Related Research Articles
Gentoo Linux is a Linux distribution built using the Portage package management system. Unlike a binary software distribution, the source code is compiled locally according to the user's preferences and is often optimized for the specific type of computer. Precompiled binaries are available for some larger packages or those with no available source code.

Advanced package tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian, and Debian-based Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code.
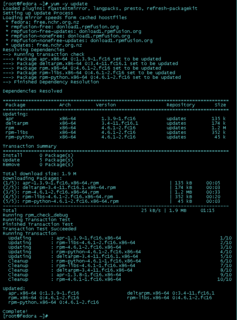
The Yellowdog Updater, Modified (YUM) is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for computers running the Linux operating system using the RPM Package Manager. Though YUM has a command-line interface, several other tools provide graphical user interfaces to YUM functionality.
up2date, also known as the Red Hat Update Agent, is a tool used by older versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS and Fedora Core that downloads and installs new software and upgrades the operating system. It functions as a front-end to the RPM Package Manager and adds advanced features such as automatic dependency resolution. The file /etc/sysconfig/rhn/sources specifies where up2date will search for packages.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. Fedora Linux serves as its upstream source. All of Red Hat's official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform.

CentOS is a Linux distribution that provides a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board.
phpLDAPadmin is a web app for administering Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers. It's written in the PHP programming language, and is licensed under the GNU General Public License. The application is available in 14 languages and supports UTF-8 encoded directory strings.
Free Java implementations are software projects that implement Oracle's Java technologies and are distributed under free software licences, making them free software. Sun released most of its Java source code as free software in May 2007, so it can now almost be considered a free Java implementation. Java implementations include compilers, runtimes, class libraries, etc. Advocates of free and open source software refer to free or open source Java virtual machine software as free runtimes or free Java runtimes.
BioLinux is a term used in a variety of projects involved in making access to bioinformatics software on a Linux platform easier using one or more of the following methods:

Compiz is a compositing window manager for the X Window System, using 3D graphics hardware to create fast compositing desktop effects for window management. Effects, such as a minimization animation or a cube workspace, are implemented as loadable plugins. Because it conforms to the ICCCM conventions, Compiz can be used as a substitute for the default Mutter or Metacity, when using GNOME Panel, or KWin in KDE Plasma Workspaces. Internally Compiz uses the OpenGL library as the interface to the graphics hardware.

PulseAudio is a network-capable sound server program distributed via the freedesktop.org project. It runs mainly on Linux, various BSD distributions such as FreeBSD and OpenBSD, macOS, as well as Illumos distributions and the Solaris operating system.
A software repository, or repo for short, is a storage location for software packages. Often a table of contents is also stored, along with metadata. A software repository is typically managed by source control or repository managers. Package managers allow automatically installing and updating repositories.

Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project which is sponsored primarily by Red Hat with additional support and sponsors from other companies and organizations. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. Fedora is the upstream source for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
IcedTea is a build and integration project for OpenJDK launched by Red Hat in June 2007. IcedTea also includes some addon libraries: IcedTea-Web is a free software implementation of Java Web Start and the Java web browser applet plugin. IcedTea-Sound is a collection of plugins for the Java sound subsystem, including the PulseAudio provider which used to be included with IcedTea. The Free Software Foundation recommends that all Java programmers use IcedTea as their development environment.

RPM Package Manager (RPM) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the .rpm file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.

Russian Fedora Remix was a remix of the Fedora Linux Linux distribution adapted for Russia that was active in 2008–2019. It was neither a copy of the original Fedora nor a new Linux distribution. The project aimed to ensure that Fedora fully satisfied the needs of Russian users with many additional features provided out of the box. In autumn 2019 the project was phased out because its leaders announced that it "had fulfilled its purpose by 100%" and all of the Russian-centric improvements were officially included in Fedora repositories, and Russian Fedora software maintainers became regular Fedora maintainers.

Linux-libre is a modified version of the Linux kernel that contains no binary blobs, obfuscated code, or code released under proprietary licenses. In the Linux kernel, they are mostly used for proprietary firmware images. While generally redistributable, binary blobs do not give the user the freedom to audit, modify, or, consequently, redistribute their modified versions. The GNU Project keeps Linux-libre in synchronization with the mainline Linux kernel.
Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. Fedora attempts to maintain a six-month release schedule, offering new versions in May and November.

DNF or Dandified YUM is the next-generation version of the Yellowdog Updater, Modified (yum), a package manager for .rpm-based distributions. DNF was introduced in Fedora 18 in 2013, it has been the default package manager since Fedora 22 in 2015, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8., and OpenMandriva; and also an alternate package manager for Mageia.

Flatpak, formerly known as xdg-app, is a utility for software deployment and package management for Linux. It is advertised as offering a sandbox environment in which users can run application software in isolation from the rest of the system.
References
- ↑ Christopher Negus and Christine Bresnahan (2012). Linux Bible. John Wiley & Sons. p. 239. ISBN 978-1118218549.
- ↑ Andy McKay (2009). The Definitive Guide to Plone. Apress. p. 21. ISBN 978-1430218937.
- ↑ "RPM Fusion". Linux Weekly News. 2007-09-12.
- ↑ "rpm.livna.org repositories for Fedora 8 (Werewolf) now available".
- ↑ "rpm.livna.org repositories for Fedora 9 (Sulphur) now available".
- ↑ "rpm.livna.org". Archived from the original on 2008-09-08.
- ↑ "Please Read". 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-12-01.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Dribble FAQ". Archived from the original on 2008-09-16.
- ↑ "Freshrpms history".