Related Research Articles

Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole.
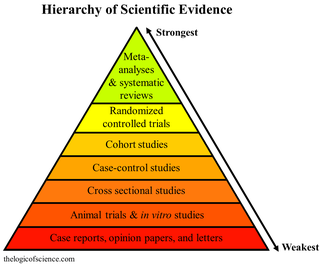
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. It is thus a basic methodology of metascience. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.

Multimethodology or multimethod research includes the use of more than one method of data collection or research in a research study or set of related studies. Mixed methods research is more specific in that it includes the mixing of qualitative and quantitative data, methods, methodologies, and/or paradigms in a research study or set of related studies. One could argue that mixed methods research is a special case of multimethod research. Another applicable, but less often used label, for multi or mixed research is methodological pluralism. All of these approaches to professional and academic research emphasize that monomethod research can be improved through the use of multiple data sources, methods, research methodologies, perspectives, standpoints, and paradigms.

Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context. Qualitative research is often used to explore complex phenomena or to gain insight into people's experiences and perspectives on a particular topic. It is particularly useful when researchers want to understand the meaning that people attach to their experiences or when they want to uncover the underlying reasons for people's behavior. Qualitative methods include ethnography, grounded theory, discourse analysis, and interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative research methods have been used in sociology, anthropology, political science, psychology, communication studies, social work, folklore, educational research, information science and software engineering research.
Educational research refers to the systematic collection and analysis of data related to the field of education. Research may involve a variety of methods and various aspects of education including student learning, interaction, teaching methods, teacher training, and classroom dynamics.

In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods. This way, it is assessed what advantages and disadvantages they have and for what research goals they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations depend on philosophical background assumptions. Examples are how to conceptualize the studied phenomena and what constitutes evidence for or against them. When understood in the widest sense, methodology also includes the discussion of these more abstract issues.

A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provide the researcher/author and the audiences with a general image of the existing knowledge on the topic under question. A good literature review can ensure that a proper research question has been asked and a proper theoretical framework and/or research methodology have been chosen. To be precise, a literature review serves to situate the current study within the body of the relevant literature and to provide context for the reader. In such case, the review usually precedes the methodology and results sections of the work.

A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic, then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.

Research design refers to the overall strategy utilized to carry out research that defines a succinct and logical plan to tackle established research question(s) through the collection, interpretation, analysis, and discussion of data.
In statistics, (between-) study heterogeneity is a phenomenon that commonly occurs when attempting to undertake a meta-analysis. In a simplistic scenario, studies whose results are to be combined in the meta-analysis would all be undertaken in the same way and to the same experimental protocols. Differences between outcomes would only be due to measurement error. Study heterogeneity denotes the variability in outcomes that goes beyond what would be expected due to measurement error alone.

A research question is "a question that a research project sets out to answer". Choosing a research question is an essential element of both quantitative and qualitative research. Investigation will require data collection and analysis, and the methodology for this will vary widely. Good research questions seek to improve knowledge on an important topic, and are usually narrow and specific.
The Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre) is part of the Faculty of Education and Society at University College London. Its work is concerned with systematic reviews which use transparent and explicit methodologies for reviewing research evidence in order to be clear about what we know from research and how we know it.
Critical appraisal in evidence based medicine, is the use of explicit, transparent methods to assess the data in published research, applying the rules of evidence to factors such as internal validity, adherence to reporting standards, conclusions, generalizability and risk-of-bias. Critical appraisal methods form a central part of the systematic review process. They are used in evidence synthesis to assist clinical decision-making, and are increasingly used in evidence-based social care and education provision.
Evidence-based library and information practice (EBLIP) or evidence-based librarianship (EBL) is the use of evidence-based practices (EBP) in the field of library and information science (LIS). This means that all practical decisions made within LIS should 1) be based on research studies and 2) that these research studies are selected and interpreted according to some specific norms characteristic for EBP. Typically such norms disregard theoretical studies and qualitative studies and consider quantitative studies according to a narrow set of criteria of what counts as evidence. If such a narrow set of methodological criteria are not applied, it is better instead to speak of research based library and information practice.

