
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with, and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex. These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have greater reproductive success than others within a population, for example because they are more attractive or prefer more attractive partners to produce offspring. Successful males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to one or more fertile females. Females can maximise the return on the energy they invest in reproduction by selecting and mating with the best males.

Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. During sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an offspring that inherits traits from each parent. By convention, organisms that produce smaller, more mobile gametes are called male, while organisms that produce larger, non-mobile gametes are called female. An organism that produces both types of gamete is hermaphrodite.

Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecious species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is monomorphism, when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other.

The green algae are a group of chlorophyll-containing autotrophic eukaryotes consisting of the phylum Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister group that contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as a sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid (spherical), and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae, many of which live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds.

Evolution of sexual reproduction describes how sexually reproducing animals, plants, fungi and protists could have evolved from a common ancestor that was a single-celled eukaryotic species. Sexual reproduction is widespread in eukaryotes, though a few eukaryotic species have secondarily lost the ability to reproduce sexually, such as Bdelloidea, and some plants and animals routinely reproduce asexually without entirely having lost sex. The evolution of sexual reproduction contains two related yet distinct themes: its origin and its maintenance. Bacteria and Archaea (prokaryotes) have processes that can transfer DNA from one cell to another, but it is unclear if these processes are evolutionarily related to sexual reproduction in Eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, true sexual reproduction by meiosis and cell fusion is thought to have arisen in the last eukaryotic common ancestor, possibly via several processes of varying success, and then to have persisted.
In biology, gonochorism is a sexual system where there are two sexes and each individual organism is either male or female. The term gonochorism is usually applied in animal species, the vast majority of which are gonochoric.
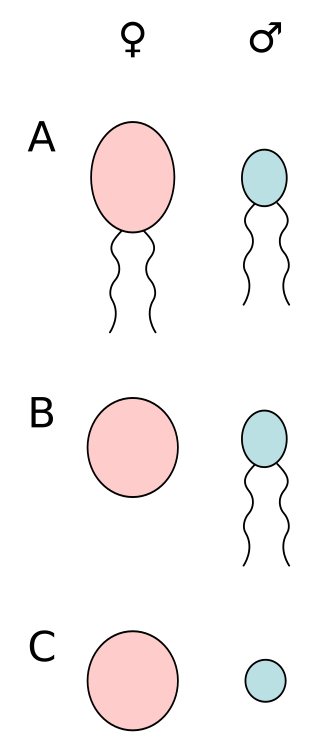
Anisogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves the union or fusion of two gametes that differ in size and/or form. The smaller gamete is male, a sperm cell, whereas the larger gamete is female, typically an egg cell. Anisogamy is predominant among multicellular organisms. In both plants and animals, gamete size difference is the fundamental difference between females and males.
Dioecy is a characteristic of certain species that have distinct unisexual individuals, each producing either male or female gametes, either directly or indirectly. Dioecious reproduction is biparental reproduction. Dioecy has costs, since only the female part of the population directly produces offspring. It is one method for excluding self-fertilization and promoting allogamy (outcrossing), and thus tends to reduce the expression of recessive deleterious mutations present in a population. Plants have several other methods of preventing self-fertilization including, for example, dichogamy, herkogamy, and self-incompatibility.

Sequential hermaphroditism is one of the two types of hermaphroditism, the other type being simultaneous hermaphroditism. It occurs when the organism's sex changes at some point in its life. A sequential hermaphrodite produces eggs and sperm at different stages in life. Sequential hermaphroditism occurs in many fish, gastropods, and plants. Species that can undergo these changes do so as a normal event within their reproductive cycle, usually cued by either social structure or the achievement of a certain age or size. In some species of fish, sequential hermaphroditism is much more common than simultaneous hermaphroditism.

Male is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs.

Oogamy is a form of anisogamy where the gametes differ in both size and form. In oogamy the large female gamete is immotile, while the small male gamete is mobile. Oogamy is a common form of anisogamy, with almost all animals and land plants being oogamous.
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sexes in multicellular lifeforms and are thought to be the ancestor to distinct sexes. They also occur in multicellular organisms such as fungi.

Environmental sex determination is the establishment of sex by a non-genetic cue, such as nutrient availability, experienced within a discrete period after fertilization. Environmental factors which often influence sex determination during development or sexual maturation include light intensity and photoperiod, temperature, nutrient availability, and pheromones emitted by surrounding plants or animals. This is in contrast to genotypic sex determination, which establishes sex at fertilization by genetic factors such as sex chromosomes. Under true environmental sex determination, once sex is determined, it is fixed and cannot be switched again. Environmental sex determination is different from some forms of sequential hermaphroditism in which the sex is determined flexibly after fertilization throughout the organism’s life.

Schistocephalus solidus is a tapeworm of fish, fish-eating birds and rodents. This hermaphroditic parasite belongs to the Eucestoda subclass, of class Cestoda. This species has been used to demonstrate that cross-fertilization produces a higher infective success rate than self-fertilization.

Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes (diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes.
Maria R. Servedio is a Canadian-American professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Her research spans a wide range of topics in evolutionary biology from sexual selection to evolution of behavior. She largely approaches these topics using mathematical models. Her current research interests include speciation and reinforcement, mate choice, and learning with a particular focus on evolutionary mechanisms that promote premating (prezygotic) isolation. Through integrative approaches and collaborations, she uses mathematical models along with experimental, genetic, and comparative techniques to draw conclusions on how evolution occurs. She has published extensively on these topics and has more than 50 peer-reviewed articles. She served as Vice President in 2018 of the American Society of Naturalists, and has been elected to serve as President in 2023.
Gynogenesis, a form of parthenogenesis, is a system of asexual reproduction that requires the presence of sperm without the actual contribution of its DNA for completion. The paternal DNA dissolves or is destroyed before it can fuse with the egg. The egg cell of the organism is able to develop, unfertilized, into an adult using only maternal genetic material. Gynogenesis is often termed "sperm parasitism" in reference to the somewhat pointless role of male gametes. Gynogenetic species, "gynogens" for short, are unisexual, meaning they must mate with males from a closely related bisexual species that normally reproduces sexually.
Trioecy, tridioecy or subdioecy, is a sexual system characterized by the coexistence of males, females, and hermaphrodites. It has been found in both plants and animals. Trioecy, androdioecy and gynodioecy may be described as mixed mating systems.

Monoecy is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system comparable with gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy, and contrasted with dioecy where individual plants produce cones or flowers of only one sex and with bisexual or hermaphroditic plants in which male and female gametes are produced in the same flower.

A sexual system is a distribution of male and female function across organisms in a species. The terms reproductive system and mating system have also been used as synonyms.













