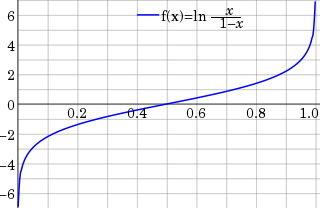
In statistics, the logit function is the quantile function associated with the standard logistic distribution. It has many uses in data analysis and machine learning, especially in data transformations.

The Weber–Fechner laws are two related scientific laws in the field of psychophysics, known as Weber's law and Fechner's law. Both relate to human perception, more specifically the relation between the actual change in a physical stimulus and the perceived change. This includes stimuli to all senses: vision, hearing, taste, touch, and smell.
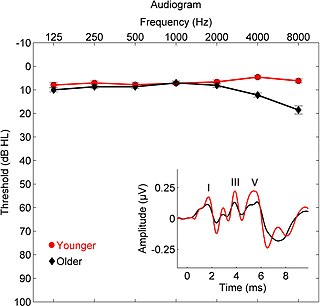
The absolute threshold of hearing (ATH), also known as the absolute hearing threshold or auditory threshold, is the minimum sound level of a pure tone that an average human ear with normal hearing can hear with no other sound present. The absolute threshold relates to the sound that can just be heard by the organism. The absolute threshold is not a discrete point and is therefore classed as the point at which a sound elicits a response a specified percentage of the time.
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which "All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments". By contrast, item response theory treats the difficulty of each item as information to be incorporated in scaling items.
Psychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions".
In the branch of experimental psychology focused on sense, sensation, and perception, which is called psychophysics, a just-noticeable difference or JND is the amount something must be changed in order for a difference to be noticeable, detectable at least half the time. This limen is also known as the difference limen, difference threshold, or least perceptible difference.
In statistics, a generalized linear model (GLM) is a flexible generalization of ordinary linear regression. The GLM generalizes linear regression by allowing the linear model to be related to the response variable via a link function and by allowing the magnitude of the variance of each measurement to be a function of its predicted value.
Stevens' power law is an empirical relationship in psychophysics between an increased intensity or strength in a physical stimulus and the perceived magnitude increase in the sensation created by the stimulus. It is often considered to supersede the Weber–Fechner law, which is based on a logarithmic relationship between stimulus and sensation, because the power law describes a wider range of sensory comparisons, down to zero intensity.

Audiometry is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subject's hearing levels with the help of an audiometer, but may also measure ability to discriminate between different sound intensities, recognize pitch, or distinguish speech from background noise. Acoustic reflex and otoacoustic emissions may also be measured. Results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose hearing loss or diseases of the ear, and often make use of an audiogram.

In probability theory and statistics, the probit function is the quantile function associated with the standard normal distribution. It has applications in data analysis and machine learning, in particular exploratory statistical graphics and specialized regression modeling of binary response variables.
In neuroscience and psychophysics, an absolute threshold was originally defined as the lowest level of a stimulus – light, sound, touch, etc. – that an organism could detect. Under the influence of signal detection theory, absolute threshold has been redefined as the level at which a stimulus will be detected a specified percentage of the time. The absolute threshold can be influenced by several different factors, such as the subject's motivations and expectations, cognitive processes, and whether the subject is adapted to the stimulus.
The absolute threshold can be compared to the difference threshold, which is the measure of how different two stimuli must be for the subject to notice that they are not the same.
Mathematical psychology is an approach to psychological research that is based on mathematical modeling of perceptual, thought, cognitive and motor processes, and on the establishment of law-like rules that relate quantifiable stimulus characteristics with quantifiable behavior. The mathematical approach is used with the goal of deriving hypotheses that are more exact and thus yield stricter empirical validations. There are five major research areas in mathematical psychology: learning and memory, perception and psychophysics, choice and decision-making, language and thinking, and measurement and scaling.
The Rasch model, named after Georg Rasch, is a psychometric model for analyzing categorical data, such as answers to questions on a reading assessment or questionnaire responses, as a function of the trade-off between the respondent's abilities, attitudes, or personality traits, and the item difficulty. For example, they may be used to estimate a student's reading ability or the extremity of a person's attitude to capital punishment from responses on a questionnaire. In addition to psychometrics and educational research, the Rasch model and its extensions are used in other areas, including the health profession, agriculture, and market research.
In psychophysics, sensory threshold is the weakest stimulus that an organism can sense. Unless otherwise indicated, it is usually defined as the weakest stimulus that can be detected half the time, for example, as indicated by a point on a probability curve. Methods have been developed to measure thresholds in any of the senses.

