
The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic, is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency is the supreme magistracy of the country, the position is the highest office in France. The powers, functions and duties of prior presidential offices, in addition to their relation with the prime minister and government of France, have over time differed with the various constitutional documents since the Second Republic.

A popular initiative is a form of direct democracy by which a petition meeting certain hurdles can force a legal procedure on a proposition. The hurdles the petition has to meet vary between countries, typically signatures by a certain number of registered voters.

The National Assembly was the authoritative legislative body of the Republic of China, from 1947 to 2005. Along with the Control Yuan and the Legislative Yuan, the National Assembly formed the tricameral parliament of the Republic of China.

The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fifth and current constitution of the Republic of China (ROC), ratified by the Kuomintang during the Constituent National Assembly session on 25 December 1946, in Nanjing, and adopted on 25 December 1947. The constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.

The Fifth Republic is France's current republican system of government. It was established on 4 October 1958 by Charles de Gaulle under the Constitution of the Fifth Republic.
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions, thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.

A constituent assembly is a body assembled for the purpose of drafting or revising a constitution. Members of a constituent assembly may be elected by popular vote, drawn by sortition, appointed, or some combination of these methods. Assemblies are typically considered distinct from a regular legislature, although members of the legislature may compose a significant number or all of its members. As the fundamental document constituting a state, a constitution cannot normally be modified or amended by the state's normal legislative procedures in some jurisdictions; instead a constitutional convention or a constituent assembly, the rules for which are normally laid down in the constitution, must be set up. A constituent assembly is usually set up for its specific purpose, which it carries out in a relatively short time, after which the assembly is dissolved. A constituent assembly is a form of representative democracy.

The current Constitution of France was adopted on 4 October 1958. It is typically called the Constitution of the Fifth Republic(French: la Constitution de la Cinquième République), and it replaced the Constitution of the Fourth Republic of 1946 with the exception of the preamble per a 1971 decision of the Constitutional Council. The current Constitution regards the separation of church and state, democracy, social welfare, and indivisibility as core principles of the French state.
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of more than one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but they can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises at times when action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote. In consensus democracy the supermajority rule is applied in most cases.
Constitutional reform in the Philippines, also known as charter change, refers to the political and legal processes needed to amend the current 1987 Constitution of the Philippines. Under the common interpretation of the Constitution, amendments can be proposed by one of three methods: a People's Initiative, a Constituent Assembly or a Constitutional Convention.

A referendum on the method of the election of the president was held in France on 28 October 1962. The question was whether to have the President of the French Republic elected by direct popular vote, rather than by an electoral college. It was approved by 62.3% of voters with a 77.0% turnout. The reform was controversial because it strengthened the executive at the expense of Parliament, and because of the disputed constitutionality of the procedure used.
The May 1958 crisis, also known as the Algiers putsch or the coup of 13 May, was a political crisis in France during the turmoil of the Algerian War of Independence (1954–1962) which led to the collapse of the Fourth Republic and its replacement by the Fifth Republic led by Charles de Gaulle who returned to power after a twelve-year absence. It started as a political uprising in Algiers on 13 May 1958 and then became a military coup d'état led by a coalition headed by Algiers deputy and reserve airborne officer Pierre Lagaillarde, French Generals Raoul Salan, Edmond Jouhaud, Jean Gracieux, and Jacques Massu, and by Admiral Philippe Auboyneau, commander of the Mediterranean fleet. The coup was supported by former Algerian Governor General Jacques Soustelle and his activist allies.

Article 49 of the French Constitution is an article of the French Constitution, the fundamental law of the Fifth French Republic. It sets out and structures the political responsibility of the government towards the parliament. It is part of Title V: "On relations between the parliament and the government", and with the intention of maintaining the stability of the French executive the section provides legislative alternatives to the parliament. It was written into the constitution to counter the perceived weakness of the Fourth Republic, such as "deadlock" and successive rapid government takeovers, by giving the government the ability to pass bills without the approbation of the parliament, possible under Section 3 of Article 49.
The Constitution of the Philippines is the constitution or the supreme law of the Republic of the Philippines. Its final draft was completed by the Constitutional Commission on October 12, 1986, and ratified by a nationwide plebiscite on February 2, 1987.
The Constitutional law on the Modernisation of the Institutions of the Fifth Republic was enacted into French constitutional law by the Parliament of France in July 2008, to reform state institutions.

The Constitution of Turkey, formally known as the Constitution of the Republic of Türkiye, also known as the Constitution of 1982, is Turkey's fundamental law. It establishes the organization of the government, and sets out the principles and rules of the state's conduct along with its responsibilities in regards to its citizens. The constitution also establishes the rights and responsibilities of the latter while setting the guidelines for the delegation and exercise that sovereignty belongs entirely and without doubt to the people.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.

The French constitution of 4 October 1958 was revised many times in its early years. Changes to this fundamental law have become more frequent since the 1990s, for two major reasons:
- public projects for institutional modernization
- adaptation to European Union and other international law.
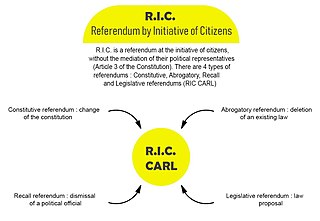
The Référendum d'initiative Citoyenne is the name given to the proposal for a constitutional amendment in France to permit consultation of the citizenry by referendum concerning the proposition or abrogation of laws, the revocation of politicians' mandates, and constitutional amendment.
Referendums in the Philippines are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. Referendums can either by national or local in scope. In the Philippines, "referendums" and "plebiscites" mean different things.












