
Advertising is a marketing communication that employs an openly sponsored, non-personal message to promote or sell a product, service or idea. Sponsors of advertising are typically businesses wishing to promote their products or services. Advertising is differentiated from public relations in that an advertiser pays for and has control over the message. It differs from personal selling in that the message is non-personal, i.e., not directed to a particular individual. Advertising is communicated through various mass media, including traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, outdoor advertising or direct mail; and new media such as search results, blogs, social media, websites or text messages. The actual presentation of the message in a medium is referred to as an advertisement.

Marketing is the process of exploring, creating, and delivering value to meet the needs of a target market in terms of goods and services; potentially including selection of a target audience; selection of certain attributes or themes to emphasize in advertising; operation of advertising campaigns; attendance at trade shows and public events; design of products and packaging attractive to buyers; defining the terms of sale, such as price, discounts, warranty, and return policy; product placement in media or with people believed to influence the buying habits of others; agreements with retailers, wholesale distributors, or resellers; and attempts to create awareness of, loyalty to, and positive feelings about a brand. Marketing is typically done by the seller, typically a retailer or manufacturer. Sometimes tasks are contracted to a dedicated marketing firm or advertising agency. More rarely, a trade association or government agency advertises on behalf of an entire industry or locality, often a specific type of food, food from a specific area, or a city or region as a tourism destination.
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how changing elements of the marketing mix impacts customer behavior.
Personalized marketing, also known as one-to-one marketing or individual marketing, is a marketing strategy by which companies leverage data analysis and digital technology to deliver individualized messages and product offerings to current or prospective customers. Advancements in data collection methods, analytics, digital electronics, and digital economics, have enabled marketers to deploy more effective real-time and prolonged customer experience personalization tactics.
Mass marketing is a marketing strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and appeal the whole market with one offer or one strategy, which supports the idea of broadcasting a message that will reach the largest number of people possible. Traditionally, mass marketing has focused on radio, television and newspapers as the media used to reach this broad audience. By reaching the largest audience possible, exposure to the product is maximized, and in theory this would directly correlate with a larger number of sales or buys into the product.

Banner blindness is a phenomenon in web usability where visitors to a website consciously or unconsciously ignore banner-like information. A broader term covering all forms of advertising is ad blindness, and the mass of banners that people ignore is called banner noise.
Personalization consists of tailoring a service or a product to accommodate specific individuals, sometimes tied to groups or segments of individuals. A wide variety of organizations use personalization to improve customer satisfaction, digital sales conversion, marketing results, branding, and improved website metrics as well as for advertising. Personalization is a key element in social media and recommender systems. Personalization is affecting every sector of society -- work, leisure, and citizenship.
In marketing, promotion refers to any type of marketing communication used to inform target audiences of the relative merits of a product, service, brand or issue, most of the time persuasive in nature. It helps marketers to create a distinctive place in customers' mind, it can be either a cognitive or emotional route. The aim of promotion is to increase brand awareness, create interest, generate sales or create brand loyalty. It is one of the basic elements of the market mix, which includes the four Ps, i.e., product, price, place, and promotion.

In marketing, brand loyalty describes a consumer's positive feelings towards a brand, and their dedication to purchasing the brand's products and/or services repeatedly, regardless of deficiencies, a competitor's actions, or changes in the environment. It can also be demonstrated with other behaviors such as positive word-of-mouth advocacy. Corporate brand loyalty is where an individual buys products from the same manufacturer repeatedly and without wavering, rather than from other suppliers. Loyalty implies dedication and should not be confused with habit with its less-than-emotional engagement and commitment. Businesses whose financial and ethical values rest in large part on their brand loyalty are said to use the loyalty business model.
Search engine marketing (SEM) is a form of Internet marketing that involves the promotion of websites by increasing their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) primarily through paid advertising. SEM may incorporate search engine optimization (SEO), which adjusts or rewrites website content and site architecture to achieve a higher ranking in search engine results pages to enhance pay per click (PPC) listings and increase the Call to action (CTA) on the website.

Digital marketing is the component of marketing that uses the Internet and online based digital technologies such as desktop computers, mobile phones and other digital media and platforms to promote products and services. Its development during the 1990s and 2000s changed the way brands and businesses use technology for marketing. As digital platforms became increasingly incorporated into marketing plans and everyday life, and as people increasingly use digital devices instead of visiting physical shops, digital marketing campaigns have become prevalent, employing combinations of search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing, e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, display advertising, e–books, and optical disks and games have become commonplace. Digital marketing extends to non-Internet channels that provide digital media, such as television, mobile phones, callback, and on-hold mobile ring tones. The extension to non-Internet channels differentiates digital marketing from online advertising.
A touchpoint can be defined as any way consumers can interact with a business organization, whether it be person-to-person, through a website, an app or any form of communication. When consumers come in contact with these touchpoints it gives them the opportunity to compare their prior perceptions of the business and form an opinion.
A click path or clickstream is the sequence of hyperlinks one or more website visitors follows on a given site, presented in the order viewed. A visitor's click path may start within the website or at a separate third party website, often a search engine results page, and it continues as a sequence of successive webpages visited by the user. Click paths take call data and can match it to ad sources, keywords, and/or referring domains, in order to capture data.
A target market is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service.
Media planning is generally outsourced and entails sourcing and selecting optimal media platforms for a client's brand or product to use. The goal of media planning is to determine the best combination of media to achieve the clients objectives.
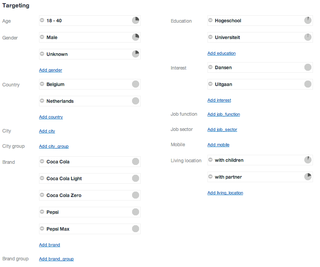
Targeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or psychographic focused on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. Targeted advertising is concentrated in certain traits and consumers who are likely to have a strong preference. These individuals will receive messages instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a particular product's attributes. This eliminates waste.
Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms and websites to promote a product or service. Although the terms e-marketing and digital marketing are still dominant in academia, social media marketing is becoming more popular for both practitioners and researchers. Most social media platforms have built-in data analytics tools, enabling companies to track the progress, success, and engagement of ad campaigns. Companies address a range of stakeholders through social media marketing, including current and potential customers, current and potential employees, journalists, bloggers, and the general public. On a strategic level, social media marketing includes the management of a marketing campaign, governance, setting the scope and the establishment of a firm's desired social media "culture" and "tone."
Wait marketing is a marketing strategy in which a company delivers a promotional message to a consumer while he or she is forced to wait for something else. These messages can include posters in buses and subways or video clips at fuel pumps.
Behavioral analytics is a recent advancement in business analytics that reveals new insights into the behavior of consumers on eCommerce platforms, online games, web and mobile applications, and IoT. The rapid increase in the volume of raw event data generated by the digital world enables methods that go beyond typical analysis by demographics and other traditional metrics that tell us what kind of people took what actions in the past. Behavioral analysis focuses on understanding how consumers act and why, enabling accurate predictions about how they are likely to act in the future. It enables marketers to make the right offers to the right consumer segments at the right time.
Marketing automation refers to software platforms and technologies designed for marketing departments and organizations to more effectively market on multiple channels online and automate repetitive tasks.





