
Albertosaurus is a genus of large tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in northwestern North America during the early to middle Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period, about 71 million years ago. The type species, A. sarcophagus, was apparently restricted in range to the modern-day Canadian province of Alberta, after which the genus is named, although an indeterminate species has been discovered in the Corral de Enmedio and Packard Formations of Mexico. Scientists disagree on the content of the genus and some recognize Gorgosaurus libratus as a second species.(citation needed)

Lyon Sprague de Camp was an American writer of science fiction, fantasy and non-fiction. In a career spanning 60 years, he wrote over 100 books, including novels and works of non-fiction, including biographies of other fantasy authors. He was a major figure in science fiction in the 1930s and 1940s.

Troodon is a former wastebasket taxon and a potentially dubious genus of relatively small, bird-like theropod dinosaurs definitively known from the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period. It includes at least one species, Troodon formosus, known from Montana. Discovered in October 1855, T. formosus was among the first dinosaurs found in North America, although it was thought to be a lizard until 1877. Several well-known troodontid specimens from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta were once believed to be members of this genus. However, recent analyses in 2017 have found this genus to be undiagnostic and referred some of these specimens to the genus Stenonychosaurus some to the genus Latenivenatrix, and some to the genus Pectinodon. The genus name is Ancient Greek for "wounding tooth", referring to the teeth, which were different from those of most other theropods known at the time of their discovery. The teeth bear prominent, apically oriented serrations. These "wounding" serrations, however, are morphometrically more similar to those of herbivorous reptiles, and suggest a possibly omnivorous diet.

Stenonychosaurus is a genus of troodontid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada, as well as possibly the Two Medicine Formation. The type and only species, S. inequalis, was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. S. inequalis was reassigned in 1987 by Phil Currie to the genus Troodon, which was reverted by the recognition of Stenonychosaurus as a separate genus from the possibly dubious Troodon in 2017 by Evans et al. and also later in the same year by Van der Reest and Currie.

Maiasaura is a large herbivorous saurolophine hadrosaurid ("duck-billed") dinosaur genus that lived in the area currently covered by the state of Montana and the province of Alberta, Canada, in the Upper Cretaceous Period, about 76.7 million years ago.

Parasaurolophus is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur that lived in what is now western North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 76.5–73 million years ago. It was a large herbivore that could reach over 9 metres (30 ft) long and weigh over 5 metric tons, and were able to move as a biped and a quadruped. Three species are universally recognized: P. walkeri, P. tubicen, and the short-crested P. cyrtocristatus. Additionally, a fourth species, P. jiayinensis, has been proposed, although it is more commonly placed in the separate genus Charonosaurus. Remains are known from Alberta, New Mexico, and Utah, as well as possibly Heilongjiang if Charonosaurus is in fact part of the genus. The genus was first described in 1922 by William Parks from a skull and partial skeleton found in Alberta.
Polyodontosaurus is a potentially dubious genus of troodontid dinosaur named in 1932 by Charles W. Gilmore for a left dentary from the Dinosaur Park Formation. It had been considered a synonym of Stenonychosaurus or Troodon for a significant time, before being declared a nomen dubium. The only known species is the type, P. grandis.

The Best of L. Sprague de Camp is a collection of writings by American science fiction and fantasy author L. Sprague de Camp, first published in hardback by Nelson Doubleday in February 1978 and in paperback by Ballantine Books in May of the same year as a volume in its Classic Library of Science Fiction. The book was reprinted by Ballantine in May 1986. It was reissued in trade paperback and ebook editions by Phoenix Pick in December 2014. It has also been translated into German.

Aristotle and the Gun and Other Stories is a collection of short stories by American science fiction and fantasy author L. Sprague de Camp. It was published in hardcover in August 2002 by the Gale Group as part of its Five Star Speculative Fiction Series.

Years in the Making: the Time-Travel Stories of L. Sprague de Camp is a collection of science fiction stories by American author L. Sprague de Camp, edited by Mark L. Olson and illustrated by Bob Eggleton. It was first published in hardcover by NESFA Press in February 2005, with a NESFA/Science Fiction Book Club edition following in September of the same year.

