GMT on 6 December 1958 by the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency in conjunction with the NASA, using a Juno II rocket. This spacecraft was intended as a lunar probe, but failed to go past the Moon and into a heliocentric orbit as planned. It did however reach an altitude of 102,360 km before falling back to Earth. The revised spacecraft objectives were to measure radiation in the outer Van Allen radiation belt using two Geiger-Müller tubes and to test the trigger mechanism for a lunar photographic experiment.

Pioneer 4 was an American spin-stabilized uncrewed spacecraft launched as part of the Pioneer program on a lunar flyby trajectory and into a heliocentric orbit making it the first probe of the United States to escape from the Earth's gravity. It carried a payload similar to Pioneer 3: a lunar radiation environment experiment using a Geiger–Müller tube detector and a lunar photography experiment. It passed within 58,983 km of the Moon's surface. However, Pioneer 4 did not come close enough to trigger its photoelectric sensor. The spacecraft was still in solar orbit as of 1969. It was the only successful lunar probe launched by the U.S. in 12 attempts between 1958 and 1963; only in 1964 would Ranger 7 surpass its success by accomplishing all of its mission objectives.

Pioneer P-3 was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to take images of the lunar surface with a television-like system, estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A mid-course propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space.

Pioneer P-30 was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch on September 25, 1960. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A mid-course propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space.

Pioneer P-31 was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to take images of the lunar surface with a television-like system, estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A midcourse propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space.

Venera 1, also known as Venera-1VA No.2 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 8 was the first spacecraft to fly past Venus, as part of the Soviet Union's Venera programme. Launched in February 1961, it flew past Venus on 19 May of the same year; however, radio contact with the probe was lost before the flyby, resulting in it returning no data.

Ranger 2 was a flight test of the Ranger spacecraft system of the NASA Ranger program designed for future lunar and interplanetary missions. Ranger 2 was designed to test various systems for future exploration and to conduct scientific observations of cosmic rays, magnetic fields, radiation, dust particles, and a possible hydrogen gas "tail" trailing the Earth.

Pioneer 5 was a spin-stabilized space probe in the NASA Pioneer program used to investigate interplanetary space between the orbits of Earth and Venus. It was launched on 11 March 1960 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 17A at 13:00:00 UTC with an on-orbit dry mass of 43 kilograms (95 lb). It was a 0.66 metres diameter sphere with 1.4 metres span across its four solar panels and achieved a solar orbit of 0.806 × 0.995 AU.
Explorer 2 was an American unmanned space mission within the Explorer program. Intended to be a repetition of the previous Explorer 1 mission, which placed a satellite into medium Earth orbit, the spacecraft was unable to reach orbit due to a failure in the launch vehicle during launch.

Helios-A and Helios-B are a pair of probes that were launched into heliocentric orbit to study solar processes. As a joint venture of West Germany's space agency DLR and NASA the probes were launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, on December 10, 1974, and January 15, 1976, respectively. As built by the main contractor, Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, they were the first space probes built outside the United States and the Soviet Union to leave Earth's orbit.

Thor was a US space launch vehicle derived from the PGM-17 Thor intermediate-range ballistic missile. The Thor rocket was the first member of the Delta rocket family of space launch vehicles. The last launch of a direct derivative of the Thor missile occurred in 2018 as the first stage of the final Delta II.

Explorer S-1, also known as NASA S-1 or Explorer 7X, was a NASA Earth science satellite equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study the environment around the Earth. The spacecraft and its Juno II launch vehicle were destroyed five seconds after launch on 16 July 1959, in a spectacular launch failure caused by complications with the launch vehicle's power supply. A relaunch of the mission in October 1959, Explorer 7 (S-1A), was successful.

Galileo was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989 by Space ShuttleAtlantis. Galileo arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet.

















