In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place when some kind of radiant excitation intersects a localized phenomenon. For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted σ (sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process.
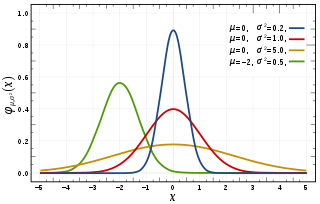
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is

In mathematical physics and mathematics, the Pauli matrices are a set of three 2 × 2 complex matrices which are Hermitian, involutory and unitary. Usually indicated by the Greek letter sigma, they are occasionally denoted by tau when used in connection with isospin symmetries.
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-1⁄2 massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way.

The Pareto distribution, named after the Italian civil engineer, economist, and sociologist Vilfredo Pareto, is a power-law probability distribution that is used in description of social, quality control, scientific, geophysical, actuarial, and many other types of observable phenomena; the principle originally applied to describing the distribution of wealth in a society, fitting the trend that a large portion of wealth is held by a small fraction of the population. The Pareto principle or "80-20 rule" stating that 80% of outcomes are due to 20% of causes was named in honour of Pareto, but the concepts are distinct, and only Pareto distributions with shape value of log45 ≈ 1.16 precisely reflect it. Empirical observation has shown that this 80-20 distribution fits a wide range of cases, including natural phenomena and human activities.

Noether's theorem or Noether's first theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system with conservative forces has a corresponding conservation law. The theorem was proven by mathematician Emmy Noether in 1915 and published in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function, from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action. This theorem only applies to continuous and smooth symmetries over physical space.
In probability theory, a compound Poisson distribution is the probability distribution of the sum of a number of independent identically-distributed random variables, where the number of terms to be added is itself a Poisson-distributed variable. The result can be either a continuous or a discrete distribution.
In probability theory and statistics, the generalized extreme value (GEV) distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions developed within extreme value theory to combine the Gumbel, Fréchet and Weibull families also known as type I, II and III extreme value distributions. By the extreme value theorem the GEV distribution is the only possible limit distribution of properly normalized maxima of a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables. Note that a limit distribution needs to exist, which requires regularity conditions on the tail of the distribution. Despite this, the GEV distribution is often used as an approximation to model the maxima of long (finite) sequences of random variables.
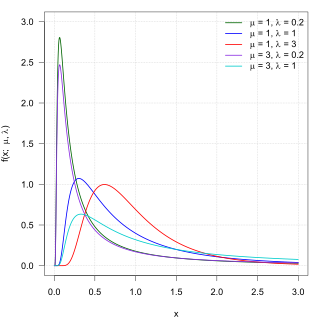
In probability theory, the inverse Gaussian distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support on (0,∞).

The Newman–Penrose (NP) formalism is a set of notation developed by Ezra T. Newman and Roger Penrose for general relativity (GR). Their notation is an effort to treat general relativity in terms of spinor notation, which introduces complex forms of the usual variables used in GR. The NP formalism is itself a special case of the tetrad formalism, where the tensors of the theory are projected onto a complete vector basis at each point in spacetime. Usually this vector basis is chosen to reflect some symmetry of the spacetime, leading to simplified expressions for physical observables. In the case of the NP formalism, the vector basis chosen is a null tetrad: a set of four null vectors—two real, and a complex-conjugate pair. The two real members often asymptotically point radially inward and radially outward, and the formalism is well adapted to treatment of the propagation of radiation in curved spacetime. The Weyl scalars, derived from the Weyl tensor, are often used. In particular, it can be shown that one of these scalars— in the appropriate frame—encodes the outgoing gravitational radiation of an asymptotically flat system.
Covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy (CMA-ES) is a particular kind of strategy for numerical optimization. Evolution strategies (ES) are stochastic, derivative-free methods for numerical optimization of non-linear or non-convex continuous optimization problems. They belong to the class of evolutionary algorithms and evolutionary computation. An evolutionary algorithm is broadly based on the principle of biological evolution, namely the repeated interplay of variation and selection: in each generation (iteration) new individuals are generated by variation, usually in a stochastic way, of the current parental individuals. Then, some individuals are selected to become the parents in the next generation based on their fitness or objective function value . Like this, over the generation sequence, individuals with better and better -values are generated.
Expected shortfall (ES) is a risk measure—a concept used in the field of financial risk measurement to evaluate the market risk or credit risk of a portfolio. The "expected shortfall at q% level" is the expected return on the portfolio in the worst of cases. ES is an alternative to value at risk that is more sensitive to the shape of the tail of the loss distribution.
A ratio distribution is a probability distribution constructed as the distribution of the ratio of random variables having two other known distributions. Given two random variables X and Y, the distribution of the random variable Z that is formed as the ratio Z = X/Y is a ratio distribution.
In probability theory and statistics, the normal-gamma distribution is a bivariate four-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a normal distribution with unknown mean and precision.
Tail value at risk (TVaR), also known as tail conditional expectation (TCE) or conditional tail expectation (CTE), is a risk measure associated with the more general value at risk. It quantifies the expected value of the loss given that an event outside a given probability level has occurred.

In probability theory and statistics, the normal-inverse-gamma distribution is a four-parameter family of multivariate continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a normal distribution with unknown mean and variance.
Financial models with long-tailed distributions and volatility clustering have been introduced to overcome problems with the realism of classical financial models. These classical models of financial time series typically assume homoskedasticity and normality cannot explain stylized phenomena such as skewness, heavy tails, and volatility clustering of the empirical asset returns in finance. In 1963, Benoit Mandelbrot first used the stable distribution to model the empirical distributions which have the skewness and heavy-tail property. Since -stable distributions have infinite -th moments for all , the tempered stable processes have been proposed for overcoming this limitation of the stable distribution.
Least-squares support-vector machines (LS-SVM) for statistics and in statistical modeling, are least-squares versions of support-vector machines (SVM), which are a set of related supervised learning methods that analyze data and recognize patterns, and which are used for classification and regression analysis. In this version one finds the solution by solving a set of linear equations instead of a convex quadratic programming (QP) problem for classical SVMs. Least-squares SVM classifiers were proposed by Johan Suykens and Joos Vandewalle. LS-SVMs are a class of kernel-based learning methods.
Lagrangian field theory is a formalism in classical field theory. It is the field-theoretic analogue of Lagrangian mechanics. Lagrangian mechanics is used to analyze the motion of a system of discrete particles each with a finite number of degrees of freedom. Lagrangian field theory applies to continua and fields, which have an infinite number of degrees of freedom.

In the theory of Lie groups, Lie algebras and their representation theory, a Lie algebra extensione is an enlargement of a given Lie algebra g by another Lie algebra h. Extensions arise in several ways. There is the trivial extension obtained by taking a direct sum of two Lie algebras. Other types are the split extension and the central extension. Extensions may arise naturally, for instance, when forming a Lie algebra from projective group representations. Such a Lie algebra will contain central charges.


























