
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It is the 15th largest state by area, and the 14th largest by population. Hindi is the official language of the state. The city of Ranchi is its capital and Dumka its sub-capital. The state is known for its waterfalls, hills and holy places; Baidyanath Dham, Parasnath, Dewri and Rajrappa are major religious sites.

Ranchi is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area of what is present-day Chhattisgarh. The Jharkhand state was formed on 15 November 2000 by carving out the Bihar divisions of Chota Nagpur and Santhal Parganas. Ranchi has been selected as one of the hundred Indian cities to be developed as a smart city under PM Narendra Modi's flagship Smart Cities Mission.

The University of Calcutta is a public state university located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It has 151 affiliated undergraduate colleges and 16 institutes in Kolkata and nearby areas. It was established on 24 January 1857 and is the oldest multidisciplinary university of Indian Subcontinent and South East Asian Region. Today, the university's jurisdiction is limited to a few districts of West Bengal, but at the time of its establishment it had a catchment area ranging from Kabul to Myanmar. Within India, it is recognized as a "Five-Star University" and accredited an "A++" grade by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC).

Deoghar is a major city in Jharkhand, India. It is a holy sacred place of Hinduism. The city is primarily known for Baidyanath Temple, one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of God Shiva. The sacred temples of the city make this a place for pilgrimage and tourists. The city is administrative headquarter of Deoghar District which comes under Santhal Parganas division of Jharkhand.

Bokaro, officially known as Bokaro Steel City, is a large and planned city in Jharkhand, India. It is the fourth most populous city in the state and one of the first planned cities of India. Bokaro is the administrative headquarters of Bokaro district. The city is located on the banks of Garga River and on the fringes of Bokaro river and is surrounded by hill ranges at Giridih and Ramgarh districts. It is one of the most peaceful cities in India. As per 2011 census, the city's population was 563,417 and 1,100,000 of its metropolitan area. The city span across 183 km in geographic area.

The Subarnarekha River flows through the Indian states of Jharkhand, West Bengal and Odisha.

Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra is a government funded technical institute (GFTI) situated at Ranchi, Jharkhand, India. It was established in 1955 at Mesra, Ranchi, by the industrialist B. M. Birla. The institute was later headed by G. P. Birla, and the present chairman of the board of governors is C. K. Birla. It was declared as a deemed university under Section 3 of the UGC Act.
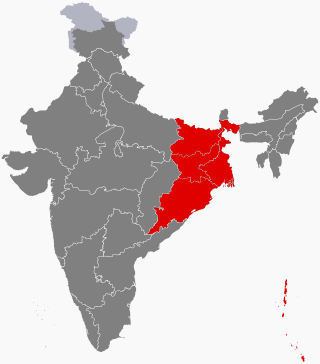
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha from which it inherits its various Eastern Indo-Aryan languages.
Patratu is a census town in the Patratu in the Ramgarh subdivision of the Ramgarh district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.

Jaipal Singh Munda was an Indian politician, writer, and sportsman. He was the member of the Constituent Assembly which debated on the new Constitution of the Indian Union. He captained the Indian field hockey team to clinch gold in the 1928 Summer Olympics in Amsterdam.

Ramgarh district is one of the 24 districts in the Indian state of Jharkhand. It was also a military district during the British Regime, referred to then as Ramgarh district.

Ram Dayal Munda, known as R. D. Munda, was an Indian scholar and regional music exponent. He was awarded the Padma Shri of the year 2010 for his contribution to the field of art.

Science City, Kolkata is a science centre and science park in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It is the largest science centre in Asia containing a science museum, science park and auditoriums. It is managed by National Council of Science Museums (NCSM), Ministry of Culture, Government of India. It is located at the crossing of Eastern Metropolitan Bypass and J. B. S. Haldane Avenue in East Topsia. Saroj Ghose, the first director general of NCSM, is credited with having conceptualised this centre in 1997.

Central institute of Psychiatry Ranchi is an institute that is directly governed by the Government of India. It is situated in Kanke, Ranchi in Jharkhand state of India.

Kolkata Town Hall in Roman Doric style, was built in 1813 by the architect and engineer Major General John Henry Garstin (1756–1820) with a fund of 700,000 Rupees raised from a lottery to provide the Europeans with a place for social gatherings.
Birsa Munda Athletics Stadium is a stadium in Ranchi, Jharkhand, India. It is used mostly for football matches and athletics. The stadium has hosted the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2011 National Games of India. It has seating capacity of 35,000 spectators.

Ranchi Junction railway station, station code RNC, is the A category railway station serving the capital city of Ranchi in the Ranchi district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi station is also the headquarters of the Ranchi division of the South Eastern Railway zone of the Indian Railways. The Ranchi Junction railway station is connected to most of the major cities in India by the railway network.
Hatia railway station, station code HTE, is the railway station serving the capital city of Ranchi in the Ranchi district in the Indian state of Jharkhand. Hatia Station belongs to the Ranchi division of the South Eastern Railway Zone of the Indian Railways. Hatia railway station is connected to most of the major cities in India by the railway network. It is situated on Ranchi–Rourkela railway section.
Eylex Films Pvt is a chain of multiplex and single screen theatres. Eylex films pioneered the multiplex model in Jharkhand and Bihar. Its first multiplex was established in Ranchi in 2007 – the first Multiplex in the city of Ranchi and States like Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha and Assam.
