PRISMA is an evidence-based minimum set of items aimed at helping scientific authors to report a wide array of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, primarily used to assess the benefits and harms of a health care intervention. PRISMA focuses on ways in which authors can ensure a transparent and complete reporting of this type of research. The PRISMA standard superseded the earlier QUOROM standard. It offers the replicability of a systematic literature review. Researchers have to figure out research objectives that answer the research question, states the keywords, a set of exclusion and inclusion criteria. In the review stage, relevant articles were searched, irrelevant ones are removed. Articles are analyzed according to some pre-defined categories.
The discipline of evidence-based toxicology (EBT) strives to transparently, consistently, and objectively assess available scientific evidence in order to answer questions in toxicology, the study of the adverse effects of chemical, physical, or biological agents on living organisms and the environment, including the prevention and amelioration of such effects. EBT has the potential to address concerns in the toxicological community about the limitations of current approaches to assessing the state of the science. These include concerns related to transparency in decision making, synthesis of different types of evidence, and the assessment of bias and credibility. Evidence-based toxicology has its roots in the larger movement towards evidence-based practices.
The non-profit Evidence-based Toxicology Collaboration (EBTC) comprises a group of scientists and experts with ties to governmental and non-governmental agencies, chemical and pharmaceutical companies, and academia that have banded together to promote the use of what are known as "evidence-based approaches" in toxicology. The discipline of evidence-based toxicology (EBT) is a process for transparently, consistently, and objectively assessing available scientific evidence in order to answer questions in toxicology. EBT has the potential to address concerns in the toxicological community about the limitations of current approaches. These include concerns related to transparency in decision making, synthesis of different types of evidence, and the assessment of bias and credibility. The evidence-based methods and approaches now being proposed for toxicology are widely used in medicine, which is the basis for their nomenclature. The need to improve how the performance of toxicological test methods is assessed was the main impetus for translating these tools to toxicology.
Lesley Ann Stewart is a Scottish academic whose research interests are in the development and application of evidence synthesis methods, particularly systematic reviews and individual participant data meta-analysis. She is head of department for the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at the University of York and director for the NIHR Evidence Synthesis Programme. She was one of the founders of the Cochrane Collaboration in 1993. Stewart served as president of the Society for Research Synthesis Methodology (2013-2016) and was a founding co-editor in chief of the academic journal Systematic Reviews (2010–2021).
Metascience is the use of scientific methodology to study science itself. Metascience seeks to increase the quality of scientific research while reducing inefficiency. It is also known as "research on research" and "the science of science", as it uses research methods to study how research is done and find where improvements can be made. Metascience concerns itself with all fields of research and has been described as "a bird's eye view of science". In the words of John Ioannidis, "Science is the best thing that has happened to human beings ... but we can do it better."
Public policy research is a multidisciplinary field that delves into the systematic examination and comprehensive analysis of policy matters and their far-reaching implications on society as a whole. The field explores diverse facets of public policy including political and administrative systems, institutions, actors, norms and traditions, communication and knowledge practices and the conception, execution and evaluation of policy decisions. Public policy research and policy analysis is conducted in multiple sectors including academic institutions, think tanks, consulting firms, not for profit organisations and government agencies. It is a major subfield of political science but is also a subfield in many other areas including public health and political economy. Research involves consideration of the interplay between various stakeholders, including policymakers, interest groups, and the general public, as well as an examination of the societal, economic, and political factors that shape policy decision-making processes. Public policy researchers explore the complexities of policy formulation with the aim to contribute both to understanding and improving the policy process overall, and to enhancing public policy effectiveness and societal well-being in specific policy arenas.
References
- 1 2 Hall, Judith A.; Tickle-Degnen, Linda; Rosenthal, Robert; Mosteller, Frederick (1993-11-23). "Hypotheses and Problems in Research Synthesis". In Cooper, Harris; Hedges, Larry V. (eds.). The Handbook of Research Synthesis. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 9781610441377.
- 1 2 Suri H (2011-08-03). "Purposeful Sampling in Qualitative Research Synthesis". Qualitative Research Journal . 11 (2): 63–75. doi:10.3316/QRJ1102063. ISSN 1443-9883.
- ↑ Wyborn C, Louder E, Harrison J, Montambault J, Montana J, Ryan M, Bednarek A, Nesshöver C, Pullin A (August 2018). "Understanding the Impacts of Research Synthesis". Environmental Science & Policy . 86: 72–84. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2018.04.013 .
- 1 2 Denyer D, Tranfield D, van Aken JE (March 2008). "Developing Design Propositions through Research Synthesis". Organization Studies . 29 (3): 393–413. doi:10.1177/0170840607088020. ISSN 0170-8406. S2CID 143261509.
- ↑ Barnett-Page E, Thomas J (August 2009). "Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: a critical review". BMC Medical Research Methodology . 9 (1): 59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-9-59 . PMC 3224695 . PMID 19671152.
- ↑ Campbell M, Katikireddi SV, Sowden A, Thomson H (January 2019). "Lack of transparency in reporting narrative synthesis of quantitative data: a methodological assessment of systematic reviews". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology . 105: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.08.019. PMC 6327109 . PMID 30196129.