
A pyramid is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilateral, or of any polygon shape. As such, a pyramid has at least three outer triangular surfaces. The square pyramid, with a square base and four triangular outer surfaces, is a common version.

Teotihuacan is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, 40 kilometers (25 mi) northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as the site of many of the most architecturally significant Mesoamerican pyramids built in the pre-Columbian Americas, namely the Pyramid of the Sun and the Pyramid of the Moon. At its zenith, perhaps in the first half of the first millennium, Teotihuacan was the largest city in the Americas, considered as the first advanced civilization on the North American continent, with a population estimated at 125,000 or more, making it at least the sixth-largest city in the world during its epoch.

Chalchiuhtlicue[t͡ʃaːɬt͡ʃiwˈt͡ɬikʷeː] is an Aztec deity of water, rivers, seas, streams, storms, and baptism. Chalchiuhtlicue is associated with fertility, and she is the patroness of childbirth. Chalchiuhtlicue was highly revered in Aztec culture at the time of the Spanish conquest, and she was an important deity figure in the Postclassic Aztec realm of central Mexico. Chalchiuhtlicue belongs to a larger group of Aztec rain gods, and she is closely related to another Aztec water god called Chalchiuhtlatonal.

Cholula, officially Cholula de Rivadavia, is a city and district located in the metropolitan area of Puebla, Mexico. Cholula is best known for its Great Pyramid, with the Iglesia de Nuestra Señora de los Remedios sanctuary on top, as well as its numerous churches.
Tollan, Tolan, or Tolán is a name used for the capital cities of two empires of Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica; first for Teotihuacan, and later for the Toltec capital, Tula, both in Mexico. The name has also been applied to the Postclassic Mexican settlement Cholula.

The Great Pyramid of Cholula, also known as Tlachihualtepetl, is a complex located in Cholula, Puebla, Mexico. It is the largest archaeological site of a pyramid (temple) in the New World, as well as the largest pyramid by volume known to exist in the world today. The adobe brick pyramid stands 25 metres (82 ft) above the surrounding plain, which is significantly shorter than the Great Pyramid of Giza's height of 146.6 metres (481 ft), but much wider, measuring 300 by 315 metres in its final form, compared to the Great Pyramid's base dimensions of 230.3 by 230.3 metres. The pyramid is a temple that traditionally has been viewed as having been dedicated to the god Quetzalcoatl. The architectural style of the building was linked closely to that of Teotihuacan in the Valley of Mexico, although influence from the Gulf Coast is evident as well, especially from El Tajín.

Mesoamerican pyramids form a prominent part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture. Although similar in some ways to Egyptian pyramids, these New World structures have flat tops and stairs ascending their faces. The largest pyramid in the world by volume is the Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the east-central Mexican state of Puebla. The builders of certain classic Mesoamerican pyramids have decorated them copiously with stories about the Hero Twins, the feathered serpent Quetzalcoatl, Mesoamerican creation myths, ritualistic sacrifice, etc. written in the form of hieroglyphs on the rises of the steps of the pyramids, on the walls, and on the sculptures contained within.

A teocalli is a Mesoamerican pyramid surmounted by a temple. The pyramid is terraced, and some of the most important religious rituals in Pre-Columbian Mexico took place in the temple at the top of the pyramid.

In the Book of Ether in the Book of Mormon, Jared was the primary ancestor of the Jaredites. He is not to be confused with another Jared, a later Jaredite king who dethroned his father, Omer.

The Aztec religion is a polytheistic and monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of teotl was construed as the supreme god Ometeotl, as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies.
Xelhua is one of the seven giants in Aztec mythology who escaped the flood by ascending the mountain of Tlaloc in the terrestrial paradise and afterwards built the Great Pyramid of Cholula. One of the six giants sons of Mixcoatl, the personification of the Milky Way. A Dominican friar wrote this account:
Before the great inundation which took place 4,800 years after the erection of the world, the country of Anahuac was inhabited by giants, all of whom either perished in the inundation or were transformed into fishes, save seven who fled into caverns. When the waters subsided, one of the giants, called Xelhua, surnamed the 'Architect,' went to Cholula, where, as a memorial of the Tlaloc which had served for an asylum to himself and his six brethren, he built an artificial hill in the form of a pyramid. He ordered bricks to be made in the province of Tlalmanalco, at the foot of the Sierra of Cecotl, and in order to convey them to Cholula he placed a file of men who passed them from hand to hand. The gods beheld, with wrath, an edifice the top of which was to reach the clouds. Irritated at the daring attempt of Xelhua, they hurled fire on the pyramid. Numbers of the workmen perished. The work was discontinued, and the monument was afterwards dedicated to Quetzalcoatl.
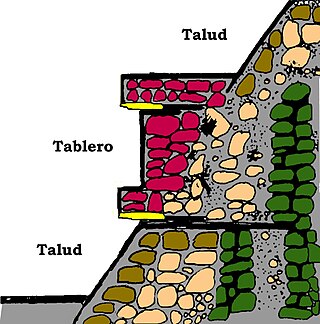
Talud-tablero is an architectural style most commonly used in platforms, temples, and pyramids in Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, becoming popular in the Early Classic Period of Teotihuacan. Talud-tablero consists of an inward-sloping surface or panel called the talud, with a panel or structure perpendicular to the ground sitting upon the slope called the tablero. This may also be referred to as the slope-and-panel style.

