
Branchiopoda is a class of crustaceans. It comprises fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca, Notostraca and the Devonian Lepidocaris. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus.

Centipedes are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda of the subphylum Myriapoda, an arthropod group which includes millipedes and other multi-legged animals. Centipedes are elongated segmented (metameric) creatures with one pair of legs per body segment. All centipedes are venomous and can inflict painful stings, injecting their venom through pincer-like appendages known as forcipules or toxicognaths, which are actually modified legs instead of fangs. Despite the name, no centipede has exactly 100 pairs of legs; number of legs ranges from 15 pairs to 191 pairs, always an odd number.

Myriapods are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.

Megaloptera is an order of insects. It contains the alderflies, dobsonflies and fishflies, and there are about 300 known species.

The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness. It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located some 700 m away. The Rhynie chert contains exceptionally preserved plant, fungus, lichen and animal material preserved in place by an overlying volcanic deposit. The bulk of the Devonian fossil bed consists of primitive plants, along with arthropods, lichens, algae and fungi.

The Palaeodictyopteroidea or Paleodictyopterida are an extinct superorder of Palaeozoic beaked insects, characterised by unique mouthparts consisting of 5 stylets. They represent the first important terrestrial herbivores, and the first major group of herbivorous insects. They appear during the Middle Carboniferous and continue through to the Late Permian. This large and diverse group includes 50% of all known Paleozoic insects. Palaeodictyopteroidea nymphs possessed movable wing pads and appear to have been able to perform simple flapping flight.

Meganisoptera is an extinct order of large dragonfly-like insects, informally known as griffenflies or (incorrectly) as giant dragonflies. The order was formerly named Protodonata, the "proto-Odonata", for their similar appearance and supposed relation to modern Odonata. They range in Palaeozoic times. Though most were only slightly larger than modern dragonflies, the order includes the largest known insect species, such as the late Carboniferous Meganeura monyi and the even larger early Permian Meganeuropsis permiana, with wingspans of up to 71 centimetres (28 in).
The most recent understanding of the evolution of insects is based on studies of the following branches of science: molecular biology, insect morphology, paleontology, insect taxonomy, evolution, embryology, bioinformatics and scientific computing. It is estimated that the class of insects originated on Earth about 480 million years ago, in the Ordovician, at about the same time terrestrial plants appeared. Insects are thought to have evolved from a group of crustaceans. The first insects were landbound, but about 400 million years ago in the Devonian period one lineage of insects evolved flight, the first animals to do so. The oldest insect fossil has been proposed to be Rhyniognatha hirsti, estimated to be 400 million years old, but the insect identity of the fossil has been contested. Global climate conditions changed several times during the history of Earth, and along with it the diversity of insects. The Pterygotes underwent a major radiation in the Carboniferous while the Endopterygota underwent another major radiation in the Permian.
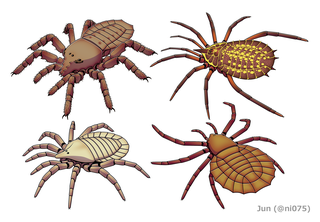
The order Trigonotarbida is a group of extinct arachnids whose fossil record extends from the late Silurian to the early Permian. These animals are known from several localities in Europe and North America, as well as a single record from Argentina. Trigonotarbids can be envisaged as spider-like arachnids, but without silk-producing spinnerets. They ranged in size from a few millimetres to a few centimetres in body length and had segmented abdomens (opisthosoma), with the dorsal exoskeleton (tergites) across the backs of the animals' abdomens, which were characteristically divided into three or five separate plates. Probably living as predators on other arthropods, some later trigonotarbid species were quite heavily armoured and protected themselves with spines and tubercles. About seventy species are currently known, with most fossils originating from the Carboniferous coal measures.

Pneumodesmus newmani is a species of myriapod that lived during the late Wenlock epoch of the Silurian period around 428 million years ago. Although a 2017 study dates its occurrence based on zircon data analysis as the Early Devonian (Lochkovian), the 2023 study confirmed the age identification of the 2004 study through palynological, palaeobotanical and ziron analyses incorporating newly discovered additional data. It is one of the first myriapods, and among the oldest creatures to have lived on land. It was discovered in 2004, and is known from a single specimen from Stonehaven, Aberdeenshire, Scotland.
Rhyniella is a genus of fossil springtails (Collembola) from the Rhynie chert, which formed during the Pragian stage of the Early Devonian. One species has been described, Rhyniella praecursor. For some time it was believed to be the only hexapod from the Early Devonian

Euthycarcinoidea are an enigmatic group of extinct possibly amphibious arthropods that ranged from Cambrian to Triassic times. Fossils are known from Europe, North America, Argentina, Australia and Antarctica.
Samarendra Nath Maulik was an Indian entomologist who worked at the Natural History Museum, London and specialized in the systematics of the leaf beetles. He worked briefly at the University of Calcutta as a professor of Zoology. A structure on the hind femur, particularly of flea beetles, and used in their leaping motion has sometimes been called as "Maulik's organ".

Arthropods are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species.

Lepidocaris rhyniensis is an extinct species of crustacean. It is the only species known from the order Lipostraca, and is the only abundant animal in the Pragian-aged Rhynie chert deposits. It resembles modern Anostraca, to which it is probably closely related, although its relationships to other orders remain unclear. The body is 3 mm (0.12 in) long, with 23 body segments and 19 pairs of appendages, but no carapace. It occurred chiefly among charophytes, probably in alkaline temporary pools.

The subphylum Hexapoda or hexapods comprises the largest clade of arthropods and includes most of the extant arthropod species. It includes the crown group class Insecta, as well as the much smaller class Entognatha, which includes three orders of wingless arthropods that were once considered insects: Collembola (springtails), Protura (coneheads) and Diplura. The insects and springtails are very abundant and are some of the most important pollinators, basal consumers, scavengers/detritivores and micropredators in terrestrial environments.
The Panther Mountain Formation is a geologic formation in New York. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period. It is located in the counties of Albany, Madison, Oneida, Otsego, and Schoharie. It is well known for its fossil arthropods preserved as flattened cuticles, including Attercopus and Dracochela.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2017 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2017.
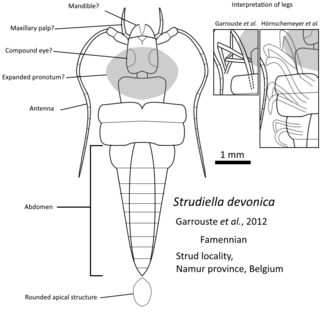
Strudiella devonica is a species of extinct arthropod from the Devonian. It was recovered in the Strud environment from the Bois des Mouches Formation, Upper Famennian. It was originally described as the first complete Late Devonian terrestrial insect, but due to its poor state of preservation, its affinity is discussed.
Leverhulmia is an extinct genus of arthropod, known from a single partial specimen with preserved gut contents, found in the Windyfield (Rhynie) chert.















