
The General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) is an academic qualification in a range of particular subjects, taken in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. State schools in Scotland use the Scottish Qualifications Certificate instead. Private schools in Scotland may choose to use GCSEs from England.
Further education in the United Kingdom and Ireland is additional education to that received at secondary school that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It may be at any level in compulsory secondary education, from entry to higher level qualifications such as awards, certificates, diplomas and other vocational, competency-based qualifications through awarding organisations including City and Guilds, Edexcel (BTEC) and OCR. FE colleges may also offer HE qualifications such as HNC, HND, foundation degree or PGCE. The colleges are also a large service provider for apprenticeships where most of the training takes place at the apprentices' workplace, supplemented with day release into college.
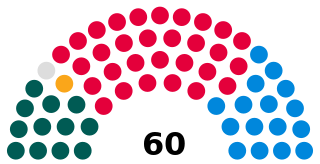
The Senedd, officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and Senedd Cymru in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees to certain taxes, and scrutinises the Welsh Government. It is a bilingual institution, with both Welsh and English being the official languages of its business. From its creation in May 1999 until May 2020, the Senedd was known as the National Assembly for Wales.

The Welsh Government is the devolved government of Wales. The government consists of ministers and deputy ministers. It is led by the first minister, usually the leader of the largest party in the Senedd, who selects ministers and deputy ministers with the approval of the Senedd. The government is responsible for tabling policy in devolved areas for consideration by the Senedd and implementing policy that has been approved by it.
This article provides an overview of education in Wales from early childhood to university and adult skills. Largely state funded and free-at-the-point-of-use at a primary and secondary level, education is compulsory for children in Wales aged five to sixteen years old. It differs to some extent in structure and content to other parts of the United Kingdom, in the later case particularly in relation to the teaching of the Welsh language.

WJEC is an examination board providing examinations, professional development and educational resources to schools and colleges in Wales, England and Northern Ireland under its own name and the Eduqas brand.
The Welsh Baccalaureate, or Welsh Bacc, is an educational qualification delivered in secondary schools and colleges across Wales. The Welsh Government says that it gives broader experiences than traditional learning programmes, developing transferable skills useful for education and employment. The Welsh Bacc is offered at Advanced, National Foundation and National/Foundation level, and is studied alongside a range of academic and vocational qualifications.
A national qualifications framework (NQF) is a formal system describing qualifications. 47 countries participating in the Bologna Process are committed to producing a national qualifications framework. Other countries not part of this process also have national qualifications frameworks.
The Senedd constituencies and electoral regions are the electoral districts used to elect Members of the Senedd to the Senedd, and have been used in some form since the first election of the then National Assembly for Wales in 1999. New boundaries were introduced for the 2007 elections and currently consist of forty constituencies and five regions. The five electoral regions are: Mid and West Wales, North Wales, South Wales Central, South Wales East, and South Wales West, with the forty constituencies listed below. Voting last took place in all districts in the 2021 Senedd election, and is not used for local government.
A postgraduate certificate (abbreviated as PGCert, PG Cert or PGC is a postgraduate qualification at the level of a master's degree.

Welsh law is an autonomous part of the English law system composed of legislation made by the Senedd. Wales is part of the legal jurisdiction of England and Wales, one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. However, due to devolution, the law in Wales is increasingly distinct from the law in England, since the Senedd, the devolved parliament of Wales, can legislate on non-reserved matters.

The Senedd Commission is the corporate body for the Senedd of Wales. The Commission is responsible for ensuring the property, staff and services are provided for the Senedd. The Commission consists of the Llywydd of the Senedd and four Members from different political parties, who each have different portfolios of work. The Commission is supported by staff in the Commission and Support Service. Prior to 2020, the body was known as the National Assembly for Wales Commission.
A Welsh Government sponsored body (WGSB) is a non-departmental public body directly funded by the Welsh Government. Under the Government of Wales Act 1998 the bodies were sponsored by the National Assembly for Wales and were known as an Assembly sponsored public body, and this was changed by the Schedule 3 of the Wales Act 2017 which amended the Government of Wales Act 2006.
In the United Kingdom, an awarding body is an examination board which sets examinations and awards qualifications, such as GCSEs and A-levels. Additionally, these Awarding Bodies provide professional awards in the form of tertiary level Certificates, Diplomas, Advanced Diplomas, Graduate Diplomas, and Post Graduate Diplomas. There are eight main examination boards in the United Kingdom:
In the UK education sector, there are a wide range of qualification types offered by the United Kingdom awarding bodies. Qualifications range in size and type, can be academic, vocational or skills-related, and are grouped together into different levels of difficulty. In England, Wales and Northern Ireland, qualifications are divided into Higher Education qualifications, which are on the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (FHEQ) and are awarded by bodies with degree awarding powers, and Regulated qualifications, which are on the Regulated Qualifications Framework (RQF) and are accredited by Ofqual in England, the Council for the Curriculum, Examinations and Assessment in Northern Ireland and Qualifications Wales in Wales. In Scotland, qualifications are divided into Higher Education qualifications, Scottish Qualifications Authority qualifications and Scottish Vocational Qualifications/Modern Apprenticeships, which are on the Scottish Credit and Qualifications Framework (SCQF). Scottish Higher Education Qualifications are on both the SCQF and the FHEQ.
A graduate certificate is an educational credential representing completion of specialized training at the college or university level. A graduate certificate can be awarded by universities upon completion of certain coursework indicating mastering of a specific subject area. Graduate certificates represent training at different levels in different countries, for example a graduate certificate is at master's degree level in Ireland, but is at a bachelor's degree level in the United Kingdom. In both cases, the graduate certificate represents less work than a degree at the same level.
Essential Skills Wales (ESW) is a suite of skills qualifications, available in Wales. Each Essential Skills Wales qualification is equivalent to an E grade at GCE AS-Level. Essential Skills Wales has replaced the earlier Key Skills in Wales and Wider Key Skills schemes. Skills covered are in the areas of communication, application of number, and ICT. ESW is also embedded within Welsh educational initiatives including the Welsh Baccalaureate and the Apprenticeship programme.

The 2016 National Assembly for Wales election was held on Thursday 5 May 2016, to elect members (AMs) of the National Assembly for Wales, now known as the Senedd. It was the fifth election for the National Assembly, the third election taken under the rules of the Government of Wales Act 2006 and the first since the Wales Act 2014.

The Wales Act 2017 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It sets out amendments to the Government of Wales Act 2006 and devolves further powers to Wales. The legislation is based on the proposals of the St David's Day Command Paper.
The national qualification frameworks in the United Kingdom are qualifications frameworks that define and link the levels and credit values of different qualifications.









