Related Research Articles

Medieval music encompasses the sacred and secular music of Western Europe during the Middle Ages, from approximately the 6th to 15th centuries. It is the first and longest major era of Western classical music and followed by the Renaissance music; the two eras comprise what musicologists generally term as early music, preceding the common practice period. Following the traditional division of the Middle Ages, medieval music can be divided into Early (500–1000), High (1000–1300), and Late (1300–1400) medieval music.
Semiology is a branch of Gregorian Chant research. Semiology refers specifically to the study of the neumes as found in the earliest fully notated manuscripts of Gregorian Chant, the oldest of which have been dated to the 9th century. The first application of the term 'semiology' for the study of Latin chant was made by Dom Eugène Cardine (1905–1988), a monk of the Abbey of Solesmes. In this context, 'semiology' is understood as 'the study of musical signs'. Text and neumatic notation, together with significative letters adjoined to the neumes, presents an effective and integrated mnemonic for the rhythmical interpretation and the melody. While Gregorian palaeography offers a description of the various neumes and their rhythmical and melodic values, Gregorian semiology explains their meaning for practical interpretation.
Plainsong or plainchant is a body of chants used in the liturgies of the Western Church. When referring to the term plainsong, it is those sacred pieces that are composed in Latin text. Plainsong was the exclusive form of Christian church music until the ninth century, and the introduction of polyphony.

Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries, with later additions and redactions. Although popular legend credits Pope Gregory I with inventing Gregorian chant, scholars believe that it arose from a later Carolingian synthesis of the Old Roman chant and Gallican chant.
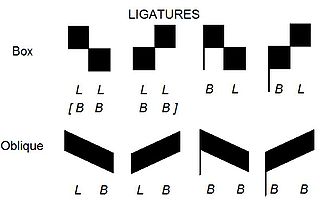
In music notation, a ligature is a graphic symbol that tells a musician to perform two or more notes in a single gesture, and on a single syllable. It was primarily used from around 800 to 1650 AD. Ligatures are characteristic of neumatic (chant) and mensural notation. The notation and meaning of ligatures has changed significantly throughout Western music history, and their precise interpretation is a continuing subject of debate among musicologists.
A chant is the iterative speaking or singing of words or sounds, often primarily on one or two main pitches called reciting tones. Chants may range from a simple melody involving a limited set of notes to highly complex musical structures, often including a great deal of repetition of musical subphrases, such as Great Responsories and Offertories of Gregorian chant. Chant may be considered speech, music, or a heightened or stylized form of speech. In the later Middle Ages some religious chant evolved into song.

Christian music is music that has been written to express either personal or a communal belief regarding Christian life and faith. Common themes of Christian music include praise, worship, penitence and lament, and its forms vary widely around the world. Church music, hymnals, gospel and worship music are a part of Christian media and also include contemporary Christian music which itself supports numerous Christian styles of music, including hip hop, rock, contemporary worship and urban contemporary gospel.

A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation.

Gregorian is a German band headed by Frank Peterson that performs Gregorian chant-inspired versions of modern pop and rock songs. The band features both vocal harmony and instrumental accompaniment. They competed in Unser Lied für Stockholm, the German national selection for the Eurovision Song Contest 2016, and placed 5th in the first round of public voting with the song "Masters of Chant", failing to make the Top 3 with 9.06% of the public vote.

Alla breve – also known as cut time or cut common time – is a musical meter notated by the time signature symbol , which is the equivalent of 2
2. The term is Italian for "on the breve", originally meaning that the beat was counted on the breve.

In music notation, a note value indicates the relative duration of a note, using the texture or shape of the notehead, the presence or absence of a stem, and the presence or absence of flags/beams/hooks/tails. Unmodified note values are fractional powers of two, for example one, one-half, one fourth, etc.

Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measured rhythmic durations in terms of numerical proportions between note values. Its modern name is inspired by the terminology of medieval theorists, who used terms like musica mensurata or cantus mensurabilis to refer to the rhythmically defined polyphonic music of their age, as opposed to musica plana or musica choralis, i.e., Gregorian plainchant. Mensural notation was employed principally for compositions in the tradition of vocal polyphony, whereas plainchant retained its own, older system of neume notation throughout the period. Besides these, some purely instrumental music could be written in various forms of instrument-specific tablature notation.
Gallican chant refers to the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Gallican rite of the Roman Catholic Church in Gaul, prior to the introduction and development of elements of the Roman rite from which Gregorian chant evolved. Although the music was largely lost, traces are believed to remain in the Gregorian corpus.
Ambrosian chant is the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Ambrosian rite of the Roman Catholic Church, related to but distinct from Gregorian chant. It is primarily associated with the Archdiocese of Milan, and named after St. Ambrose much as Gregorian chant is named after Gregory the Great. It is the only surviving plainchant tradition besides the Gregorian to maintain the official sanction of the Roman Catholic Church.
Mozarabic chant is the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Visigothic/Mozarabic rite of the Catholic Church, related to the Gregorian chant. It is primarily associated with Hispania under Visigothic rule and later with the Mozarabs and was replaced by the chant of the Roman rite following the Christian Reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula. Although its original medieval form is largely lost, a few chants have survived with readable musical notation, and the chanted rite was later revived in altered form and continues to be used in a few isolated locations in Spain, primarily in Toledo.

Beneventan chant is a liturgical plainchant repertory of the Roman Catholic Church, used primarily in the orbit of the southern Italian ecclesiastical centers of Benevento and Monte Cassino distinct from Gregorian chant and related to Ambrosian chant. It was officially supplanted by the Gregorian chant of the Roman rite in the 11th century, although a few Beneventan chants of local interest remained in use.
Old Roman chant is the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Roman rite of the early Christian Church. It was formerly performed in Rome, and, although it is closely related to Gregorian chant, the two are distinct. Gregorian Chant gradually supplanted Old Roman Chant between the 11th century and the 13th century AD. Unlike other chant traditions, Old Roman chant and Gregorian chant share essentially the same liturgy and the same texts. Many of their melodies are also closely related. Although primarily associated with the churches of Rome, the Old Roman chant was also performed in parts of central Italy, and it was possibly performed much more widely.

In music, a notehead is the part of a note, usually elliptical in shape, whose placement on the staff indicates the pitch, to which modifications are made that indicate duration. Noteheads may be the same shape but colored completely black or white, indicating the note value. In a whole note, the notehead, shaped differently than shorter notes, is the only component of the note. Shorter note values attach a stem to the notehead, and possibly beams or flags. The longer double whole note can be written with vertical lines surrounding it, two attached noteheads, or a rectangular notehead. An "x" shaped notehead may be used to indicate percussion, percussive effects, or speaking. A square, diamond, or box shaped notehead may be used to indicate a natural or artificial harmonic. A small notehead can be used to indicate a grace note.
In medieval music theory, the Latin term modus can be used in a variety of distinct senses. The most commonly used meaning today relates to the organisation of pitch in scales. Other meanings refer to the notation of rhythms.
Theodore Cyrus Karp was an American musicologist. His principal area of study was Secular music, mainly mediaeval monophony, especially the music of the trouvères. He was a major contributor in this area to the Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians.
References
- ↑ Rayburn, John (1964). Gregorian Chant: A History of the Controversy Concerning Its Rhythm. Greenwood Press. p. 61.