
Basque is the only surviving Paleo-European language spoken in Europe, predating the arrival of speakers of the Indo-European languages that dominate the continent today. Basque is spoken by the Basques and other residents of the Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Basque is classified as a language isolate, with no relationship to any other language having been established. The Basques are indigenous to and primarily inhabit the Basque Country. The Basque language is spoken by 806,000 Basques in all territories. Of these, 93.7% (756,000) are in the Spanish area of the Basque Country and the remaining 6.3% (50,000) are in the French portion.

In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards to infer the properties of that ancestor. The comparative method may be contrasted with the method of internal reconstruction in which the internal development of a single language is inferred by the analysis of features within that language. Ordinarily, both methods are used together to reconstruct prehistoric phases of languages; to fill in gaps in the historical record of a language; to discover the development of phonological, morphological and other linguistic systems and to confirm or to refute hypothesised relationships between languages.

The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongol residents of Inner Mongolia, with an estimated 5.7+ million speakers.

Proto-Germanic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
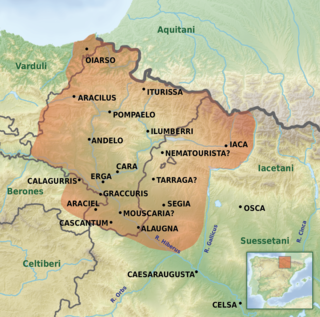
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides with present-day Navarre, western Aragon and northeastern La Rioja, in the Iberian Peninsula. The Vascones are often considered ancestors of the present-day Basques to whom they left their name.
The Iberian language was the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre-Migration Era. An ancient Iberian culture can be identified as existing between the 7th and 1st centuries BC, at least.
In phonology, apocope is the loss (elision) of a word-final vowel. In a broader sense, the term can refer to the loss of any final sound from a word.

The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine and in the areas south of the Pyrenees in the valleys of the Basque Country before the Roman conquest. It probably survived in Aquitania north of the Pyrenees until the Early Middle Ages.
In linguistics, prothesis, or less commonly prosthesis is the addition of a sound or syllable at the beginning of a word without changing the word's meaning or the rest of its structure. A vowel or consonant added by prothesis is called prothetic or less commonly prosthetic.
In articulatory phonetics, fortition, also known as strengthening, is a consonantal change that increases the degree of stricture. It is the opposite of the more common lenition. For example, a fricative or an approximant may become a stop. Although not as typical of sound change as lenition, fortition may occur in prominent positions, such as at the beginning of a word or stressed syllable; as an effect of reducing markedness; or due to morphological leveling.
The origin of the Basques and the Basque language is a controversial topic that has given rise to numerous hypotheses. Modern Basque, a descendant or close relative of Aquitanian and Proto-Basque, is the only pre-Indo-European language that is extant in western Europe. The Basques have therefore long been supposed to be a remnant of a pre-Indo-European population of Europe.

Proto-Albanian is the ancestral reconstructed language of Albanian, before the Gheg–Tosk dialectal diversification. Albanoid and other Paleo-Balkan languages had their formative core in the Balkans after the Indo-European migrations in the region. Whether descendants or sister languages of what was called Illyrian by classical sources, Albanian and Messapic, on the basis of shared features and innovations, are grouped together in a common branch in the current phylogenetic classification of the Indo-European language family. The precursor of Albanian can be considered a completely formed independent IE language since at least the first millennium BCE, with the beginning of the early Proto-Albanian phase.
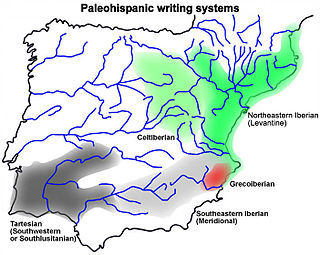
The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language, but has also been used to write Proto-Basque as seen in the Hand of Irulegi. The Iberian language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and the Greco-Iberian alphabet. To understand the relationship between northeastern Iberian and southeastern Iberian scripts, one should point out that they are two different scripts with different values for the same signs. However, it is clear they have a common origin and the most accepted hypothesis is that northeastern Iberian script was derived from the southeastern Iberian script. Some researchers have concluded that it is linked to the Phoenician alphabet alone, but others believe the Greek alphabet also had a role.

Koldo Mitxelena Elissalt was an eminent Spanish Basque linguist. He taught in the Department of Philology at the University of the Basque Country, and was a member of the Royal Academy of the Basque Language.
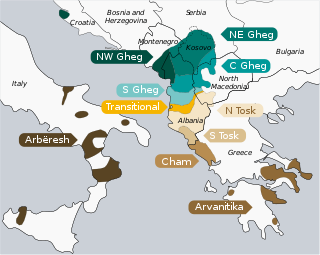
Albanian is an Indo-European language and the only surviving representative of the Albanoid branch, which belongs to the Paleo-Balkan group. Standard Albanian is the official language of Albania and Kosovo, and a co-official language in North Macedonia and Montenegro, as well as a recognized minority language of Italy, Croatia, Romania and Serbia. It is also spoken in Greece and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. Albanian is estimated to have as many as 7.5 million native speakers.

The Vasconic languages are a putative family of languages that includes Basque and the extinct Aquitanian language. The extinct Iberian language is sometimes tentatively included.
The Goidelic substrate hypothesis refers to the hypothesized language or languages spoken in Ireland before the arrival of the Goidelic languages.
Basque is a pre-Indo-European language spoken in the Basque Country, extending over a strip along eastern areas of the Bay of Biscay in Spain and France, straddling the western Pyrenees. It is classified as a language isolate, having no demonstrable genetic relation to any other known language, with the sole exception of the extinct Aquitanian language, which is considered to be an ancestral form of Basque.

The Albanian–Eastern Romance linguistic parallels are subject of historical and contact linguistic research applied to the Albanian and Eastern Romance languages. It has also been studied to understand the history of Albanian and Eastern Romance speakers. The common phonological, morphological and syntactical features of the two language families have been studied for more than a century. Both are part of the Balkan sprachbund but there are certain elements shared only by Albanian and Eastern Romance languages that descended from Common Romanian. Aside from Latin, and from shared Greek, Slavic and Turkish elements, other characteristics and words are attributed to the Palaeo-Balkan linguistic base. Similarities between Eastern Romance and Albanian are not limited to their common Balkan features and the assumed common lexical items: the two language families share calques and proverbs, and display analogous phonetic changes, some of the latter especially shared between Tosk Albanian and Common Romanian.










