
A therapsid is a member of the clade Therapsida which is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders.

Cynodonts are eutheriodont therapsids belonging to the clade Cynodontia that first appeared in the Late Permian, and extensively diversified after the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Cynodonts occupied a variety of ecological niches, both as carnivores and as herbivores. Mammals are cynodonts, as are their extinct ancestors and close relatives (Mammaliaformes), having evolved from advanced probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. All other cynodont lines went extinct, with the last known non-mammaliaform cynodont group, the Tritylodontidae, having its youngest records in the Early Cretaceous.
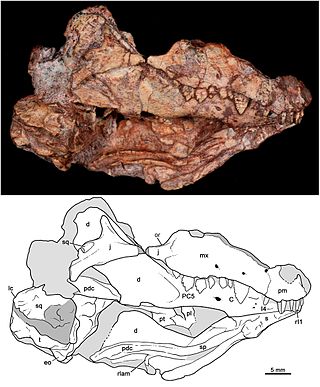
Probainognathidae is an extinct family of insectivorous cynodonts which lived in what is now South America during the Middle to Late Triassic. The family was established by Alfred Romer in 1973 and includes two genera, Probainognathus from the Chañares Formation of Argentina and Bonacynodon from the Dinodontosaurus Assemblage Zone of Brazil. Probainognathids were closely related to the clade Prozostrodontia, which includes mammals and their close relatives.

Probainognathus meaning “progressive jaw” is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived around 235 to 221.5 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in what is now Argentina. Together with the genus Bonacynodon from Brazil, Probainognathus forms the family Probainognathidae. Probainognathus was a relatively small, carnivorous or insectivorous cynodont. Like all cynodonts, it was a relative of mammals, and it possessed several mammal-like features. Like some other cynodonts, Probainognathus had a double jaw joint, which not only included the quadrate and articular bones like in more basal synapsids, but also the squamosal and surangular bones. A joint between the dentary and squamosal bones, as seen in modern mammals, was however absent in Probainognathus.

Tritylodon is an extinct genus of tritylodonts, one of the most advanced group of cynodont therapsids. They lived in the Early Jurassic and possibly Late Triassic periods along with dinosaurs. They also shared many characteristics with mammals, and were once considered mammals because of overall skeleton construction. That was changed due to them retaining the vestigial amniote jawbones and a different skull structure. Tritylodons are now regarded as non-mammalian synapsids.
Tritylodontidae is an extinct family of small to medium-sized, highly specialized mammal-like cynodonts, with several mammalian traits including erect limbs, endothermy and details of the skeleton. They were the last-known family of the non-mammaliaform synapsids, persisting into the Early Cretaceous.

Tritheledontidae, the tritheledontids or ictidosaurs, is an extinct family of small to medium-sized cynodonts. They were highly mammal-like, specialized cynodonts, although they still retained a few reptile-like anatomical traits. Tritheledontids were mainly carnivorous or insectivorous, though some species may have developed omnivory. Their skeletons show that they had a close relationship to mammals. Tritheledontids or their closest relatives may have given rise to the mammaliaforms. The tritheledontids were one of the longest lived non-mammalian therapsid lineages, living from the late Triassic to the Jurassic period. Tritheledontids became extinct in the Jurassic period, possibly due to competition with prehistoric mammals such as the eutriconodonts. They are known from finds in South America and South Africa, indicating that they may have lived only on the supercontinent of Gondwana. The family Tritheledontidae was named by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1912. The family is often misspelled "Trithelodontidae".
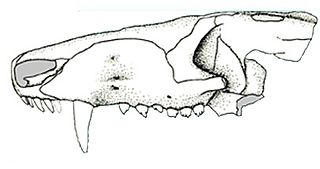
Prozostrodon is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to the ancestors of mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of 6.7 centimetres (2.6 in), indicating that the whole animal may have been the size of a cat. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey.
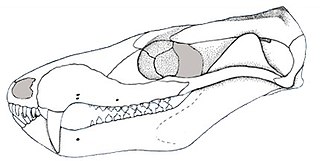
Brasilodon is an extinct genus of small, mammal-like cynodonts that lived in what is now Brazil during the Norian age of the Late Triassic epoch, about 225.42 million years ago. While no complete skeletons have been found, the length of Brasilodon has been estimated at 12 centimetres (4.7 in). Its dentition shows that it was most likely an insectivore. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species B. quadrangularis. Brasilodon belongs to the family Brasilodontidae, whose members were some of the closest relatives of mammals, the only cynodonts alive today. Two other brasilodontid genera, Brasilitherium and Minicynodon, are now considered to be junior synonyms of Brasilodon.

