Related Research Articles

Neurosurgery, or neurological surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, surgical treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebrovascular system.

The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins and mechanical injuries.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related wear and tear of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.
Neuromeres are morphologically or molecularly defined transient segments of the early developing brain. Rhombomeres are such segments that make up the rhombencephalon or hindbrain. More controversially, some argue that there exist early developmental segments that give rise to structures of the midbrain (mesomeres) and forebrain (prosomeres).
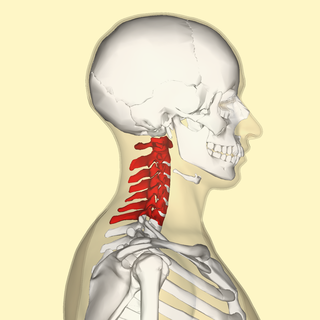
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five to six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.

A cervical fracture, commonly called a broken neck, is a catastrophic fracture of any of the seven cervical vertebrae in the neck. Examples of common causes in humans are traffic collisions and diving into shallow water. Abnormal movement of neck bones or pieces of bone can cause a spinal cord injury resulting in loss of sensation, paralysis, or usually instant death.

Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition in which there are anatomic changes and a loss of function of varying degrees of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine of sufficient magnitude as to cause symptoms. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The anulus fibrosus, the rigid outer shell of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar hyperlordosis; narrowing of the space available for the spinal tract within the vertebra ; or narrowing of the space through which a spinal nerve exits with resultant inflammation and impingement of a spinal nerve, causing a radiculopathy.

In anatomy and neurology, the ventral root or anterior root is the efferent motor root of a spinal nerve.

Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a neurosurgical or orthopedic surgical technique that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine and prevents any movement between the fused vertebrae. There are many types of spinal fusion and each technique involves using bone grafting—either from the patient (autograft), donor (allograft), or artificial bone substitutes—to help the bones heal together. Additional hardware is often used to hold the bones in place while the graft fuses the two vertebrae together.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), more specifically it is part of the sympathetic nervous system, a division of the ANS most commonly associated with the fight or flight response. The ANS is composed of pathways that lead to and from ganglia, groups of nerve cells. A ganglion allows a large amount of divergence in a neuronal pathway and also enables a more localized circuitry for control of the innervated targets. The SCG is the only ganglion in the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. It is the largest and most rostral (superior) of the three cervical ganglia. The SCG innervates many organs, glands and parts of the carotid system in the head.

Hangman's fracture is the colloquial name given to a fracture of both pedicles, or pars interarticulares, of the axis vertebra (C2).

Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a surgical procedure to treat nerve root or spinal cord compression by decompressing the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cervical spine with a discectomy, followed by inter-vertebral fusion to stabilize the corresponding vertebrae. This procedure is used when other non-surgical treatments have failed.
Vertebral fixation is an orthopedic surgical procedure in which two or more vertebrae are anchored to each other through a synthetic "vertebral fixation device", with the aim of reducing vertebral mobility and thus avoiding possible damage to the spinal cord and/or spinal roots.

Laminoplasty is an orthopaedic/neurosurgical surgical procedure for treating spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal cord. The main purpose of this procedure is to provide relief to patients who may suffer from symptoms of numbness, pain, or weakness in arm movement. The procedure involves cutting the lamina on both sides of the affected vertebrae and then "swinging" the freed flap of bone open thus relieving the pressure on the spinal cord. The spinous process may be removed to allow the lamina bone flap to be swung open. The bone flap is then propped open using small wedges or pieces of bone such that the enlarged spinal canal will remain in place.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and entering the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from 13 mm in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm in the thoracic area.

The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord.
Minimally invasive spine surgery, also known as MISS, has no specific meaning or definition. Basically, it is marketing language that implies a lack of severe invasion, that may or may not be the case. The old style open-spine surgery for a simple disc problem used to require a 5-6 inch incision and a month in the hospital, 60 years ago. Miss techniques utilize more modern technology, advanced imaging techniques and special medical equipment to reduce tissue trauma, bleeding, radiation exposure, hospital stays and recovery by minimizing the size of the incision. Modern endoscopic procedures can be done through a 2 to 5 mm skin opening, with no internal cutting. By contrast, procedures done with a microscope require skin openings of approximately one inch, or more. Since the one inch cut goes all the way down, it can only be called relatively MISS.
Curtis Dickman is an American Neurosurgeon at Barrow Neurological Institute, and is recognized internationally for his pioneering work in the field of Thoracoscopic Neurosurgery. He serves as Director of the Spine Research Laboratory and Associate Chief of the Spine Section at Barrow Neurological Institute.

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate.
References
- ↑ Subach, Brian R.; Haid, RW; Traynelis, VC; Sasso, RC; Subach, BR; Fiore, AJ; Rodts, GE (15 Jan 2002). "Posterior Cervical Fixation Using a New Polyaxial Screw and Rod System: Technique and Surgical Results". Neurosurg Focus. 12 (1): E8. PMID 16212335.
| This surgery article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |