Related Research Articles

Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.
In archaeology, a tool stone is a type of stone that is used to manufacture stone tools, or tools that use stone as raw material.

The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lithology may refer to either a detailed description of these characteristics, or a summary of the gross physical character of a rock. Examples of lithologies in the second sense include sandstone, slate, basalt, or limestone.

Greywacke or graywacke is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness, dark color, and poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or sand-size lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic strata. The larger grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume.

Arkose or arkosic sandstone is a detrital sedimentary rock, specifically a type of sandstone containing at least 25% feldspar. Arkosic sand is sand that is similarly rich in feldspar, and thus the potential precursor of arkose.

In geology, a mélange is a large-scale breccia, a mappable body of rock characterized by a lack of continuous bedding and the inclusion of fragments of rock of all sizes, contained in a fine-grained deformed matrix. The mélange typically consists of a jumble of large blocks of varied lithologies. Both tectonic and sedimentary processes can form mélange.
Detritus is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion. A fragment of detritus is called a clast. Detrital particles can consist of lithic fragments, or of monomineralic fragments. These particles are often transported through sedimentary processes into depositional systems such as riverbeds, lakes or the ocean, forming sedimentary successions. Diagenetic processes can transform these sediments into rock through cementation and lithification, forming sedimentary rocks such as sandstone. These rocks can then in turn again be weathered and eroded to form a second generation of sediment. Detrital grains commonly weather at different rates, according to the Goldich dissolution series, which dictates that early crystallizing minerals are less stable at the earth's surface than late crystallizing minerals.

A quartz arenite or quartzarenite is a sandstone composed of greater than 90% detrital quartz. Quartz arenites are the most mature sedimentary rocks possible, and are often referred to as ultra- or super-mature, and are usually cemented by silica. They often exhibit both textural and compositional maturity. The two primary sedimentary depositional environments that produce quartz arenites are beaches/upper shoreface and aeolian processes.
The Folk classification, in geology, is a technical descriptive classification of sedimentary rocks devised by Robert L. Folk, an influential sedimentary petrologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Texas.

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.
Lithic may refer to:
Lithic fragments, or lithics, are pieces of other rocks that have been eroded down to sand size and now are sand grains in a sedimentary rock. They were first described and named by Bill Dickinson in 1970. Lithic fragments can be derived from sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic rocks. A lithic fragment is defined using the Gazzi-Dickinson point-counting method and being in the sand-size fraction. Sand grains in sedimentary rocks that are fragments of larger rocks that are not identified using the Gazzi-Dickinson method are usually called rock fragments instead of lithic fragments. Sandstones rich in lithic fragments are called lithic sandstones.
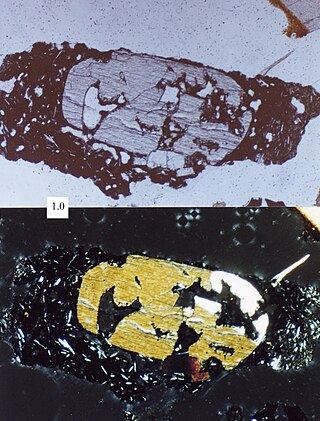
The Gazzi-Dickinson method is a point-counting technique used in geology to statistically measure the components of a sedimentary rock, chiefly sandstone. The main focus part of the technique is counting all sand-sized components as separate grains, regardless of what they are connected to. Gazzi-Dickinson point counting is used in the creation of ternary diagrams, such as QFL diagrams.

A QFL diagram or QFL triangle is a type of ternary diagram that shows compositional data from sandstones and modern sands, point counted using the Gazzi-Dickinson method. The abbreviations used are as follows:

Lithic sandstones, or lithic arenites, or litharenites, are sandstones with a significant (>5%) component of lithic fragments, though quartz and feldspar are usually present as well, along with some clayey matrix. Lithic sandstones can have a speckled or gray color, and are usually associated with one specific type of lithic fragment.

Minchinbury Sandstone is a component of the Wianammatta Group of sedimentary rocks in the Sydney Basin of eastern Australia.
Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the origin of sediments. The Earth is a dynamic planet, and all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Rocks exposed to the surface are sooner or later broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosional history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.
The Alajuela Formation, originally Alhajuela Formation (Tau), is a Late Miocene geologic formation in the Panama Canal Zone of central Panama.
References
- ↑ Dickinson, William R. (1970). "Interpreting detrital modes of graywacke and arkose". SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology. 40: 695–707. doi:10.1306/74D72018-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D.