The Precambrian is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinised name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time.

The Hadean is a geologic eon of Earth history preceding the Archean. It began with the formation of the Earth about 4.6 billion years ago and ended, as defined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), 4 billion years ago. As of 2016, the ICS describes its status as "informal". The term was coined by American geologist Preston Cloud, after the Greek mythical underworld Hades, originally to label the period before the earliest-known rocks on Earth. W. Brian Harland later coined an almost synonymous term, the Priscoan Period, from priscus, the Latin word for 'ancient'. Other, older texts refer to the eon as the Pre-Archean.

The lunar geological timescale divides the history of Earth's Moon into five generally recognized periods: the Copernican, Eratosthenian, Imbrian, Nectarian, and Pre-Nectarian. The boundaries of this time scale are related to large impact events that have modified the lunar surface, changes in crater formation through time, and the size-frequency distribution of craters superposed on geological units. The absolute ages for these periods have been constrained by radiometric dating of samples obtained from the lunar surface. However, there is still much debate concerning the ages of certain key events, because correlating lunar regolith samples with geological units on the Moon is difficult, and most lunar radiometric ages have been highly affected by an intense history of bombardment.
The Nectarian Period of the lunar geologic timescale runs from 3920 million years ago to 3850 million years ago. It is the period during which the Nectaris Basin and other major basins were formed by large impact events. Ejecta from Nectaris form the upper part of the densely cratered terrain found in lunar highlands.

The Eoarchean is the first era of the Archean Eon of the geologic record for which the Earth has a solid crust. It spans 400 million years from the end of the Hadean Eon 4 billion years ago to the start of the Paleoarchean Era 3600 Mya. The beginnings of life on Earth have been dated to this era and evidence of cyanobacteria date to 3500 Mya, just outside this era. At that time, the atmosphere was without oxygen and the pressure values ranged from 10 to 100 bar.

Schiller is an oddly shaped lunar impact crater located in the southwestern sector of the Moon. To the east is the crater Bayer and to the southeast is Rost.

Zucchius is a prominent lunar impact crater located near the southwestern limb. Because of its location the crater appears oblong-shaped due to foreshortening. It lies just to the south-southwest of the crater Segner, and northeast of the much larger walled plain Bailly. To the southeast is Bettinus, a formation only slightly larger than Zucchius.
The Cryptic era is an informal term for the earliest geologic evolution of the Earth and Moon. It is the oldest (informal) era of the Hadean eon, and it is commonly accepted to have begun close to 4533 million years ago when the Earth and Moon formed. No samples exist to date the transition between the Cryptic era and the following Basin Groups era for the Moon, though sometimes it is stated that this era ended 4150 million years ago for one or both of these bodies. Neither this time period, nor any other Hadean subdivision, has been officially recognized by the International Commission on Stratigraphy.

The oldest dated rocks formed on Earth, as an aggregate of minerals that have not been subsequently broken down by erosion or melted, are more than 4 billion years old, formed during the Hadean Eon of Earth's geological history. Meteorites that were formed in other planetary systems can pre-date Earth. Particles from the Murchison meteorite were dated in January 2020 to be 7 billion years old.
Basin Groups refers to 9 subdivisions of the lunar Pre-Nectarian geologic period. It is the second era of the Hadean.

The Borealis quadrangle is a quadrangle on Mercury surrounding the north pole down to 65° latitude. It was mapped in its entirety by the MESSENGER spacecraft, which orbited the planet from 2008 to 2015, excluding areas of permanent shadow near the north pole. Only approximately 25% of the quadrangle was imaged by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during its flybys in 1974 and 1975. The quadrangle is now called H-1.

The Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB), or lunar cataclysm, is a hypothesized event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, at a time corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. According to the hypothesis, during this interval, a disproportionately large number of asteroids collided with the early terrestrial planets in the inner Solar System, including Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. These came from both post-accretion and planetary instability-driven populations of impactors. Although generally accepted, it remains difficult to prove conclusively.