Riograndia is an extinct genus of tritheledontid cynodonts from the Late Triassic of South America. The type and only species is Riograndia guaibensis. Remains have been found in the Caturrita Formation of the geopark of Paleorrota. It was a small non-mammalian cynodont, with several advanced features also present in mammals. Several specimens of Riograndia guaibensis have been found in the towns of Candelária and Faxinal do Soturno in the Caturrita Formation. The genus defines the Riograndia Assemblage Zone.

Lumkuia is an extinct genus of cynodonts, fossils of which have been found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the South African Karoo Basin that date back to the early Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, Lumkuia fuzzi, which was named in 2001 on the basis of the holotype specimen BP/1/2669, which can now be found at the Bernard Price Institute in Johannesburg, South Africa. The genus has been placed in its own family, Lumkuiidae. Lumkuia is not as common as other cynodonts from the same locality such as Diademodon and Trirachodon.

Protheriodon is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts which existed in the Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil during the middle Triassic period. It contains the species Protheriodon estudianti. It was first described by Argentine palaeontologist José Bonaparte, who assigned it to the family Brasilodontidae. More recent studies have however recovered it in a more basal position than other brasilodontids, just outside Prozostrodontia.
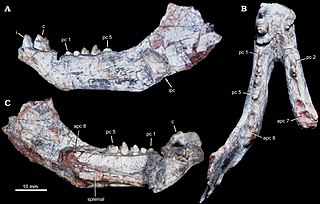
Candelariodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous probainognathian cynodonts from the Middle to Late Triassic Santa Maria Formation of the Paraná Basin in Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Candelariodon is known from a partial mandible having some complete teeth. It was first named by Téo Veiga de Oliveira, Cesar Leandro Schultz, Marina Bento Soares and Carlos Nunes Rodrigues in 2011 and the type species is Candelariodon barberenai.

Prozostrodontia is a clade of cynodonts including mammaliaforms and their closest relatives such as Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae. It was erected as a node-based taxon by Liu and Olsen (2010) and defined as the least inclusive clade containing Prozostrodon brasiliensis, Tritylodon langaevus, Pachygenelus monus, and Mus musculus. Prozostrodontia is diagnosed by several characters, including:

Gomphodontia is a clade of cynognathian cynodonts that includes the families Diademodontidae, Trirachodontidae, and Traversodontidae. Gomphodonts are distinguished by wide and closely spaced molar-like postcanine teeth, which are convergent with those of mammals. Other distinguishing characteristics of gomphodonts include deep zygomatic arches, upper postcanines with three or more cusps spanning their widths and lower postcanines with two cusps spanning their widths. They are thought to have been herbivorous or omnivorous. Gomphodonts first appeared in the Early Triassic and became extinct at the end of the Late Triassic. Fossils are known from southern Africa, Argentina and southern Brazil, eastern North America, Europe, China, and Antarctica.

Aleodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived from the Middle to the Late Triassic. Relatively few analyses have been conducted to identify the phylogenetic placement of Aleodon, however those that have place Aleodon as a sister taxon to Chiniquodon. Two species of Aleodon are recognized: A. brachyramphus which was discovered in Tanzania, and A. cromptoni which was discovered most recently in Brazil.

The Candelária Formation, in other literature also referred to as Candelária Sequence, is a sedimentary formation of the Santa Maria Group in the Paraná Basin in Rio Grande do Sul, southeastern Brazil. The formation dates to the Carnian of the Late Triassic, locally referred to as Tuvalian, from 231.4 to approximately 222 Ma.

Pseudotherium is an extinct genus of prozostrodontian cynodonts from the Late Triassic of Argentina. It contains one species, P. argentinus, which was first described in 2019 from remains found in the La Peña Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin.
Agudotherium is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts from the Late Triassic Candelária Formation of the Paraná Basin in southern Brazil. The genus contains one species, Agudotherium gassenae. A. gassenae is known from three specimens, all consisting of partial lower jaws.

Santacruzgnathus is an extinct genus of small cynodonts from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Santacruzodon Assemblage Zone of Brazil. It contains one species, S. abdalai. Santacruzgnathus is known from a single partial lower jaw with four postcanine teeth, only one of which is well-preserved. Some features of the specimen, including the slender shape of the jaw and the incipiently double-rooted teeth, indicate that the animal was an early member of Prozostrodontia, a group that includes mammals and their close relatives.
