The Magic School Bus In the Time of the Dinosaurs is the sixth book in Joanna Cole and Bruce Degen's The Magic School Bus series.

"A Gun for Dinosaur" is a classic time travel science fiction story by American writer L. Sprague de Camp as part of his Rivers of Time series. It tells the story of four men who travel into the past to hunt dinosaurs.
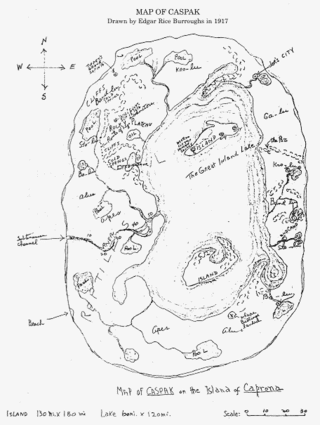
Caprona is a fictional island in the literary universe of Edgar Rice Burroughs' Caspak Trilogy, including The Land That Time Forgot, The People That Time Forgot, and Out of Time's Abyss. They were published as serial novels in 1918, and collected in book form in 1924.

Dinosaur Train is a computer-animated television series aimed at preschoolers ages 3 to 6. Created by Craig Bartlett, who created Nickelodeon's Hey Arnold!, the series features a Tyrannosaurus rex named Buddy who, together with his adopted Pteranodon family, takes the Dinosaur Train to explore his time period, and have adventures with a variety of dinosaurs. It is co-produced by The Jim Henson Company in association with the Infocomm Media Development Authority, Sparky Animation, FableVision, Snee-Oosh, Inc., Reel FX, and Sea to Sky Entertainment. As of September 2018, PBS Kids had ordered 11 more episodes, taking the total number of episodes to 100. A film based on the series from Universal Pictures and Universal 1440 Entertainment titled, Dinosaur Train: Adventure Island premiered on April 12, 2021.
Dinosaur paleobiogeography is the study of dinosaur geographic distribution, based on evidence in the fossil record.
March of the Dinosaurs is a CGI film which has aired on ITV 1 in the UK on 23 April 2011 and released on DVD on 27 May 2011. The film was produced by Wide-Eyed Entertainment in association with Yap Films, and executive produced by Jasper James, who had previously worked on the Walking with... series and Prehistoric Park. Set 70 million years ago in the Cretaceous in North America, the film follows the journey of a young Edmontosaurus named Scar and his herd as they migrate from Northern Alaska to Alberta during the winter. This film depicts recent findings and speculation about dinosaurs, such as North-American Tyrannosaurs having feathers, and hunting in packs, dinosaurs in the snow and migrating.

The Eden Formula, also known as Tyrannosaurus Wrecks, is a 2006 American science fiction horror film written and directed by John Carl Buechler. It stars Jeff Fahey, Dee Wallace, and Tony Todd. The film includes recycled footage from the Carnosaur films, for which Buechler had provided dinosaur effects.
You Are Umasou is a Japanese picture book series by Tatsuya Miyanishi, published by Poplar. The series has spawned animated film and anime adaptations. The fourth film My Tyrano II: Easter, Garden was planned to release in 2024 but was Delayed to 2025

"Employment" is a science fiction story by American writer L. Sprague de Camp, pioneering the concept of de-extinction. It was first published in the magazine Astounding Science-Fiction for May, 1939. The story appeared under the pseudonym Lyman R. Lyon as the magazine's policy did not allow the name of any author to be repeated on the same contents page, and de Camp had another piece in the same issue under his actual name. It first appeared in book form in the anthology Imagination Unlimited. It later appeared in the anthologies Men of Space and Time, and Science Fiction Inventions, as well as the de Camp collection The Best of L. Sprague de Camp. It was credited to de Camp's real name in all publications subsequent to its first appearance. The story has been translated into German.

"In-Group" is a science fiction short story by L. Sprague de Camp. It was first published in the magazine Marvel Science Fiction for May, 1952. and later reprinted in the magazine Skyworlds for February 1978. It first appeared in book form in the collection A Gun for Dinosaur and Other Imaginative Tales. The story has been translated into Italian and German.
















