A proposition is a central concept in philosophy of language and related fields, often characterized as the primary bearer of truth or falsity. Propositions are also often characterized as being the kind of thing that declarative sentences denote. For instance the sentence "The sky is blue" denotes the proposition that the sky is blue. However, crucially, propositions are not themselves linguistic expressions. For instance, the English sentence "Snow is white" denotes the same proposition as the German sentence "Schnee ist weiß" even though the two sentences are not the same. Similarly, propositions can also be characterized as the objects of belief and other propositional attitudes. For instance if one believes that the sky is blue, what one believes is the proposition that the sky is blue. A proposition can also be thought of as a kind of idea: Collins Dictionary has a definition for proposition as "a statement or an idea that people can consider or discuss whether it is true."

A mathematical proof is an inferential argument for a mathematical statement, showing that the stated assumptions logically guarantee the conclusion. The argument may use other previously established statements, such as theorems; but every proof can, in principle, be constructed using only certain basic or original assumptions known as axioms, along with the accepted rules of inference. Proofs are examples of exhaustive deductive reasoning which establish logical certainty, to be distinguished from empirical arguments or non-exhaustive inductive reasoning which establish "reasonable expectation". Presenting many cases in which the statement holds is not enough for a proof, which must demonstrate that the statement is true in all possible cases. A proposition that has not been proved but is believed to be true is known as a conjecture, or a hypothesis if frequently used as an assumption for further mathematical work.
In mathematics and logic, an axiomatic system is any set of axioms from which some or all axioms can be used in conjunction to logically derive theorems. A theory is a consistent, relatively-self-contained body of knowledge which usually contains an axiomatic system and all its derived theorems. An axiomatic system that is completely described is a special kind of formal system. A formal theory is an axiomatic system that describes a set of sentences that is closed under logical implication. A formal proof is a complete rendition of a mathematical proof within a formal system.
In mathematical logic, propositional logic and predicate logic, a well-formed formula, abbreviated WFF or wff, often simply formula, is a finite sequence of symbols from a given alphabet that is part of a formal language. A formal language can be identified with the set of formulas in the language.
A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that employs a degree of randomness as part of its logic or procedure. The algorithm typically uses uniformly random bits as an auxiliary input to guide its behavior, in the hope of achieving good performance in the "average case" over all possible choices of random determined by the random bits; thus either the running time, or the output are random variables.
In logic, the semantics of logic or formal semantics is the study of the semantics, or interpretations, of formal and natural languages usually trying to capture the pre-theoretic notion of entailment.
In logic, a true/false decision problem is decidable if there exists an effective method for deriving the correct answer. Zeroth-order logic is decidable, whereas first-order and higher-order logic are not. Logical systems are decidable if membership in their set of logically valid formulas can be effectively determined. A theory in a fixed logical system is decidable if there is an effective method for determining whether arbitrary formulas are included in the theory. Many important problems are undecidable, that is, it has been proven that no effective method for determining membership can exist for them.
In computational complexity theory, NL is the complexity class containing decision problems that can be solved by a nondeterministic Turing machine using a logarithmic amount of memory space.
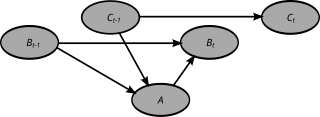
A Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN) is a Bayesian network (BN) which relates variables to each other over adjacent time steps.
The Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) is an attempt to standardize Artificial Intelligence (AI) planning languages. It was first developed by Drew McDermott and his colleagues in 1998 mainly to make the 1998/2000 International Planning Competition (IPC) possible, and then evolved with each competition. The standardization provided by PDDL has the benefit of making research more reusable and easily comparable, though at the cost of some expressive power, compared to domain-specific systems.
The method of exhaustion is a method of finding the area of a shape by inscribing inside it a sequence of polygons whose areas converge to the area of the containing shape. If the sequence is correctly constructed, the difference in area between the nth polygon and the containing shape will become arbitrarily small as n becomes large. As this difference becomes arbitrarily small, the possible values for the area of the shape are systematically "exhausted" by the lower bound areas successively established by the sequence members.
The autoepistemic logic is a formal logic for the representation and reasoning of knowledge about knowledge. While propositional logic can only express facts, autoepistemic logic can express knowledge and lack of knowledge about facts.
A propositional directed acyclic graph (PDAG) is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed acyclic graph of the following form:
In mathematical logic, a tautology is a formula or assertion that is true in every possible interpretation. An example is "x=y or x≠y". Similarly, "either the ball is green, or the ball is not green" is always true, regardless of the colour of the ball.
Infinitism is the view that knowledge may be justified by an infinite chain of reasons. It belongs to epistemology, the branch of philosophy that considers the possibility, nature, and means of knowledge.
Probabilistic logic involves the use of probability and logic to deal with uncertain situations. Probabilistic logic extends traditional logic truth tables with probabilistic expressions. A difficulty of probabilistic logics is their tendency to multiply the computational complexities of their probabilistic and logical components. Other difficulties include the possibility of counter-intuitive results, such as in case of belief fusion in Dempster–Shafer theory. Source trust and epistemic uncertainty about the probabilities they provide, such as defined in subjective logic, are additional elements to consider. The need to deal with a broad variety of contexts and issues has led to many different proposals.
Evidence for a proposition is what supports the proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the supported proposition is true. What role evidence plays and how it is conceived varies from field to field.
In machine learning and natural language processing, the pachinko allocation model (PAM) is a topic model. Topic models are a suite of algorithms to uncover the hidden thematic structure of a collection of documents. The algorithm improves upon earlier topic models such as latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) by modeling correlations between topics in addition to the word correlations which constitute topics. PAM provides more flexibility and greater expressive power than latent Dirichlet allocation. While first described and implemented in the context of natural language processing, the algorithm may have applications in other fields such as bioinformatics. The model is named for pachinko machines—a game popular in Japan, in which metal balls bounce down around a complex collection of pins until they land in various bins at the bottom.
Church refers to both a family of LISP-like probabilistic programming languages for specifying arbitrary probabilistic programs, as well as a set of algorithms for performing probabilistic inference in the generative models those programs define. Church was originally developed at MIT, primarily in the computational cognitive science group, run by Joshua Tenenbaum. Several different inference algorithms and concrete languages are in existence, including Bher, MIT-Church, Cosh, Venture, and Anglican.
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in elementary algebra the values of the variables are numbers. Second, Boolean algebra uses logical operators such as conjunction (and) denoted as ∧, disjunction (or) denoted as ∨, and the negation (not) denoted as ¬. Elementary algebra, on the other hand, uses arithmetic operators such as addition, multiplication, subtraction and division. Boolean algebra is therefore a formal way of describing logical operations, in the same way that elementary algebra describes numerical operations.

