
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhibit visual deterioration, such as the enzymatic browning reaction in apples after they are cut during food preparation. By preserving food, food waste can be reduced, which is an important way to decrease production costs and increase the efficiency of food systems, improve food security and nutrition and contribute towards environmental sustainability. For instance, it can reduce the environmental impact of food production.

Suet is the raw, hard fat of beef, lamb or mutton found around the loins and kidneys.

Animal fats and oils are lipids derived from animals: oils are liquid at room temperature, and fats are solid. Chemically, both fats and oils are composed of triglycerides. Although many animal parts and secretions may yield oil, in commercial practice, oil is extracted primarily from rendered tissue fats from livestock animals like pigs, chickens and cows. Dairy products yield animal fat and oil products such as butter.

Tallow is a rendered form of beef or mutton suet, primarily made up of triglycerides.

Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent fatty-acid in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C and a pKa of 4.50.
The Rath Packing Company was a meatpacking company located in Waterloo, Iowa, between 1891 and 1985.

Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing takes many forms, from grinding grain into raw flour, home cooking, and complex industrial methods used in the making of convenience foods. Some food processing methods play important roles in reducing food waste and improving food preservation, thus reducing the total environmental impact of agriculture and improving food security.
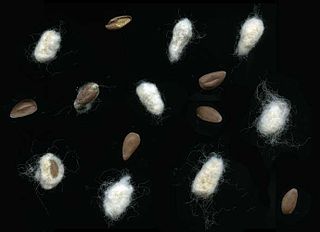
Cottonseed oil is cooking oil from the seeds of cotton plants of various species, mainly Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium herbaceum, that are grown for cotton fiber, animal feed, and oil.

Shortening is any fat that is a solid at room temperature and is used to make crumbly pastry and other food products.

Schmaltz is rendered (clarified) chicken or goose fat. It is an integral part of traditional Ashkenazi Jewish cuisine, where it has been used for centuries in a wide array of dishes, such as chicken soup, latkes, matzah brei, chopped liver, matzah balls, fried chicken, and many others, either as a cooking fat, spread, or flavor enhancer.
Enfleurage is a process that uses odorless fats that are solid at room temperature to capture the fragrant compounds, such as volatile oils, produced by plants. The process can be "cold" enfleurage or "hot" enfleurage.

The meat-packing industry handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of meat from animals such as cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. Poultry is generally not included. This greater part of the entire meat industry is primarily focused on producing meat for human consumption, but it also yields a variety of by-products including hides, dried blood, protein meals such as meat & bone meal, and, through the process of rendering, fats.

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.
Mount Sapo is a fictional mountain supposed to exist somewhere near Rome, presumably in Italy. It appears in a fanciful rewriting of the history of soap, and it is often claimed to explain the origins of the name. The tale occurs in a number of online sources, including the website of The Soap and Detergent Association.

An animal product is any material derived from the body of a non-human animal. Examples are fat, flesh, blood, milk, eggs, and lesser known products, such as isinglass and rennet.

Lard is a semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering the fatty tissue of a pig. It is distinguished from tallow, a similar product derived from fat of cattle or sheep.

Meat and bone meal (MBM) is a product of the rendering industry. It is typically about 48–52% protein, 33–35% ash, 8–12% fat, and 4–7% water. It is primarily used in the formulation of animal feed to improve the amino acid profile of the feed. Feeding of MBM to cattle is thought to have been responsible for the spread of BSE ; therefore, in most parts of the world, MBM is no longer allowed in feed for ruminant animals. However, it is still used to feed monogastric animals.

Pork rind is the culinary term for the skin of a pig. It can be used in many different ways.