The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain but probably corresponds to the lunar Pre-Nectarian to Early Imbrian periods of 4100 to 3700 million years ago, during the interval known as the Late Heavy Bombardment. Many of the large impact basins on the Moon and Mars formed at this time. The Noachian Period is roughly equivalent to the Earth's Hadean and early Archean eons when the first life forms likely arose.
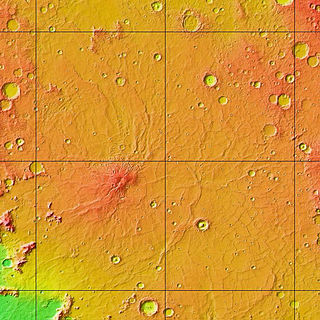
The Hesperian is a geologic system and time period on the planet Mars characterized by widespread volcanic activity and catastrophic flooding that carved immense outflow channels across the surface. The Hesperian is an intermediate and transitional period of Martian history. During the Hesperian, Mars changed from the wetter and perhaps warmer world of the Noachian to the dry, cold, and dusty planet seen today. The absolute age of the Hesperian Period is uncertain. The beginning of the period followed the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment and probably corresponds to the start of the lunar Late Imbrian period, around 3700 million years ago (Mya). The end of the Hesperian Period is much more uncertain and could range anywhere from 3200 to 2000 Mya, with 3000 Mya being frequently cited. The Hesperian Period is roughly coincident with the Earth's early Archean Eon.

Pre-Tolstojan, also Pretolstojan Period, refers to the oldest period of the history of Mercury, 4500–3900 MYA. It is the "first period of the Eomercurian Era and of the Mercurian Eon, as well as being the first period in Mercury's geologic history", and refers to its formation and the 600 million or so years in its aftermath. Mercury was formed with a tiny crust, mantle, and a giant core and as it evolved it faced heavy bombardments that created most of the craters and intercrater plains seen on the planet's surface today. Many of the smaller basins and multi-ring basins were created during this period. Considered a "dead" planet, its geology is highly diverse with craters forming the dominant terrain.
The Chaotian is a proposed time division of the geologic time scale. First proposed in 2010 as an eon, it is named after Chaos, the primeval void in Greek mythology. This proposal defines the Chaotian eon as a solar system wide time between the initiation of planetary formation and the hypothesised collision of the Protoplanet Theia with the proto-Earth.

The Freundlich-Sharonov Basin is a Pre-Nectarian impact basin on the far side of the moon. It is named after the younger craters Freundlich near the northwest margin and Sharonov near the southwest margin. It lies east of Mare Moscoviense basin and northwest of Korolev basin.
The Imbrian is a lunar geologic period divided into two epochs, the Early and Late.
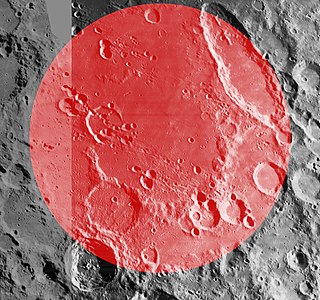
The Schiller-Zucchius Basin is a Pre-Nectarian impact basin on the near side of the moon. It is named after the elongated crater Schiller at the northeast margin and fresh crater Zucchius near the southwest margin. This basin has received the unofficial designation 'Schiller Annular Plain' among lunar observers.
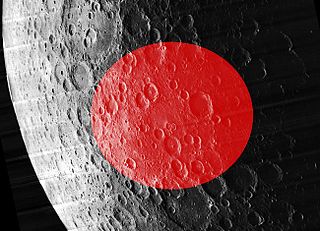
The Coulomb-Sarton Basin is a Pre-Nectarian impact basin on the far side of the moon. It is named after the crater Coulomb northeast of the center of the basin and the smaller crater Sarton just south of the center. The basin is not obvious on the lunar surface. There are only small fragments of inner rings and a rim, and the most indicative topographic feature is a smooth, low plain at the center.














