Related Research Articles
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Characteristics central to capitalism include private property, capital accumulation, wage labor, voluntary exchange, a price system and competitive markets. In a capitalist market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by every owner of wealth, property or production ability in financial and capital markets whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets.

Anti-capitalism is a political ideology and movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose capitalism. In this sense, anti-capitalists are those who wish to replace capitalism with another type of economic system, usually some form of socialism.
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a market economy is the existence of factor markets that play a dominant role in the allocation of capital and the factors of production.
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ending birth years, with 1981 to 1996 a widely accepted defining range for the generation.
Freelance, freelancer, and freelance worker, are terms commonly used for a person who is self-employed and not necessarily committed to a particular employer long-term. Freelance workers are sometimes represented by a company or a temporary agency that resells freelance labor to clients; others work independently or use professional associations or websites to get work.
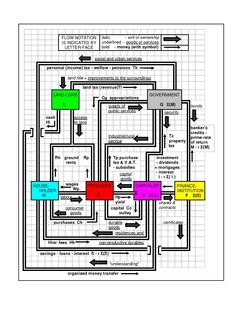
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community. As such, an economic system is a type of social system. The mode of production is a related concept. All economic systems have three basic questions to ask: what to produce, how to produce and in what quantities and who receives the output of production.
An independent contractor is a person, business, or corporation that provides goods or services under a written contract or a verbal agreement. Unlike employees, independent contractors do not work regularly for an employer but work as required, when they may be subject to law of agency. Independent contractors are usually paid on a freelance basis. Contractors often work through a limited company or franchise, which they themselves own, or may work through an umbrella company.
Anarchist economics is the set of theories and practices of economic activity within the political philosophy of anarchism. With the exception of anarcho-capitalists, who accept private ownership of the means of production and are not considered as part of the anarchist movement, anarchists are anti-capitalists, with anarchism often referred to as a stateless system of socialism.
Social peer-to-peer processes are interactions with a peer-to-peer dynamic. These peers can be humans or computers. Peer-to-peer (P2P) is a term that originated from the popular concept of the P2P distributed computer application architecture which partitions tasks or workloads between peers. This application structure was popularized by file sharing systems like Napster, the first of its kind in the late 1990s.
Post-capitalism is a state in which the economic systems of the world can no longer be described as forms of capitalism. Various individuals and political ideologies have speculated on what would define such a world. According to some classical Marxist and some social evolutionary theories, post-capitalist societies may come about as a result of spontaneous evolution as capitalism becomes obsolete. Others propose models to intentionally replace capitalism. The most notable among them are socialism and anarchism.
Criticism of capitalism ranges from expressing disagreement with the principles of capitalism in its entirety to expressing disagreement with particular outcomes of capitalism.
In business, free agents are people who work independently for themselves, rather than for a single employer. These include self-employed workers, freelancers, independent contractors and temporary workers, who altogether represent about 44 percent of the U.S. labor force. The term free agent is believed to have been coined by Daniel H. Pink, author of a 1997 cover story in Fast Company titled “Free Agent Nation.” In 2001 Pink published a book with the same name. The combination of several workplace trends – including shortened job cycles, the increase of project work, the acceptance of a new lifestyle and the emergence of the Internet and other technology – points to free agent workers becoming more of an employment norm in the coming years. In a 2011 survey sponsored by Kelly Services, free agency is on the rise across all generations, with mature workers making up two-thirds of the free agent population. The survey also revealed that 73% of free agents voluntarily choose this workstyle because they seek the freedom, flexibility and entrepreneurial benefits associated with an independent workstyle.
The Nordic model comprises the economic and social policies as well as typical cultural practices common to the Nordic countries. This includes a comprehensive welfare state and multi-level collective bargaining based on the economic foundations of free-market capitalism, with a high percentage of the workforce unionised and a large percentage of the population employed by the public sector. The Nordic model began to gain attention after World War II.
Free association, also known as free association of producers, is a relationship among individuals where there is no state, social class, hierarchy, or private ownership of means of production. Once private property is abolished, individuals are no longer deprived of access to means of production, thus enabling them to freely associate without social constraint to produce and reproduce their own conditions of existence and fulfill their individual and creative needs and desires. The term is used by anarchists and Marxists and is often considered a defining feature of a fully developed communist society.
Bring your own device —also called bring your own technology (BYOT), bring your own phone (BYOP), and bring your own personal computer (BYOPC)—refers to being allowed to use one's personally owned device, rather than being required to use an officially provided device.
Economic democracy is a socioeconomic philosophy that proposes to shift decision-making power from corporate managers and corporate shareholders to a larger group of public stakeholders that includes workers, customers, suppliers, neighbours and the broader public. No single definition or approach encompasses economic democracy, but most proponents claim that modern property relations externalize costs, subordinate the general well-being to private profit and deny the polity a democratic voice in economic policy decisions. In addition to these moral concerns, economic democracy makes practical claims, such as that it can compensate for capitalism's inherent effective demand gap.
The 'share economy' is a concept of a type of economy that is not monetarised, and is not based in a capitalist system.
In Karl Marx's critique of political economy and subsequent Marxian analyses, the capitalist mode of production refers to the systems of organizing production and distribution within capitalist societies. Private money-making in various forms preceded the development of the capitalist mode of production as such. The capitalist mode of production proper, based on wage-labour and private ownership of the means of production and on industrial technology, began to grow rapidly in Western Europe from the Industrial Revolution, later extending to most of the world.
Social ownership is any of various forms of ownership for the means of production in socialist economic systems, encompassing state ownership, employee ownership, cooperative ownership, citizen ownership of equity, common ownership and collective ownership. Historically social ownership implied that capital and factor markets would cease to exist under the assumption that market exchanges within the production process would be made redundant if capital goods were owned by a single entity or network of entities representing society, but the articulation of models of market socialism where factor markets are utilized for allocating capital goods between socially owned enterprises broadened the definition to include autonomous entities within a market economy. Social ownership of the means of production is the common defining characteristic of all the various forms of socialism.
Socialist economics comprises the economic theories, practices and norms of hypothetical and existing socialist economic systems. A socialist economic system is characterized by social ownership and operation of the means of production that may take the form of autonomous cooperatives or direct public ownership wherein production is carried out directly for use rather than for profit. Socialist systems that utilize markets for allocating capital goods and factors of production among economic units are designated market socialism. When planning is utilized, the economic system is designated as a socialist planned economy. Non-market forms of socialism usually include a system of accounting based on calculation-in-kind to value resources and goods.
References
- ↑ "Changes in the Labor Market Leads to Increase in Free Agent Workforce, According to Kelly Services, Inc." "Intuit" Retrieved 20 July 2015.
- ↑ "Intuit 2020 Report: Twenty Trends That Will Shape the Next Decade" "Intuit" Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Proprietism and Liability Shields" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "The Proprietist-Style Organization" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Proprietist Theory and the IPO Model" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Social Media and the New Individualism" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Your Brand and Your Network" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "The Gold Majority" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ↑ "Millennials and Proprietism" "Proprietism". Retrieved 19 July 2015.