
Cyc is a long-term artificial intelligence project that aims to assemble a comprehensive ontology and knowledge base that spans the basic concepts and rules about how the world works. Hoping to capture common sense knowledge, Cyc focuses on implicit knowledge that other AI platforms may take for granted. This is contrasted with facts one might find somewhere on the internet or retrieve via a search engine or Wikipedia. Cyc enables semantic reasoners to perform human-like reasoning and be less "brittle" when confronted with novel situations.
Knowledge representation and reasoning is the field of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex tasks such as diagnosing a medical condition or having a dialog in a natural language. Knowledge representation incorporates findings from psychology about how humans solve problems and represent knowledge in order to design formalisms that will make complex systems easier to design and build. Knowledge representation and reasoning also incorporates findings from logic to automate various kinds of reasoning, such as the application of rules or the relations of sets and subsets.
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard originally designed as a data model for metadata. It has come to be used as a general method for description and exchange of graph data. RDF provides a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats with Turtle currently being the most widely used notation.
CycL in computer science and artificial intelligence is an ontology language used by Doug Lenat's Cyc artificial intelligence project. Ramanathan V. Guha was instrumental in the design of early versions of the language. There is a close variant of CycL known as MELD.

RSS is a web feed that allows users and applications to access updates to websites in a standardized, computer-readable format. Subscribing to RSS feeds can allow a user to keep track of many different websites in a single news aggregator, which constantly monitor sites for new content, removing the need for the user to manually check them. News aggregators can be built into a browser, installed on a desktop computer, or installed on a mobile device.

Douglas Bruce Lenat is the CEO of Cycorp, Inc. of Austin, Texas, and has been a prominent researcher in artificial intelligence; he was awarded the biannual IJCAI Computers and Thought Award in 1976 for creating the machine learning program, AM. He has worked on machine learning, knowledge representation, "cognitive economy", blackboard systems, and what he dubbed in 1984 "ontological engineering". He has also worked in military simulations, and numerous projects for US government, military, intelligence, and scientific organizations. In 1980, he published a critique of conventional random-mutation Darwinism. He authored a series of articles in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence exploring the nature of heuristic rules.
Meta Content Framework (MCF) is a specification of a content format for structuring metadata about web sites and other data.
RDF Schema is a set of classes with certain properties using the RDF extensible knowledge representation data model, providing basic elements for the description of ontologies. It uses various forms of RDF vocabularies, intended to structure RDF resources. RDF and RDFS can be saved in a triplestore, then one can extract some knowledge from them using a query language, like SPARQL.
In computer science and artificial intelligence, ontology languages are formal languages used to construct ontologies. They allow the encoding of knowledge about specific domains and often include reasoning rules that support the processing of that knowledge. Ontology languages are usually declarative languages, are almost always generalizations of frame languages, and are commonly based on either first-order logic or on description logic.
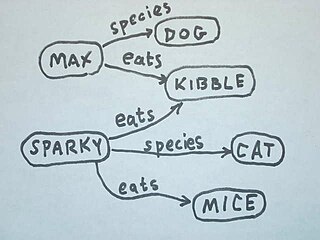
The ultimate goal of semantic technology is to help machines understand data. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, well-known technologies are RDF and OWL. These technologies formally represent the meaning involved in information. For example, ontology can describe concepts, relationships between things, and categories of things. These embedded semantics with the data offer significant advantages such as reasoning over data and dealing with heterogeneous data sources.
Haystack is a project at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to research and develop several applications around personal information management and the Semantic Web. The most notable of those applications is the Haystack client, a research personal information manager (PIM) and one of the first to be based on semantic desktop technologies. The Haystack client is published as open source software under the BSD license.
The RSS-DEV Working Group was the outgrowth of a fork in RSS format development. The private, non-commercial working group began with a dozen members in three countries, and was chaired by Rael Dornfest, researcher and developer of the Meerkat RSS-reader software.
Web syndication technologies were preceded by metadata standards such as the Meta Content Framework (MCF) and the Resource Description Framework (RDF), as well as by 'push' specifications such as Channel Definition Format (CDF). Early web syndication standards included Information and Content Exchange (ICE) and RSS. More recent specifications include Atom and GData.
Ora Lassila is a Finnish computer scientist who lives in the U.S. and works as a technologist at Amazon Web Services. He has been conducting research into the Semantic Web since 1996, and was co-author, with Tim Berners-Lee and James Hendler, of the article "The Semantic Web" which appeared in Scientific American in 2001, now the most cited paper in the Semantic Web area. His early work in this area included proposing the original RDF Specification with Ralph R. Swick and he has been an elected member of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Advisory Board since 1998. He also belongs to the steering committee of the Semantic Web Science Association.
Amit Sheth is a computer scientist at University of South Carolina in Columbia, South Carolina. He is the founding Director of the Artificial Intelligence Institute, and a Professor of Computer Science and Engineering. From 2007 to June 2019, he was the Lexis Nexis Ohio Eminent Scholar, director of the Ohio Center of Excellence in Knowledge-enabled Computing, and a Professor of Computer Science at Wright State University. Sheth's work has been cited by over 48,800 publications. He has an h-index of 106, which puts him among the top 100 computer scientists with the highest h-index. Prior to founding the Kno.e.sis Center, he served as the director of the Large Scale Distributed Information Systems Lab at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia.
Freebase was a large collaborative knowledge base consisting of data composed mainly by its community members. It was an online collection of structured data harvested from many sources, including individual, user-submitted wiki contributions. Freebase aimed to create a global resource that allowed people to access common information more effectively. It was developed by the American software company Metaweb and run publicly beginning in March 2007. Metaweb was acquired by Google in a private sale announced on 16 July 2010. Google's Knowledge Graph is powered in part by Freebase.
Knowledge extraction is the creation of knowledge from structured and unstructured sources. The resulting knowledge needs to be in a machine-readable and machine-interpretable format and must represent knowledge in a manner that facilitates inferencing. Although it is methodically similar to information extraction (NLP) and ETL, the main criterion is that the extraction result goes beyond the creation of structured information or the transformation into a relational schema. It requires either the reuse of existing formal knowledge or the generation of a schema based on the source data.
In the Semantic Web and in knowledge representation, a metaclass is a class whose instances are themselves classes. Similar to their role in programming languages, metaclasses in Semantic Web languages can have properties otherwise applicable only to individuals, while retaining the same class's ability to be classified in a concept hierarchy. This enables knowledge about instances of those metaclasses to be inferred by semantic reasoners using statements made in the metaclass. Metaclasses thus enhance the expressivity of knowledge representations in a way that can be intuitive for users. While classes are suitable to represent a population of individuals, metaclasses can, as one of their feature, be used to represent the conceptual dimension of an ontology. Metaclasses are supported in the ontology language OWL and the data-modeling vocabulary RDFS.
Datacommons.org is an open knowledge repository hosted by Google that provides a unified view across multiple public datasets, combining economic, scientific and other open datasets into an integrated data graph. The Datacommons.org site was launched in May 2018 with an initial dataset consisting of fact-checking data published in Schema.org "ClaimReview" format by several fact checkers from the International Fact-Checking Network. Google has worked with partners including the United States Census, the World Bank, and US Bureau of Labor Statistics to populate the repository, which also hosts data from Wikipedia, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and the Federal Bureau of Investigation. The service expanded during 2019 to include an RDF-style Knowledge Graph populated from a number of largely statistical open datasets. The service was announced to a wider audience in 2019. In 2020 the service improved its coverage of non-US datasets, while also increasing its coverage of bioinformatics and coronavirus.



