Related Research Articles
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve goals and meet success criteria at a specified time. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.

A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure as a "hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."
A project plan, according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), is: "...a formal, approved document used to guide both project execution and project control. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, facilitate communication among project stakeholders, and document approved scope, cost, and schedule baselines. A project plan may be summarized or detailed."

The Project Management Body of Knowledge is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose sixth edition was released in 2017. The Guide is a document resulting from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.
In a project network, a dependency is a link amongst a project's terminal elements.
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process.
A project manager is a professional in the field of project management. Project managers have the responsibility of the planning, procurement and execution of a project, in any undertaking that has a defined scope, defined start and a defined finish; regardless of industry. Project managers are first point of contact for any issues or discrepancies arising from within the heads of various departments in an organization before the problem escalates to higher authorities, as project representative.
In software development, agile practices involve discovering requirements and developing solutions through the collaborative effort of self-organizing and cross-functional teams and their customer(s)/end user(s). It advocates adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement, and it encourages flexible responses to change.
The Project Management Institute (PMI) is an American nonprofit professional organization for project management.
In time management, timeboxing allocates a fixed time period, called a timebox, within which planned activity takes place. It is used by several project management approaches and for personal time management.
Project Management Professional (PMP) is an internationally recognized professional designation offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). As of 31 July 2020, there are 1,036,367 active PMP certified individuals and 314 chartered chapters across 214 countries and territories worldwide. The exam is based on the PMI Project Management Body of Knowledge.
Feature-driven development (FDD) is an iterative and incremental software development process. It is a lightweight or Agile method for developing software. FDD blends a number of industry-recognized best practices into a cohesive whole. These practices are driven from a client-valued functionality (feature) perspective. Its main purpose is to deliver tangible, working software repeatedly in a timely manner in accordance with the Principles behind the Agile Manifesto.
Scrum is an agile framework for developing, delivering, and sustaining complex products, with an initial emphasis on software development, although it has been used in other fields including research, sales, marketing and advanced technologies. It is designed for teams of ten or fewer members, who break their work into goals that can be completed within time-boxed iterations, called sprints, no longer than one month and most commonly two weeks. The Scrum Team track progress in 15-minute time-boxed daily meetings, called daily scrums. At the end of the sprint, the team holds sprint review, to demonstrate the work done, and sprint retrospective to improve continuously.
Terms of reference (TOR) define the purpose and structures of a project, committee, meeting, negotiation, or any similar collection of people who have agreed to work together to accomplish a shared goal.
In project management, resource leveling is defined by A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge as "A technique in which start and finish dates are adjusted based on resource limitation with the goal of balancing demand for resources with the available supply." Resource leveling problem could be formulated as an optimization problem. The problem could be solved by different optimization algorithms such as exact algorithms or meta-heuristic methods.
Software quality management (SQM) is a management process that aims to develop and manage the quality of software in such a way so as to best ensure that the product meets the quality standards expected by the customer while also meeting any necessary regulatory and developer requirements, if any. Software quality managers require software to be tested before it is released to the market, and they do this using a cyclical process-based quality assessment in order to reveal and fix bugs before release. Their job is not only to ensure their software is in good shape for the consumer but also to encourage a culture of quality throughout the enterprise.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
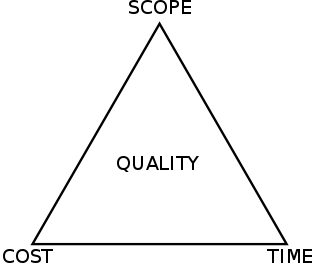
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
In software engineering, a software development process is the process of dividing software development work into distinct phases to improve design, product management, and project management. It is also known as a software development life cycle (SDLC). The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
References
- ↑ Larman, Craig (2004). "Chapter 11: Practice Tips". Agile and Iterative Development: A Manager's Guide. p. 253. ISBN 9780131111554 . Retrieved Oct 14, 2013.
- ↑ ""A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge ( PMBOK® Guide )—Fifth Edition", section 6.2.2.2 pg. 152".