
A hormone is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone, numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids, steroids, amino acid derivatives, protein or peptides, and gases.

A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.

Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic.

Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the antigen presented on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are missing "self" markers of MHC class I. This role is especially important because harmful cells that are missing MHC I markers cannot be detected and destroyed by other immune cells, such as T lymphocyte cells.

Glucocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure.

In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses such as change in the electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway.

A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. In pharmacology, antagonists have affinity but no efficacy for their cognate receptors, and binding will disrupt the interaction and inhibit the function of an agonist or inverse agonist at receptors. Antagonists mediate their effects by binding to the active site or to the allosteric site on a receptor, or they may interact at unique binding sites not normally involved in the biological regulation of the receptor's activity. Antagonist activity may be reversible or irreversible depending on the longevity of the antagonist–receptor complex, which, in turn, depends on the nature of antagonist–receptor binding. The majority of drug antagonists achieve their potency by competing with endogenous ligands or substrates at structurally defined binding sites on receptors.
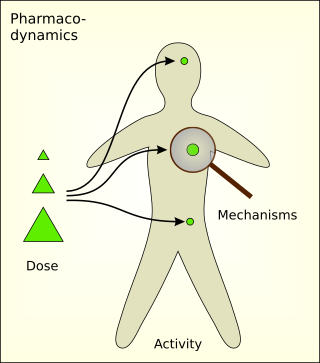
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs. The effects can include those manifested within animals, microorganisms, or combinations of organisms.

The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene.

Betaxolol is a selective beta1 receptor blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and angina. Being selective for beta1 receptors, it typically has fewer systemic side effects than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing bronchospasm as timolol may. Betaxolol also shows greater affinity for beta1 receptors than metoprolol. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye. This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to glaucoma.

Aminophylline is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate.
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host cell.
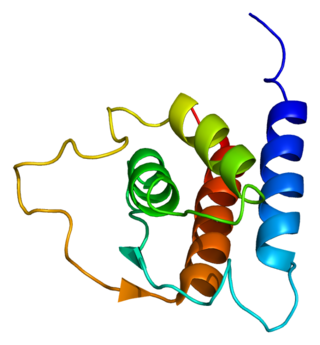
Interleukin 13 (IL-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL13 gene. IL-13 was first cloned in 1993 and is located on chromosome 5q31.1 with a length of 1.4kb. It has a mass of 13 kDa and folds into 4 alpha helical bundles. The secondary structural features of IL-13 are similar to that of Interleukin 4 (IL-4); however it only has 25% sequence identity to IL-4 and is capable of IL-4 independent signaling. IL-13 is a cytokine secreted by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells, CD4 cells, natural killer T cell, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and nuocytes. Interleukin-13 is a central regulator in IgE synthesis, goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and chitinase up-regulation. It is a mediator of allergic inflammation and different diseases including asthma.

Tetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound used as a rodenticide. It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. It is a sulfamide derivative. It can be synthesized by reacting sulfamide with formaldehyde solution in acidified water. When crystallized from acetone, it forms cubic crystals with a melting point of 255–260 °C.
Cutamesine (SA 4503) is a synthetic sigma receptor agonist which is selective for the σ1 receptor, a chaperone protein mainly found in the endoplasmic reticulum of cells in the central nervous system. These σ1 receptors play a key role in the modulation of Ca2+ release and apoptosis. Cutamesine's activation of the σ1 receptor is tied to a variety of physiological phenomena in the CNS, including activation of dopamine-releasing neurons and repression of the MAPK/ERK pathway.
Receptor theory is the application of receptor models to explain drug behavior. Pharmacological receptor models preceded accurate knowledge of receptors by many years. John Newport Langley and Paul Ehrlich introduced the concept that receptors can mediate drug action at the beginning of the 20th century. Alfred Joseph Clark was the first to quantify drug-induced biological responses. So far, nearly all of the quantitative theoretical modelling of receptor function has centred on ligand-gated ion channels and G protein-coupled receptors.
For related uses, see Rollback (disambiguation)
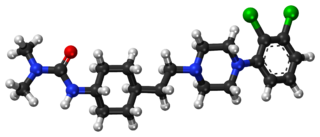
Cariprazine, sold under the brand names Vraylar and Reagila among others, is an atypical antipsychotic originated by Gedeon Richter, which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, bipolar depression, and major depressive disorder. It acts primarily as a D3 and D2 receptor partial agonist, with a preference for the D3 receptor. Cariprazine is also a partial agonist at the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor and acts as an antagonist at 5-HT2B and 5-HT2A receptors, with high selectivity for the D3 receptor. It is taken by mouth.
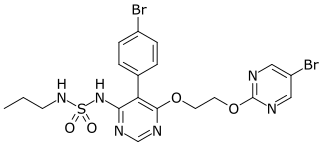
Macitentan, sold under the brand name Opsumit, is an endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) developed by Actelion and approved for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The other two ERAs marketed as of 2014 are bosentan and ambrisentan. Macitentan is a dual ERA, meaning that it acts as an antagonist of two endothelin (ET) receptor subtypes, ETA and ETB. However, macitentan has a 50-fold increased selectivity for the ETA subtype compared to the ETB subtype. The drug received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on October 13, 2013.

A Biomolecular Gradient is established by a difference in the concentration of molecules in a biological system such as individual cells, groups of cells, or an entire organism. A biomolecular gradient can exist intracellularly or extracellularly. The purposes of such gradients in biological systems vary, but include chemotaxis and functions in development. These types of gradients play a role in many different types of signaling as well as recently being implicated in cancer metastasis.
