The dose–response relationship, or exposure–response relationship, describes the magnitude of the response of an organism, as a function of exposure to a stimulus or stressor after a certain exposure time. Dose–response relationships can be described by dose–response curves. This is explained further in the following sections. A stimulus response function or stimulus response curve is defined more broadly as the response from any type of stimulus, not limited to chemicals.

Two-point discrimination (2PD) is the ability to discern that two nearby objects touching the skin are truly two distinct points, not one. It is often tested with two sharp points during a neurological examination and is assumed to reflect how finely innervated an area of skin is.
Two-alternative forced choice (2AFC) is a method for measuring the sensitivity of a person or animal to some particular sensory input, stimulus, through that observer's pattern of choices and response times to two versions of the sensory input. For example, to determine a person's sensitivity to dim light, the observer would be presented with a series of trials in which a dim light was randomly either in the top or bottom of the display. After each trial, the observer responds "top" or "bottom". The observer is not allowed to say "I do not know", or "I am not sure", or "I did not see anything". In that sense the observer's choice is forced between the two alternatives.
A Thurstonian model is a stochastic transitivity model with latent variables for describing the mapping of some continuous scale onto discrete, possibly ordered categories of response. In the model, each of these categories of response corresponds to a latent variable whose value is drawn from a normal distribution, independently of the other response variables and with constant variance. Developments over the last two decades, however, have led to Thurstonian models that allow unequal variance and non zero covariance terms. Thurstonian models have been used as an alternative to generalized linear models in analysis of sensory discrimination tasks. They have also been used to model long-term memory in ranking tasks of ordered alternatives, such as the order of the amendments to the US Constitution. Their main advantage over other models ranking tasks is that they account for non-independence of alternatives. Ennis provides a comprehensive account of the derivation of Thurstonian models for a wide variety of behavioral tasks including preferential choice, ratings, triads, tetrads, dual pair, same-different and degree of difference, ranks, first-last choice, and applicability scoring. In Chapter 7 of this book, a closed form expression, derived in 1988, is given for a Euclidean-Gaussian similarity model that provides a solution to the well-known problem that many Thurstonian models are computationally complex often involving multiple integration. In Chapter 10, a simple form for ranking tasks is presented that only involves the product of univariate normal distribution functions and includes rank-induced dependency parameters. A theorem is proven that shows that the particular form of the dependency parameters provides the only way that this simplification is possible. Chapter 6 links discrimination, identification and preferential choice through a common multivariate model in the form of weighted sums of central F distribution functions and allows a general variance-covariance matrix for the items.

Davida Young Teller was a professor in the Departments of Psychology and Physiology/Biophysics at the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington. She was a leader in the scientific study of infant visual development.

Up-and-down designs (UDDs) are a family of statistical experiment designs used in dose-finding experiments in science, engineering, and medical research. Dose-finding experiments have binary responses: each individual outcome can be described as one of two possible values, such as success vs. failure or toxic vs. non-toxic. Mathematically the binary responses are coded as 1 and 0. The goal of dose-finding experiments is to estimate the strength of treatment (i.e., the "dose") that would trigger the "1" response a pre-specified proportion of the time. This dose can be envisioned as a percentile of the distribution of response thresholds. An example where dose-finding is used is in an experiment to estimate the LD50 of some toxic chemical with respect to mice.









