Related Research Articles

Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) or Yee's method is a numerical analysis technique used for modeling computational electrodynamics. Since it is a time-domain method, FDTD solutions can cover a wide frequency range with a single simulation run, and treat nonlinear material properties in a natural way.

In physics, physical optics, or wave optics, is the branch of optics that studies interference, diffraction, polarization, and other phenomena for which the ray approximation of geometric optics is not valid. This usage tends not to include effects such as quantum noise in optical communication, which is studied in the sub-branch of coherence theory.

Computational electromagnetics (CEM), computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment using computers.

Constantine A. Balanis is a Greek-born American scientist, educator, author, and Regents Professor at Arizona State University. Born in Trikala, Greece on October 29, 1938. He is best known for his books in the fields of engineering electromagnetics and antenna theory. He emigrated to the United States in 1955, where he studied electrical engineering. He received United States citizenship in 1960.
Characteristic modes (CM) form a set of functions which, under specific boundary conditions, diagonalizes operator relating field and induced sources. Under certain conditions, the set of the CM is unique and complete (at least theoretically) and thereby capable of describing the behavior of a studied object in full.
Dr. Raymond J. Luebbers was Professor of Electrical Engineering at The Pennsylvania State University and Ohio University, a Research Scientist at the Lockheed Martin Research Laboratory in Palo Alto, CA and founder of Remcom, Inc.
Robert Emmanuel Collin was a Canadian American electrical engineer, university professor, and life fellow of the IEEE, known for his fundamental contributions in applied electromagnetism.
Ulrich Jakobus is Senior Vice President - Electromagnetic Solutions of Altair, Germany and was awarded Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2013 for leadership in hybrid computational tool development and commercialization. His research laid the foundations for the commercial electromagnetics code FEKO which is used in antenna design, antenna placement, electromagnetic compatibility, microwave components, bioelectromagnetics, radar cross section and related fields.

Weng Cho Chew is a Malaysian-American electrical engineer and applied physicist known for contributions to wave physics, especially computational electromagnetics. He is a Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue University.
Kane Shee-Gong Yee is a Chinese-American electrical engineer and mathematician. He is best known for introducing the finite-difference time-domain method (FDTD) in 1966.
Yuen Tze Lo was a Chinese American electrical engineer and academician. He was a professor emeritus at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. He is best known for his contributions to the theory and design of antennas. He is the editor of the textbook series, Antenna Handbook.
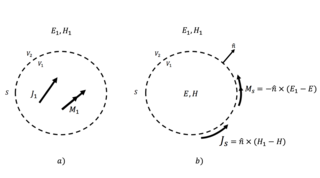
In electromagnetism, surface equivalence principle or surface equivalence theorem relates an arbitrary current distribution within an imaginary closed surface with an equivalent source on the surface. It is also known as field equivalence principle, Huygens' equivalence principle or simply as the equivalence principle. Being a more rigorous reformulation of the Huygens–Fresnel principle, it is often used to simplify the analysis of radiating structures such as antennas.
Tapan Kumar Sarkar was an Indian-American electrical engineer and Professor Emeritus at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at Syracuse University. He was best known for his contributions to computational electromagnetics and antenna theory.

The method of moments (MoM), also known as the moment method and method of weighted residuals, is a numerical method in computational electromagnetics. It is used in computer programs that simulate the interaction of electromagnetic fields such as radio waves with matter, for example antenna simulation programs like NEC that calculate the radiation pattern of an antenna. Generally being a frequency-domain method, it involves the projection of an integral equation into a system of linear equations by the application of appropriate boundary conditions. This is done by using discrete meshes as in finite difference and finite element methods, often for the surface. The solutions are represented with the linear combination of pre-defined basis functions; generally, the coefficients of these basis functions are the sought unknowns. Green's functions and Galerkin method play a central role in the method of moments.
Georges Armand Deschamps was a French American engineer and Professor Emeritus at the Department of Electrical Engineering at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He is best known for his contributions to electromagnetic theory, microwave engineering and antenna theory. He is also regarded as an early pioneer of microstrip and patch antennas, which he proposed in 1953.
Arthur Aaron Oliner was an American physicist and electrical engineer, who was professor emeritus at department of electrical and computer engineering at New York University-Polytechnic. Best known for his contributions to engineering electromagnetics and antenna theory, he is regarded as a pioneer of leaky wave theory and leaky wave antennas.
Akira Ishimaru is a Japanese-American electrical engineer and professor emeritus at Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Washington. He is best known for his contributions to the theory of wave scattering in random media.
Jean G. van Bladel was a Belgian electrical engineer, physicist and academician, who was a Professor Emeritus at Ghent University. He was best known for his contributions to electromagnetics and antenna theory.
Yang Hao is an electrical engineer, academic, and author most known for his research in wireless connectivity and metamaterials. He is the holder of the QinetiQ/Royal Academy of Engineering (RAE) Research Chair, and serves as the Director of both the EPSRC Research Centre on Future Wireless Connectivity and the EPSRC Centre for Transformation Optics and Metamaterials. He is also a Professor of Antennas and Electromagnetics, and Deputy Vice Principal for Strategic Research at Queen Mary University of London (QMUL). He is a Co-Founder and Director of AOTOMAT, and co-founded a satellite communication company called Isotropic Systems.
References
- ↑ Harrington, Roger F. (2003). Introduction to Electromagnetic Engineering. Courier Corporation. ISBN 9780486432410.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Wilton, Donald R.; Arvas, Ercument; Butler, Chalmers M.; Mautz, Joseph R. (19 October 2017). "Roger F. Harrington, 1989 IEEE AP-S Distinguished Achievement awardee". 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting. pp. 657–658. doi:10.1109/APUSNCURSINRSM.2017.8072371. ISBN 978-1-5386-3284-0. S2CID 1484406.
- ↑ Gibson, Walton C. (2004). The Method of Moments in Electromagnetics. Chapman & Hall. ISBN 9781482235791.
- 1 2 3 4 "Roger F. Harrington". fi.edu. Franklin Institute. 27 October 2014. Retrieved June 1, 2020.
- ↑ Harrington, Roger F. (1968). Field Computation by Moment Methods. Macmillan. ISBN 9780780310148.
- ↑ Bondeson, Anders; Rylander, Thomas; Ingelström, Pär (2005). Computational electromagnetics. Springer Publishing. ISBN 9780387261584.
- ↑ Harrington, Roger F. (1960). "Effects of antenna size on gain, bandwidth, and efficiency". Journal of National Bureau of Standards . 64-D: 1–12.
- ↑ McLean, James S. (May 1996). "A re-examination of the fundamental limits on the radiation Q of electrically small antennas". IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation . 44 (5): 672. Bibcode:1996ITAP...44..672M. doi:10.1109/8.496253.