Cholula was an important city of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, dating back to at least the 2nd century BCE, with settlement as a village going back at least some thousand years earlier. The site of Cholula is just west of the modern city of Puebla and served as a trading outpost. Its immense pyramid is the largest such structure in the Americas, and the largest pyramid structure by volume in the world.

Quetzalcoatl is a deity in Aztec culture and literature. Among the Aztecs, it was related to wind, Venus, Sun, merchants, arts, crafts, knowledge, and learning. It was also the patron god of the Aztec priesthood. It was one of several important gods in the Aztec pantheon, along with the gods Tlaloc, Tezcatlipoca and Huitzilopochtli. Two other gods represented by the planet Venus are Tlaloc and Xolotl.
San Andrés Cholula is the municipal seat of San Andrés Cholula Municipality located in the Metropolitan area of Puebla, in the center west of the state of Puebla in the central highlands of Mexico, 122 km east of Mexico City and eight kilometres west of the city of Puebla. It is one of the two municipalities, along with San Pedro Cholula, that make up the modern city of Cholula or Cholula de Rivadavia. The city of Cholula has been divided into two parts since the pre Hispanic period, when the Toltecs-Chichimecas revolted, took over and pushed the formerly dominant Olmec –Xicallancas to the eastern side of the city. This side of the city is defined as the Great Pyramid of Cholula and east. The city has remained more or less divided since under different political organizations. However, the two halves share a common religious and social tradition which binds the city as a whole. San Andrés is known for being historically indigenous and still contains a larger indigenous population. It is also home to a number of colonial era churches decorated in Talavera tile and in a style called Indigenous or Folk Baroque. The best known example of this is the church in the Santa María Tonatzintla community.

The Iglesia de Nuestra Señora de los Remedios is a 16th-century Mexican Catholic parish church built atop the Tlachihualtepetl pyramid in the municipality of Cholula located in the central Mexican state of Puebla. The church was built with carved stone and embellished with 24-carat gilded panels and shims, called laminilla. It has an altar in the neoclassical style. It was built between May 1574 and August 1575 and consecrated on March 25, 1629. The base on which the church is built is one of the largest pyramids of the ancient world, being 54 metres (177 ft) high, covering 54 acres and shaped by several superimposed structures over the course of six centuries.
San Andrés Cholula Municipality is a municipality in Puebla in south-eastern Mexico. It forms part of the Metropolitan area of Puebla, and as of 2011, it is the fastest-growing municipality that conforms the Metropolitan Area, partly because the presence of universities and the wealthiest neighborhoods are located on San Andres Cholula. Along with San Pedro Cholula and Santa Isabel Cholula, it conforms the most ancient still inhabited city in the Americas, Cholula de Rivadabia.

San Pedro Cholula is a municipality in the Mexican state of Puebla and one of two municipalities which made up the city of Cholula. The city has been divided into two sections since the pre Hispanic era, when revolting Toltec-Chichimecas pushed the formerly dominant Olmec-Xicallanca to the eastern side of the city in the 13th century. The new lords called themselves Cholutecas and built a new temple to Quetzalcoatl on the San Pedro side, which eventually eclipsed the formerly prominent Great Pyramid of Cholula, now on the San Andrés side. When the Spanish arrived in the 16th century, the city of Cholula was an important religious and economic center, but the center of power was on the San Pedro side, centered on what is now the main city plaza and the San Gabriel monastery. The division of the city persisted and San Pedro remained the more dominant, with Spanish families moving onto that side and the rest of the population quickly becoming mestizo. Today, San Pedro is still more commercial and less residential than neighboring San Andrés with most of its population employed in industry, commerce and services rather than agriculture. Although Cholula's main tourist attraction, the Pyramid, is in San Andrés, San Pedro has more tourism infrastructure such as hotels, restaurants and bars.

In Aztec mythology, Creator-gods are the only four Tezcatlipocas, the children of the creator couple Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl "Lord and Lady of Duality", "Lord and Lady of the Near and the Close", "Father and Mother of the Gods", "Father and Mother of us all", who received the gift of the ability to create other living beings without childbearing. They reside atop a mythical thirteenth heaven Ilhuicatl-Omeyocan "the place of duality".














