Related Research Articles
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort, performing a cross-section at intervals through time. It is a type of panel study where the individuals in the panel share a common characteristic.
In clinical trials, a surrogate endpoint is a measure of effect of a specific treatment that may correlate with a real clinical endpoint but does not necessarily have a guaranteed relationship. The National Institutes of Health (USA) defines surrogate endpoint as "a biomarker intended to substitute for a clinical endpoint".

The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three clinical trials (CT) and an observational study (OS). In particular, randomized controlled trials were designed and funded that addressed cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoporosis.
Clinical endpoints or clinical outcomes are outcome measures referring to occurrence of disease, symptom, sign or laboratory abnormality constituting a target outcome in clinical research trials. The term may also refer to any disease or sign that strongly motivates withdrawal of an individual or entity from the trial, then often termed a humane (clinical) endpoint.
A hierarchy of evidence is a heuristic used to rank the relative strength of results obtained from scientific research. There is broad agreement on the relative strength of large-scale, epidemiological studies. More than 80 different hierarchies have been proposed for assessing medical evidence. The design of the study and the endpoints measured affect the strength of the evidence. In clinical research, the best evidence for treatment efficacy is mainly from meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Systematic reviews of completed, high-quality randomized controlled trials – such as those published by the Cochrane Collaboration – rank the same as systematic review of completed high-quality observational studies in regard to the study of side effects. Evidence hierarchies are often applied in evidence-based practices and are integral to evidence-based medicine (EBM).
The COPSS Presidents' Award is given annually by the Committee of Presidents of Statistical Societies to a young statistician in recognition of outstanding contributions to the profession of statistics.
The COPSS Distinguished Achievement Award and Lectureship is a very high recognition of achievement and scholarship in statistical science that recognizes the highly significant impact of statistical methods on scientific investigations. The award was established in 1963 by the North American Committee of Presidents of Statistical Societies (COPSS) "to honor both the contributions of Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher and the work of a present–day statistician for their advancement of statistical theory and applications." The COPSS Distinguished Lecture is given at the Joint Statistical Meetings in North America and is subsequently published in a statistics journal. The lecturer receives a plaque and a cash award of US$1000. It is given every year if a nominee considered eligible and worthy is found, which one was in all but five years up to 1984, and in all years since. In June 2020, the name of the award was changed to its current name after discussions concerning Fisher's controversial views on race and eugenics.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to clinical research:

Sheila Macdonald Bird OBE FRSE FMedSci is a Scottish biostatistician whose assessment of misuse of statistics in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) and BMJ series ‘Statistics in Question’ led to statistical guidelines for contributors to medical journals. Bird's doctoral work on non-proportional hazards in breast cancer found application in organ transplantation where beneficial matching was the basis for UK's allocation of cadaveric kidneys for a decade. Bird led the Medical Research Council (MRC) Biostatistical Initiative in support of AIDS/HIV studies in Scotland, as part of which Dr A. Graham Bird and she pioneered Willing Anonymous HIV Surveillance (WASH) studies in prisons. Her work with Cooper on UK dietary bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) exposure revealed that the 1940–69 birth cohort was the most exposed and implied age-dependency in susceptibility to clinical vCJD progression from dietary BSE exposure since most vCJD cases were younger, born in 1970–89. Bird also designed the European Union's robust surveillance for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in sheep which revolutionised the understanding of scrapie.
Marvin Zelen was Professor Emeritus of Biostatistics in the Department of Biostatistics at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (HSPH), and Lemuel Shattuck Research Professor of Statistical Science. During the 1980s, Zelen chaired HSPH's Department of Biostatistics. Among colleagues in the field of statistics, he was widely known as a leader who shaped the discipline of biostatistics. He "transformed clinical trial research into a statistically sophisticated branch of medical research."
Paul R. Rosenbaum is the Robert G. Putzel Professor Emeritus in the Department of Statistics and Data Science at Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, where he worked from 1986 through 2021. He has written extensively about causal inference in observational studies, including sensitivity analysis, optimal matching, design sensitivity, evidence factors, quasi-experimental devices, and the propensity score. With various coauthors, he has also written about health outcomes, racial disparities in health outcomes, instrumental variables, psychometrics and experimental design.
Motomi (Tomi) Mori is a Japanese biostatistician. Formerly the Walter & Clora Brownfield Professor of Cancer Biostatistics at the Knight Cancer Institute of Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU), she was named endowed professor and chair of biostatistics at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in 2020. She is the chair of the Caucus for Women in Statistics for 2021.
Nancy Flournoy is an American statistician. Her research in statistics concerns the design of experiments, and particularly the design of adaptive clinical trials; she is also known for her work on applications of statistics to bone marrow transplantation, and in particular on the graft-versus-tumor effect. She is Curators' Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Statistics at the University of Missouri.

