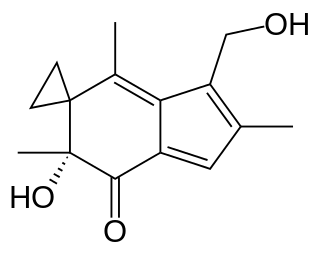
Irofulven or 6-hydroxymethylacylfulvene is an experimental antitumor agent. It belongs to the family of drugs called alkylating agents.
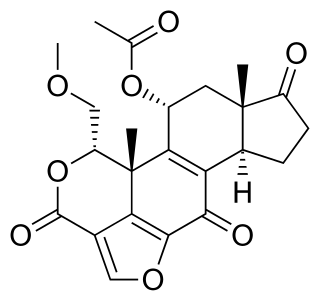
Wortmannin, a steroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii, is a non-specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration (IC50) of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly used PI3K inhibitor. It displays a similar potency in vitro for the class I, II, and III PI3K members although it can also inhibit other PI3K-related enzymes such as mTOR, DNA-PKcs, some phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) at high concentrations Wortmannin has also been reported to inhibit members of the polo-like kinase family with IC50 in the same range as for PI3K. The half-life of wortmannin in tissue culture is about 10 minutes due to the presence of the highly reactive C20 carbon that is also responsible for its ability to covalently inactivate PI3K. Wortmannin is a commonly used cell biology reagent that has been used previously in research to inhibit DNA repair, receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell proliferation.
Abagovomab is a mouse anti-idiotype monoclonal antibody whose variable epitope mirrors a tumour antigen (CA-125) highly expressed in the epithelial ovarian cancer. Abagovomab does not bind directly to CA-125, but it works as a "surrogate" antigen, enabling the immune system to identify and attack tumour cells displaying the CA-125 protein. Through this, it is hoped that the body's immune system may be able to combat any remaining individual tumour cells and thus prevent recurrence of the disease.

Cediranib is a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor tyrosine kinases.

PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP).

Iniparib was a drug candidate for cancer treatment. It was originally believed to act as an irreversible inhibitor of PARP1 and possibly other enzymes through covalent modification, but its effects against PARP were later disproven. It underwent clinical trials for treatment of some types of breast cancer, but was discontinued after disappointing phase III clinical trials.

Veliparib (ABT-888) is a potential anti-cancer drug acting as a PARP inhibitor. It kills cancer cells by blocking a protein called PARP, thereby preventing the repair of DNA or genetic damage in cancer cells and possibly making them more susceptible to anticancer treatments. Veliparib may make whole brain radiation treatment work more effectively against brain metastases from NSCLC. It has been shown to potentiate the effects of many chemotherapeutics, and as such has been part of many combination clinical trials.

Losmapimod (GW856553X) is an investigational drug being developed by Fulcrum Therapeutics for the treatment of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD); a phase III clinical trial is pending approval. Losmapimod selectively inhibits enzymes p38α/β mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are modulators of DUX4 expression and mediators of inflammation.
Treatment of lung cancer refers to the use of medical therapies, such as surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, percutaneous ablation, and palliative care, alone or in combination, in an attempt to cure or lessen the adverse impact of malignant neoplasms originating in lung tissue.
Pelareorep is a proprietary isolate of the unmodified human reovirus being developed as a systemically administered immuno-oncological viral agent for the treatment of solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Pelareorep is an oncolytic virus, which means that it preferentially lyses cancer cells. Pelareorep also promotes an inflamed tumor phenotype through innate and adaptive immune responses. Preliminary clinical trials indicate that it may have anti-cancer effects across a variety of cancer types when administered alone and in combination with other cancer therapies.

Motesanib is an experimental drug candidate originally developed by Amgen but later investigated by the Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. It is an orally administered small molecule belonging to angiokinase inhibitor class which acts as an antagonist of VEGF receptors, platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and stem cell factor receptors. It is used as the phosphate salt motesanib diphosphate. After clinical trials in thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, gastrointestinal stromal cancer, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer, the drug was not found to show sufficient efficacy for further development, and development was abandoned by Takeda.
Angiokinase inhibitors are a new therapeutic target for the management of cancer. They inhibit tumour angiogenesis, one of the key processes leading to invasion and metastasis of solid tumours, by targeting receptor tyrosine kinases. Examples include nintedanib, afatinib and motesanib.
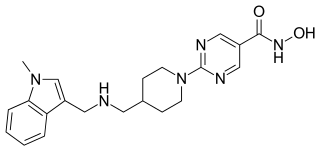
Quisinostat is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is a "second generation" histone deacetylase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. It is highly potent against class I and II HDACs.

Sonidegib (INN), sold under the brand name Odomzo, is a medication used to treat cancer.

Binimetinib, sold under the brand name Mektovi, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat various cancers. Binimetinib is a selective inhibitor of MEK, a central kinase in the tumor-promoting MAPK pathway. Inappropriate activation of the pathway has been shown to occur in many cancers. In June 2018 it was approved by the FDA in combination with encorafenib for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive melanoma. In October 2023, it was approved by the FDA for treatment of NSCLC with a BRAF V600E mutation in combination with encorafenib. It was developed by Array Biopharma.
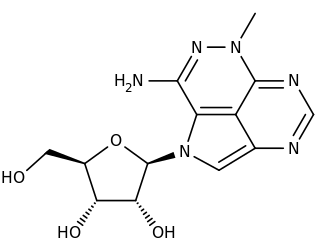
Triciribine is a cancer drug which was first synthesized in the 1970s and studied clinically in the 1980s and 1990s without success. Following the discovery in the early 2000s that the drug would be effective against tumours with hyperactivated Akt, it is now again under consideration in a variety of cancers. As PTX-200, the drug is currently in two early stage clinical trials in breast cancer and ovarian cancer being conducted by the small molecule drug development company Prescient Therapeutics.
Dostarlimab, sold under the brand name Jemperli, is a monoclonal antibody used as an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of endometrial cancer. Dostarlimab is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)–blocking monoclonal antibody.
Elizabeth Ruth Plummer is a Professor of Experimental Cancer Medicine at Newcastle University and an oncologist specialising in treating patients with melanoma. Based in Newcastle, she directs the Sir Bobby Robson Cancer Trials Research Centre, set up by the Sir Bobby Robson Foundation to run early-stage clinical trials.v Plummer and the Newcastle team won a 2010 Translational Cancer Research Prize from Cancer Research UK for work using rucaparib to treat ovarian cancer. Plummer was elected as a fellow of the UK's Academy of Medical Sciences in 2018.

Adavosertib is an experimental anti-cancer drug candidate. It is a small molecule inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase WEE1 with potential antineoplastic sensitizing activity. It is being developed by AstraZeneca. It is being investigated as a treatment for pancreatic cancer with a phase 1 trial, and ovarian cancer, in combination with another anti-cancer drug, gemcitabine, as a phase 2 trial.

Berzosertib is a drug originally invented by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and licensed to Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany for development. It acts as a potent inhibitor of the enzyme ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (ATR) and with lower potency as an inhibitor of ATM serine/threonine kinase (ATM). These enzymes are both involved in detecting DNA damage as part of cell cycle checkpoints during cell division. By inhibiting their activity, berzosertib interferes with the ability of rapidly dividing cells to detect damage to DNA, and this makes it useful as a potential treatment for some forms of cancer by causing accumulation of DNA damage in the cancer cells and thus reducing their viability. It has progressed furthest in trials for the treatment of ovarian cancer, though also shows activity against numerous other cancer types.