Jeffrey Tullis Leek is an American biostatistician and data scientist working as a Vice President, Chief Data Officer, and Professor at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. He is an author of the Simply Statistics blog, and runs several online courses through Coursera, as part of their Data Science Specialization. His most popular course is The Data Scientist's Toolbox, which he instructed along with Roger Peng and Brian Caffo. Leek is best known for his contributions to genomic data analysis and critical view of research and the accuracy of popular statistical methods.
An outcome measure, endpoint, effect measure or measure of effect is a measure within medical practice or research, which is used to assess the effect, both positive and negative, of an intervention or treatment. Measures can often be quantified using effect sizes. Outcomes measures can be patient-reported, or gathered through laboratory tests such as blood work, urine samples etc. or through medical examination. Outcomes measures should be relevant to the target of the intervention.
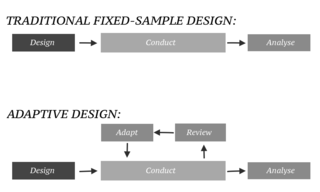
In an adaptive design of a clinical trial, the parameters and conduct of the trial for a candidate drug or vaccine may be changed based on an interim analysis. Adaptive design typically involves advanced statistics to interpret a clinical trial endpoint. This is in contrast to traditional single-arm clinical trials or randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that are static in their protocol and do not modify any parameters until the trial is completed. The adaptation process takes place at certain points in the trial, prescribed in the trial protocol. Importantly, this trial protocol is set before the trial begins with the adaptation schedule and processes specified. Adaptions may include modifications to: dosage, sample size, drug undergoing trial, patient selection criteria and/or "cocktail" mix. The PANDA provides not only a summary of different adaptive designs, but also comprehensive information on adaptive design planning, conduct, analysis and reporting.
Garnet Larae Anderson is an American biostatistician, known for her research on the health risks caused by side effects of postmenopausal hormone therapy, and more generally as one of the leading researchers in the Women's Health Initiative. She is a senior vice president at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, where she directs the Public Health Sciences Division and holds the Fred Hutch 40th Anniversary Endowed Chair; she is also an affiliate professor of biostatistics at the University of Washington.
Margaret Patricia O'Sullivan Pepe is an Irish biostatistician specializing in the evaluation of tests and biomarkers for disease screening. She is a professor of biostatistics at the University of Washington School of Public Health and a researcher at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center.
References
- ↑ "Prentice, Ross L." LC Linked Data Service: Authorities and Vocabularies. Library of Congress. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Lin, D. Y. (November 1, 2013). "An overview of Ross Prentice's contributions to statistical science". Statistics in Biosciences. 5 (2): 224–231. doi:10.1007/s12561-013-9095-8. PMC 3821774 . PMID 24223073.
- 1 2 3 "Ross L. Prentice, PhD". Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- ↑ Prentice, R. L. (1986). "A case-cohort design for epidemiologic cohort studies and disease prevention trials". Biometrika. 73 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1093/biomet/73.1.1. ISSN 0006-3444.
- ↑ Prentice, Ross L. (1989). "Surrogate endpoints in clinical trials: Definition and operational criteria". Statistics in Medicine. 8 (4): 431–440. doi:10.1002/sim.4780080407. ISSN 0277-6715. PMID 2727467.
- ↑ "Presidents' Award". Committee of Presidents of Statistical Societies. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- ↑ "R.A. Fisher Award and Lectureship". Committee of Presidents of Statistical Societies. Archived from the original on August 15, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.